Unveiling the Landscape of Democracy: A Comprehensive Guide to Electoral Results Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Democracy: A Comprehensive Guide to Electoral Results Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of Democracy: A Comprehensive Guide to Electoral Results Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape of Democracy: A Comprehensive Guide to Electoral Results Maps

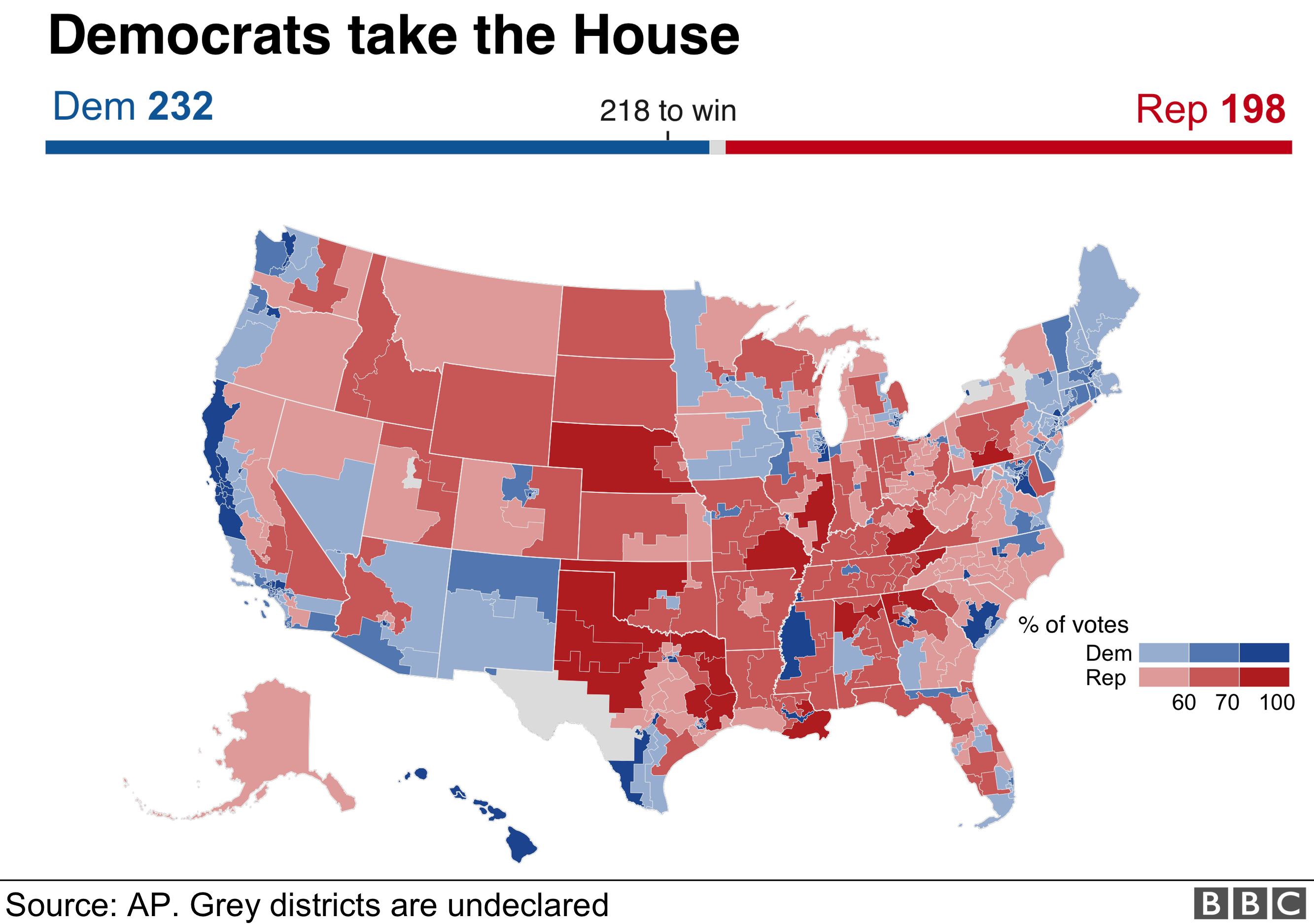
Electoral results maps, often referred to as election maps, are visual representations of the outcome of elections. These maps provide a powerful tool for understanding the distribution of votes across geographical areas, offering insights into voting patterns, political trends, and the overall electoral landscape.
