Unveiling the Dynamics of the Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Look at Wind Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Dynamics of the Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Look at Wind Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Dynamics of the Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Look at Wind Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Dynamics of the Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Look at Wind Maps
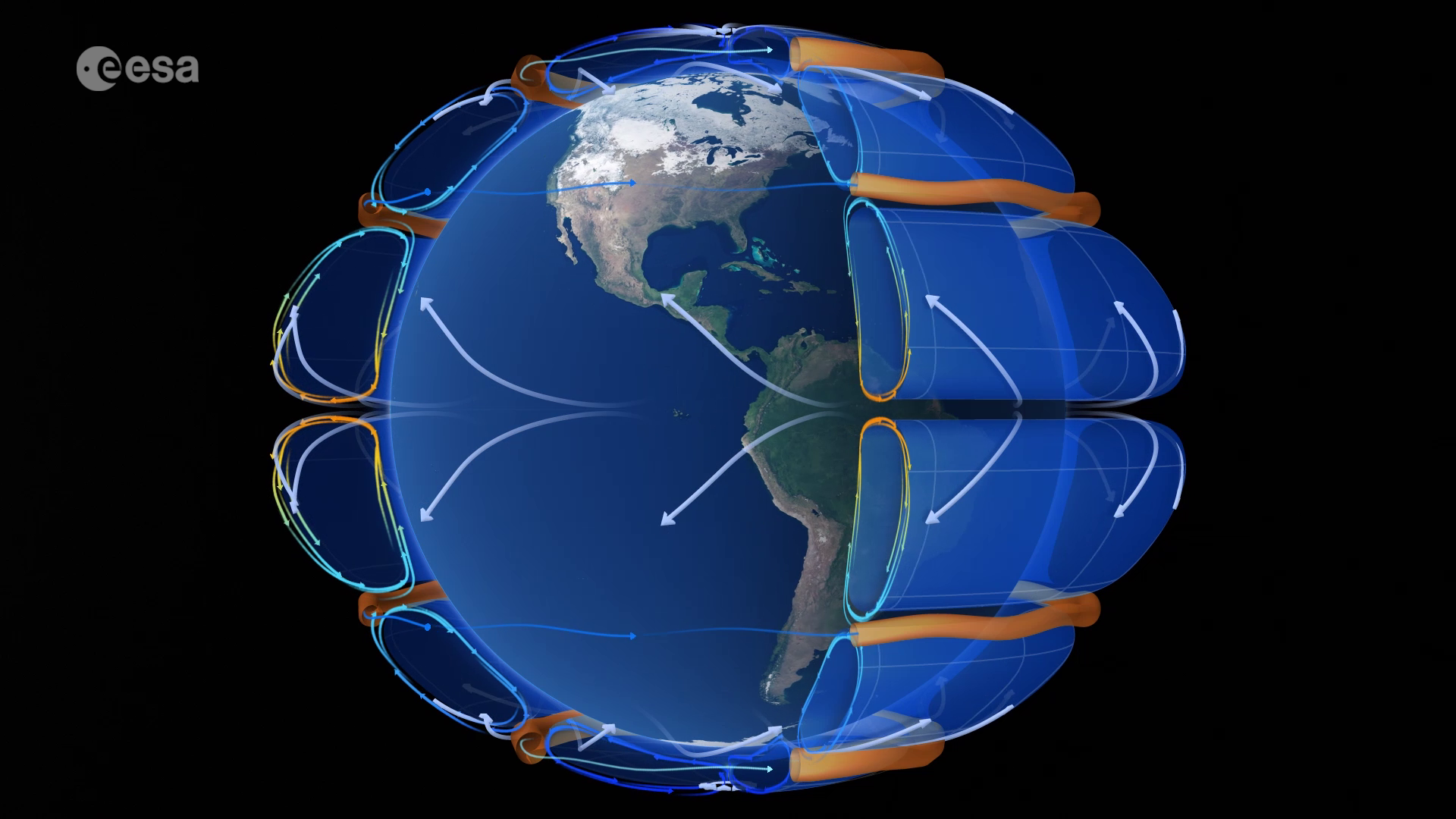
Wind, an invisible force that shapes our landscapes, drives our weather, and influences our energy production, remains a complex and fascinating aspect of the Earth’s atmosphere. Understanding wind patterns is crucial for various disciplines, from meteorology to aviation to renewable energy development. To visualize and analyze these intricate wind patterns, we rely on powerful tools known as wind maps.
