Unveiling the Power of Color: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Color: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Color: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Color: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
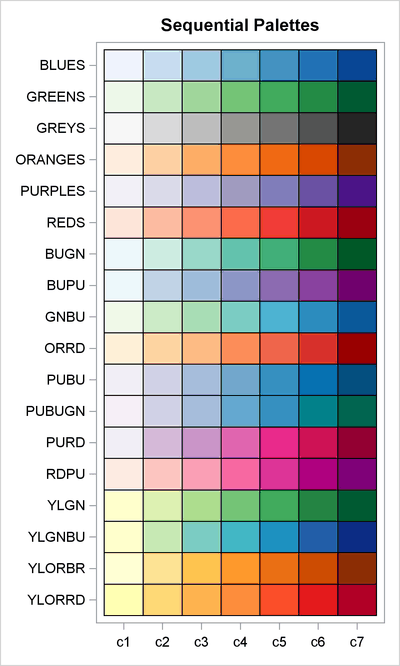
Heat maps, vibrant visual representations of data, have become indispensable tools across various fields. They leverage the intuitive power of color to convey complex information, making data analysis accessible and impactful. This article delves into the core of heat map color schemes, exploring their significance, principles, and practical applications.
Understanding the Language of Color:
Heat maps employ a spectrum of colors, typically ranging from cool hues like blue or green to warm hues like red or yellow, to represent data values. This color gradient, often referred to as a "color scale," acts as a visual language, enabling quick interpretation of data patterns.
The Significance of Color Choice:
The selection of colors for a heat map is not arbitrary. It plays a crucial role in conveying information accurately and effectively. Here’s a breakdown of the key considerations:
- Data Range: The color scale must effectively represent the entire data range, ensuring that subtle variations are discernible. For example, a data set with a narrow range might require a more nuanced color scale than one with a wider range.
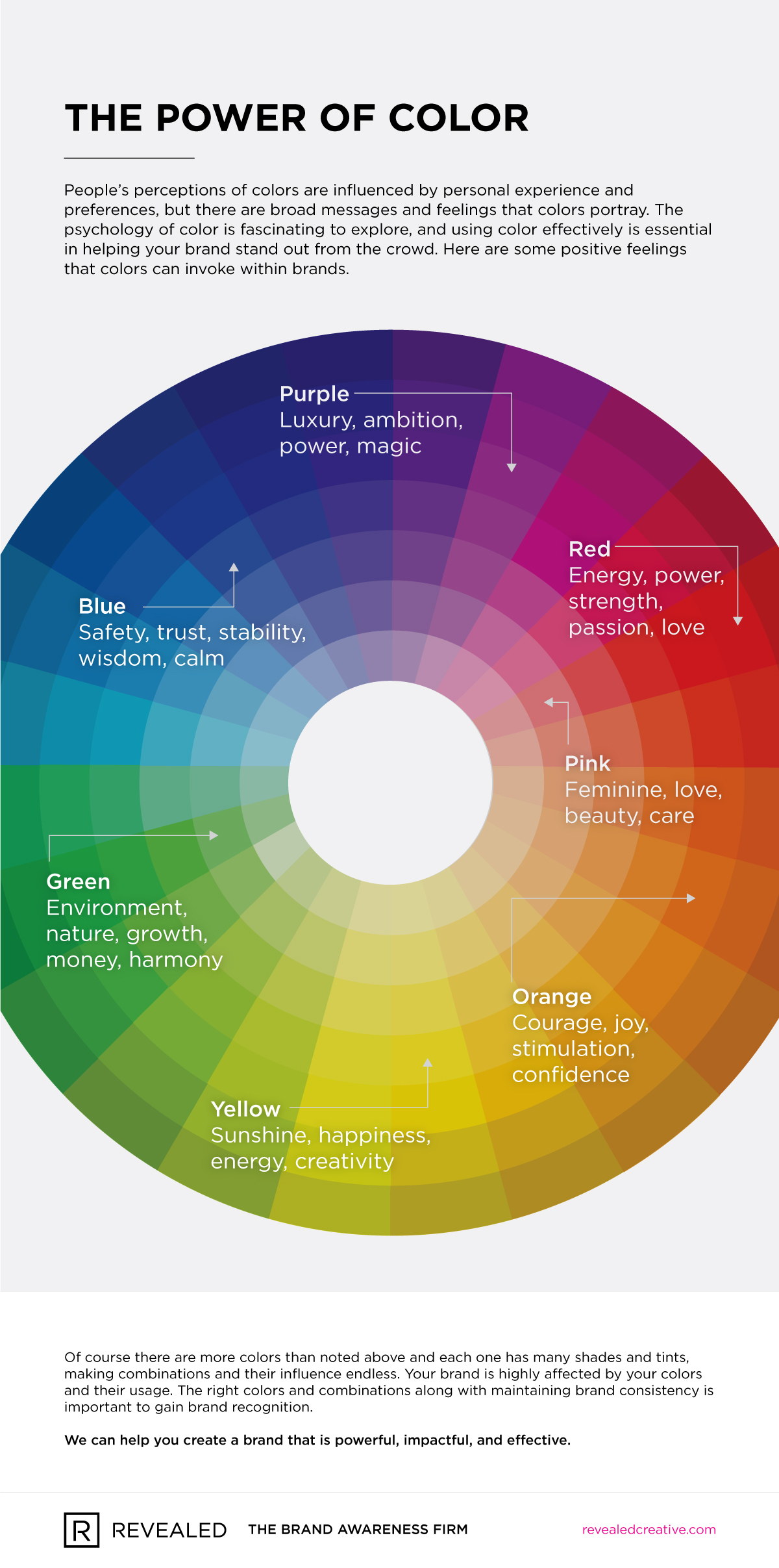
- Data Interpretation: The choice of colors should align with the intended interpretation. For instance, red is often used to highlight high values, signifying areas of interest or potential issues. Conversely, blue might represent low values, indicating areas of low activity or stability.
- Color Blindness Awareness: It is essential to consider individuals with color blindness, ensuring that the color scale remains accessible to all. This often involves selecting colors with sufficient contrast and utilizing alternative visual cues like shapes or patterns.
Common Heat Map Color Schemes:
Several established color schemes are commonly employed in heat maps. Here’s an overview of some popular options:
- Sequential Color Schemes: These schemes utilize a single color gradient, progressing from light to dark or vice versa. They are ideal for representing continuous data where the focus lies on the magnitude of values. Examples include blue-to-red, green-to-yellow, or gray-to-black gradients.
- Diverging Color Schemes: These schemes employ two contrasting color gradients, often centered around a neutral color. They are well-suited for showcasing data that deviates from a central point or baseline. Examples include red-to-white-to-blue, green-to-white-to-red, or purple-to-white-to-yellow gradients.
- Categorical Color Schemes: These schemes use distinct colors to represent different categories or groups. They are effective for representing data that falls into predefined categories, such as regions, demographics, or product types.
Beyond the Basics: Customizing Color Schemes:
While standard color schemes offer a solid foundation, customizing color scales can significantly enhance the effectiveness of a heat map. This can be achieved through:
- Color Palette Selection: Experimenting with different color palettes can help align the visual style with the context of the data and the intended audience.
- Color Saturation and Brightness: Adjusting the saturation and brightness of colors can influence the perceived intensity of data values.
- Transparency: Utilizing transparency can help highlight specific areas of interest or create a layered effect, revealing underlying patterns.
Applications of Heat Maps:
The versatility of heat maps extends across diverse domains, offering valuable insights in various contexts:
- Business Analysis: Heat maps help visualize customer behavior, website traffic, and product performance, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Marketing: They aid in understanding customer preferences, campaign effectiveness, and geographic market segmentation.
- Healthcare: Heat maps assist in identifying disease clusters, patient demographics, and treatment outcomes.
- Urban Planning: They facilitate the analysis of population density, traffic patterns, and infrastructure needs.
- Finance: Heat maps are used to analyze stock market trends, portfolio performance, and investment risk.