Deconstructing the Map: Understanding the Visual Language
At the heart of an electoral results map lies its ability to convey complex data in a readily understandable format. The map’s visual language is crucial in this process, employing various elements to illustrate the election results:
- Geographic Representation: The map itself serves as a visual representation of the geographical area in question, typically a country, state, or region. This geographical framework provides a clear visual context for the election data.
- Color Coding: Different colors are often used to represent distinct political parties, candidates, or voting outcomes. The choice of colors can be strategic, employing contrasting shades to highlight specific regions or trends.
- Shading and Intensity: The intensity of the color used can indicate the level of support for a particular party or candidate within a specific area. For example, a darker shade might represent a higher percentage of votes for a candidate, while a lighter shade represents a lower percentage.
- Symbols and Markers: Icons or symbols can be used to denote specific features, such as the location of polling stations, voter turnout rates, or demographic information. These elements add further layers of information to the map, enhancing its analytical potential.
- Legends and Keys: Clear legends and keys are essential for understanding the map’s visual language. These explanatory elements provide a detailed breakdown of the colors, symbols, and other visual elements used on the map, ensuring that the data is easily interpreted.
Beyond the Surface: The Importance of Electoral Results Maps
Electoral results maps offer valuable insights into the dynamics of elections and the political landscape. Their significance extends beyond simply visualizing the outcome of an election; they serve as powerful tools for analysis and understanding:
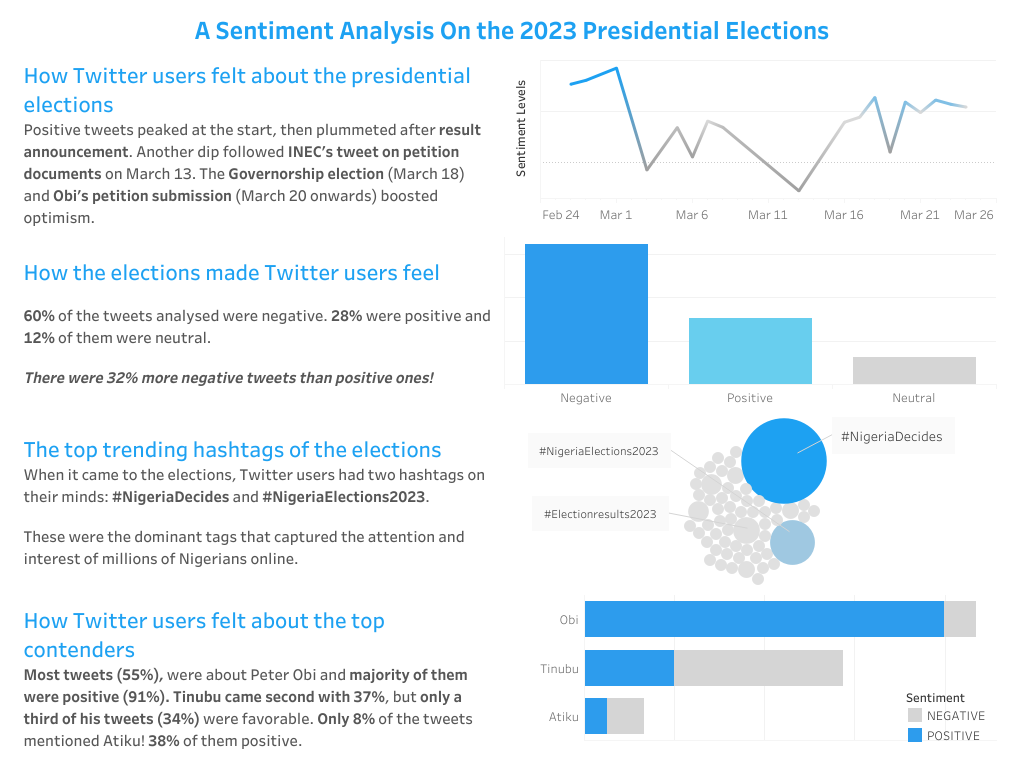
- Identifying Electoral Trends: By comparing maps from different elections, analysts can identify emerging trends in voter behavior, such as shifting political affiliations, the rise of new parties, or the emergence of regional voting patterns.