The Significance of Wind Maps
Wind maps serve as visual representations of wind speed and direction across a specific geographic area. They provide a snapshot of the wind’s behavior, allowing us to decipher its intricate patterns and glean valuable insights. Their importance stems from their ability to:
- Predict Weather Patterns: Wind maps play a pivotal role in forecasting weather conditions, as wind patterns are closely tied to atmospheric pressure gradients, temperature variations, and other meteorological phenomena. Understanding wind flow helps meteorologists predict the movement of storms, the formation of clouds, and the potential for extreme weather events.
- Optimize Renewable Energy Production: Wind energy, a clean and sustainable source of power, relies heavily on understanding wind patterns. Wind maps are indispensable for site selection and turbine placement, ensuring optimal energy generation. They help identify areas with consistent and strong wind resources, maximizing the efficiency of wind farms.
- Enhance Aviation Safety: Wind maps are crucial for aviation safety, providing pilots with real-time information on wind conditions at various altitudes. This data helps pilots navigate effectively, avoid turbulence, and optimize flight paths, contributing to a smoother and safer journey.
- Inform Environmental Studies: Wind patterns influence air quality, pollution dispersal, and the movement of pollutants. Wind maps aid in understanding how pollutants travel, helping scientists develop strategies to mitigate air pollution and protect public health.
- Support Outdoor Activities: Wind maps are valuable for outdoor enthusiasts, particularly those involved in activities like sailing, kiteboarding, and paragliding. These maps provide essential information on wind speed and direction, allowing for safer and more enjoyable experiences.
Types of Wind Maps
Wind maps come in various forms, each tailored to specific applications and data sources. Some common types include:
- Surface Wind Maps: These maps depict wind conditions near the Earth’s surface, typically within the first few hundred meters. They are frequently used in meteorology, weather forecasting, and aviation.
- Upper-Air Wind Maps: These maps showcase wind patterns at higher altitudes, often used for aviation and weather forecasting. They provide insights into jet streams and other atmospheric features.
- Wind Resource Maps: Designed specifically for renewable energy applications, these maps highlight areas with strong and consistent wind resources, aiding in wind farm development.
- Historical Wind Maps: These maps showcase wind patterns over extended periods, allowing for long-term analysis and trend identification. They are invaluable for understanding climate change impacts on wind patterns.
- Real-Time Wind Maps: Utilizing live data from weather stations and satellites, these maps provide up-to-the-minute information on wind conditions, critical for real-time applications like aviation and wind energy production.
Understanding the Components of a Wind Map
Wind maps typically display wind speed and direction using various visual elements:
- Arrows: Arrows indicate wind direction, with the arrowhead pointing towards the direction from which the wind is blowing.
- Color Gradients: Color gradients are often used to represent wind speed, with different colors corresponding to different wind speeds.
- Isobars: Lines of equal wind speed, called isobars, can be used to depict areas of similar wind conditions.
- Contour Lines: Contour lines represent areas of equal wind direction, providing a visual representation of wind flow patterns.
Interpreting Wind Maps
Interpreting wind maps requires a basic understanding of the information presented. Key elements to consider include:
- Wind Speed: Wind speed is typically measured in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h). Higher wind speeds are often represented by darker or brighter colors on the map.