FAQs on Heat Map Colors:
Q: How do I choose the right color scheme for my heat map?
A: The ideal color scheme depends on the type of data being represented and the intended message. Consider the data range, the desired level of detail, and the target audience.
Q: Can I use more than one color scheme in a single heat map?
A: While it’s possible to combine multiple color schemes, it’s generally recommended to keep it simple. Overcomplicating the visual representation can lead to confusion and hinder data interpretation.
Q: What are some common pitfalls to avoid when creating heat maps?
A: Avoid using too many colors, as this can overwhelm the viewer. Ensure sufficient contrast between colors to ensure readability. Be mindful of color blindness considerations.
Tips for Creating Effective Heat Maps:
- Start with a clear objective: Define the specific insights you want to convey through the heat map.
- Choose an appropriate color scale: Select a color scale that accurately reflects the data range and aligns with the intended interpretation.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overcrowding the heat map with unnecessary details or distractions.
- Provide context: Include a legend or key to explain the color scale and data values.
- Test your heat map: Share it with others to gather feedback and ensure clarity and effectiveness.
Conclusion:
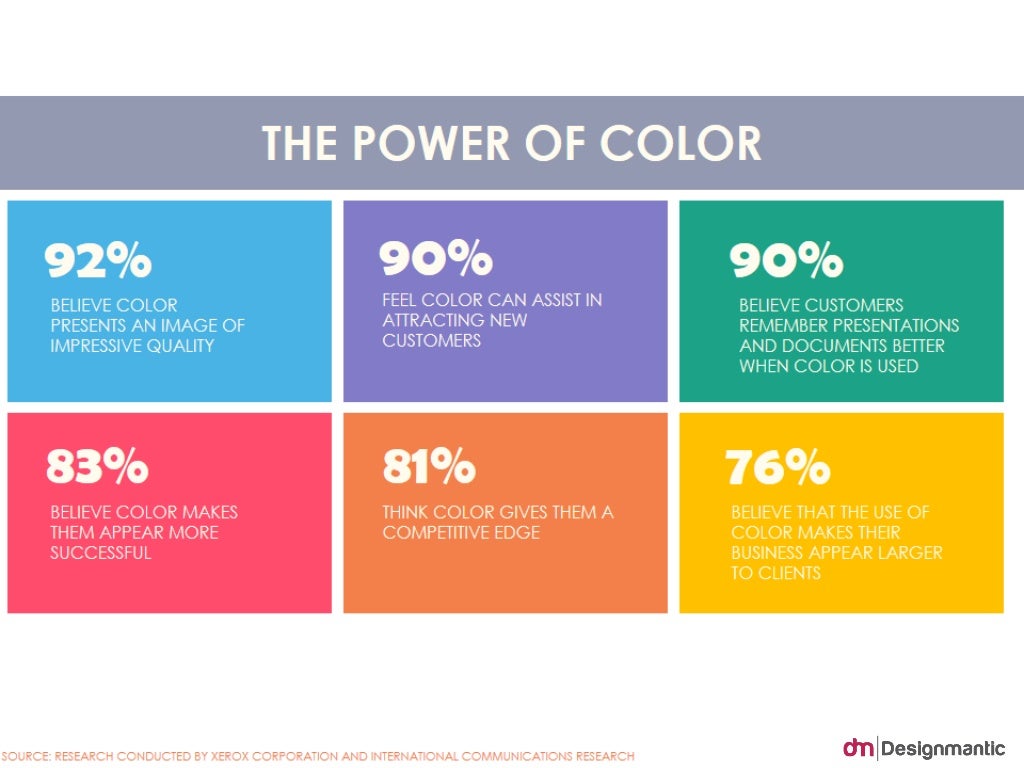
Heat maps are powerful visualization tools that leverage the intuitive language of color to convey complex information effectively. By understanding the principles of color choice, applying appropriate color schemes, and customizing them strategically, users can create compelling and insightful heat maps that drive data-driven decisions across various fields. As data visualization continues to evolve, heat maps will remain a crucial tool for unlocking valuable insights and transforming raw data into actionable knowledge.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Color: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