- Understanding Regional Differences: Electoral results maps highlight regional variations in voting preferences, providing insights into the social, economic, and political factors that shape voter behavior within different parts of a country or region.
- Analyzing Political Strategies: Political parties and candidates can use electoral results maps to analyze their performance, identify areas of strength and weakness, and inform their future campaign strategies.
- Promoting Transparency and Accountability: Electoral results maps promote transparency by providing a clear and accessible visual representation of the election results, enabling voters to understand how their votes were distributed and how the election unfolded.
- Facilitating Public Discourse: Electoral results maps can facilitate informed public discourse by providing a shared visual language for discussing election results and their implications, fostering a deeper understanding of the political landscape.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring the Nuances of Electoral Results Maps
While electoral results maps provide a valuable overview of election outcomes, it’s crucial to recognize their limitations and explore the nuances that can influence their interpretation:
- Electoral Systems: The type of electoral system employed can significantly impact the visual representation of election results. Proportional representation systems, for instance, can lead to more fragmented maps with multiple parties represented, while first-past-the-post systems might result in more homogenous maps dominated by a few parties.
- Voter Turnout: Voter turnout rates can influence the interpretation of electoral results maps. A high turnout might indicate a stronger mandate for the winning candidate or party, while a low turnout might suggest a less definitive result.
- Demographic Data: Incorporating demographic data, such as population density, age distribution, or income levels, can enhance the analytical power of electoral results maps. This additional information can help to explain voting patterns and identify correlations between demographic factors and voting preferences.
- Data Visualization Techniques: Different data visualization techniques can be employed to create electoral results maps, each with its own strengths and limitations. Choosing the appropriate visualization technique is essential for accurately representing the data and conveying its meaning effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions about Electoral Results Maps
Q: What are the different types of electoral results maps?
A: Electoral results maps can be categorized based on their purpose, data representation, or visualization techniques. Common types include:
- Choropleth Maps: These maps use color shading to represent the intensity of a variable, such as the percentage of votes for a candidate or party, across different geographical areas.
- Dot Density Maps: These maps use dots to represent the number of votes cast for a particular candidate or party, with the density of dots indicating the level of support in different areas.
- Cartogram Maps: These maps distort geographical areas based on the magnitude of a variable, such as the number of votes cast, to emphasize the relative importance of different regions.
Q: How can I find reliable electoral results maps?
A: Reliable electoral results maps are typically published by reputable organizations such as:
- Government Election Commissions: These bodies are responsible for conducting and overseeing elections, and their websites often provide official electoral results maps.
- News Organizations: Major news organizations often publish electoral results maps as part of their election coverage.
- Academic Institutions: Research institutions and universities may conduct independent analyses of election data and publish their own electoral results maps.
Q: What are the limitations of electoral results maps?
A: Electoral results maps, while valuable tools, have limitations:
- Oversimplification: Maps can oversimplify complex electoral dynamics, potentially obscuring important nuances in voting patterns.
- Geographic Bias: Maps can emphasize geographical divisions, potentially neglecting other factors that influence voter behavior.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of electoral results maps depends on the quality and reliability of the underlying election data.
Tips for Interpreting Electoral Results Maps
- Context is Key: Always consider the context of the election and the specific data being represented on the map.
- Look Beyond the Visual: Don’t rely solely on the visual representation of the map; consider the underlying data and any accompanying analysis.