- Wind Direction: Wind direction is indicated by arrows pointing towards the direction from which the wind is blowing. North is typically at the top of the map, with other cardinal directions following standard compass conventions.
- Wind Patterns: Observing the overall flow of arrows and color gradients reveals wind patterns, highlighting areas of convergence, divergence, and rotational flow.
FAQs About Wind Maps
Q: What are the limitations of wind maps?
A: Wind maps provide a snapshot of wind conditions at a specific time and location. They do not account for local variations, microclimates, or dynamic atmospheric changes.
Q: How accurate are wind maps?
A: Accuracy depends on the data sources, resolution, and the map’s intended purpose. Real-time wind maps based on live data tend to be more accurate than historical maps.
Q: How can I access wind maps?
A: Numerous online resources offer free and paid wind map services. Government agencies, weather forecasting websites, and renewable energy companies often provide access to wind maps.
Q: What are some applications of wind maps beyond weather forecasting?
A: Wind maps have applications in various fields, including:
- Urban planning: Wind maps help architects and urban planners design buildings and infrastructure that are more resilient to wind loads.
- Agriculture: Wind maps can help farmers understand wind patterns to optimize crop planting, irrigation, and pest control.
- Pollution control: Wind maps aid in understanding the dispersal of pollutants and developing strategies for mitigating air pollution.
Tips for Using Wind Maps Effectively
- Consider the map’s purpose: Before using a wind map, understand its intended purpose and the data sources used.
- Pay attention to the scale: Wind maps can vary in scale, so it’s important to understand the geographic area covered.
- Look for patterns: Observe wind direction and speed patterns to identify areas of high wind activity or areas of calm conditions.
- Compare different maps: Consult multiple wind maps from different sources to get a comprehensive view of wind conditions.
- Consult with experts: For specific applications, consult with meteorologists, wind energy experts, or other relevant professionals.
Conclusion
Wind maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding and analyzing wind patterns, contributing to advancements in various fields. They provide crucial insights for weather forecasting, renewable energy production, aviation safety, environmental studies, and outdoor activities. By effectively interpreting and utilizing wind maps, we can harness the power of wind to improve our lives and create a more sustainable future.

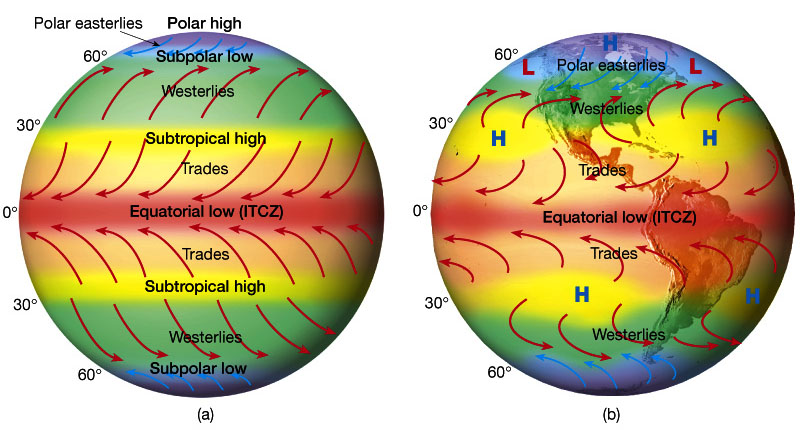



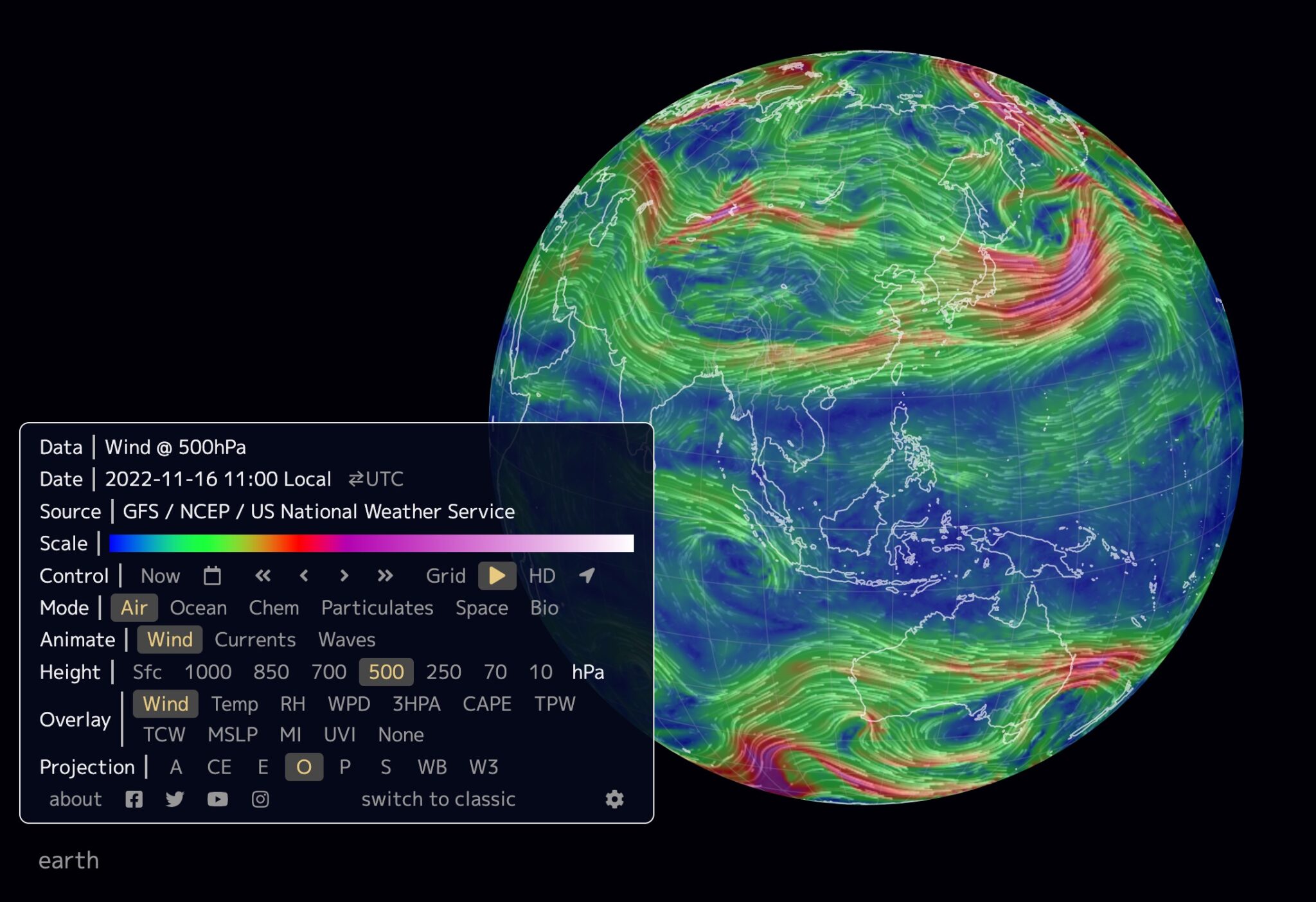
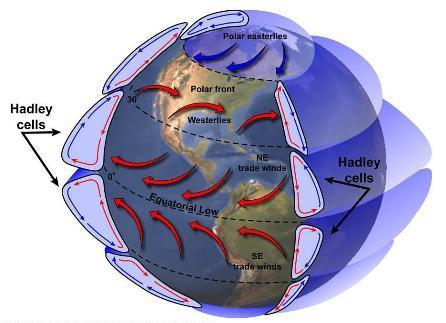

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Dynamics of the Atmosphere: A Comprehensive Look at Wind Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!