- Compare and Contrast: Compare electoral results maps from different elections to identify trends and patterns over time.
- Consider Alternative Perspectives: Explore different perspectives on the data and consider alternative interpretations of the map.
Conclusion
Electoral results maps offer a powerful visual language for understanding the dynamics of elections and the political landscape. These maps provide a valuable framework for analyzing voting patterns, identifying regional differences, and understanding the implications of election outcomes. However, it’s crucial to interpret these maps with a critical eye, considering their limitations and exploring the nuances that can influence their interpretation. By understanding the strengths and limitations of electoral results maps, we can leverage their insights to foster a more informed and engaged public discourse about elections and the future of democracy.
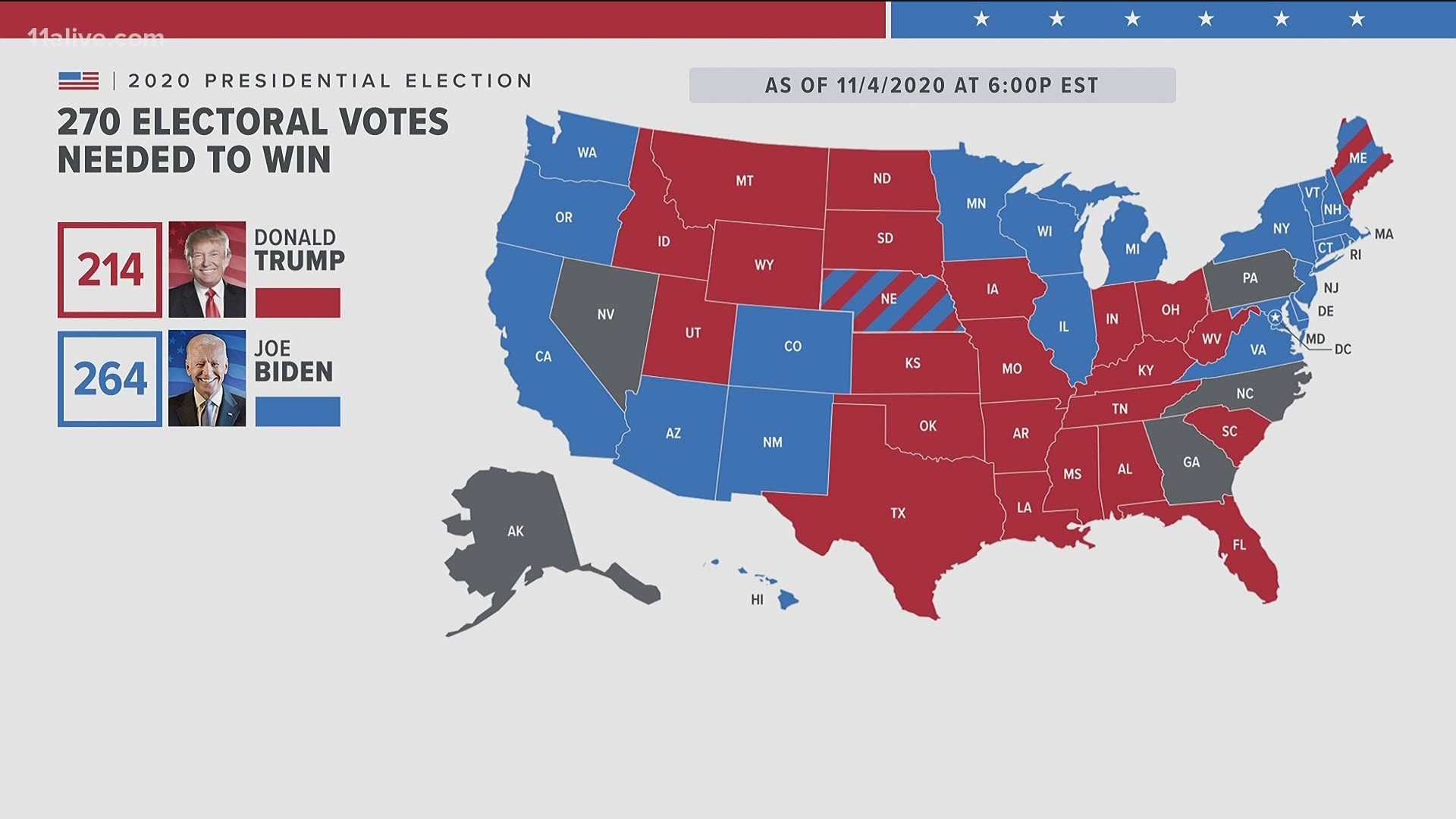
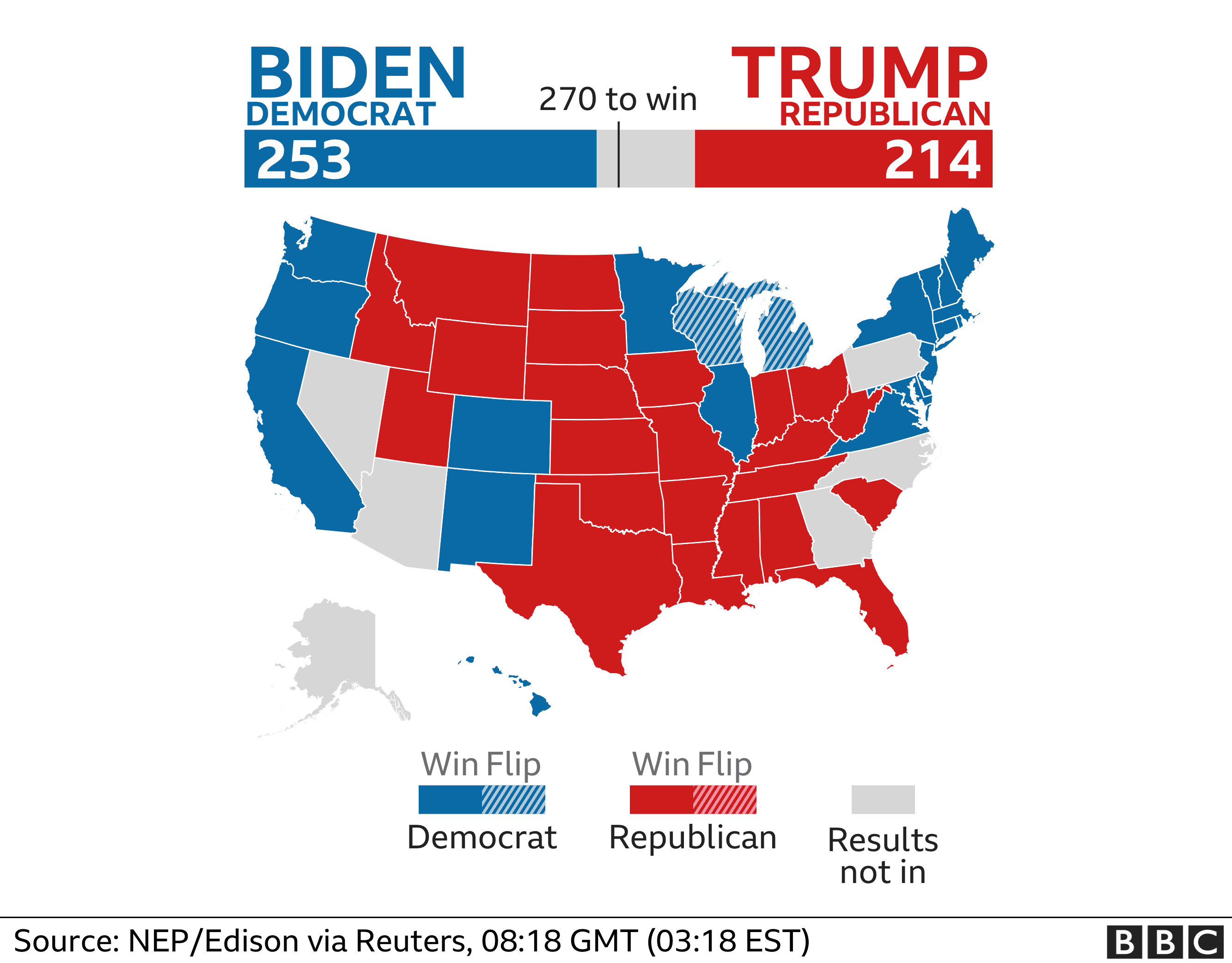
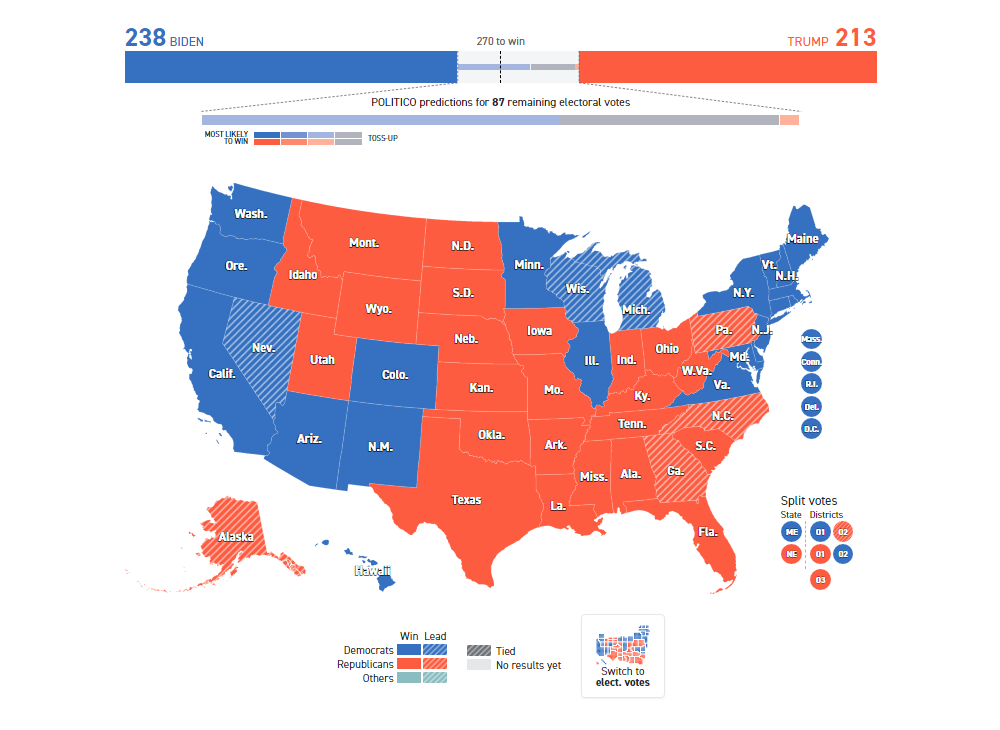


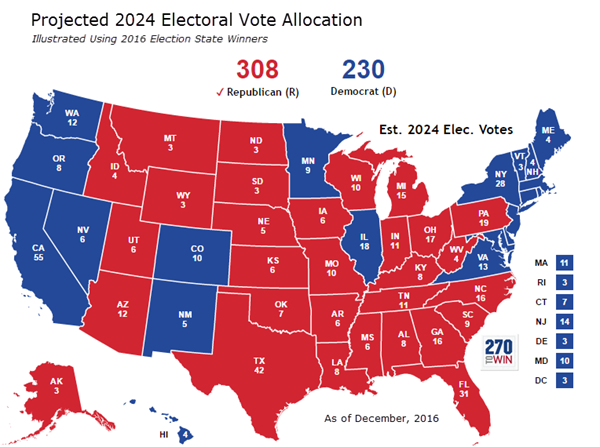
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of Democracy: A Comprehensive Guide to Electoral Results Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!