Unveiling Patterns: The Power of Map Visualizations
Related Articles: Unveiling Patterns: The Power of Map Visualizations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Patterns: The Power of Map Visualizations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Patterns: The Power of Map Visualizations
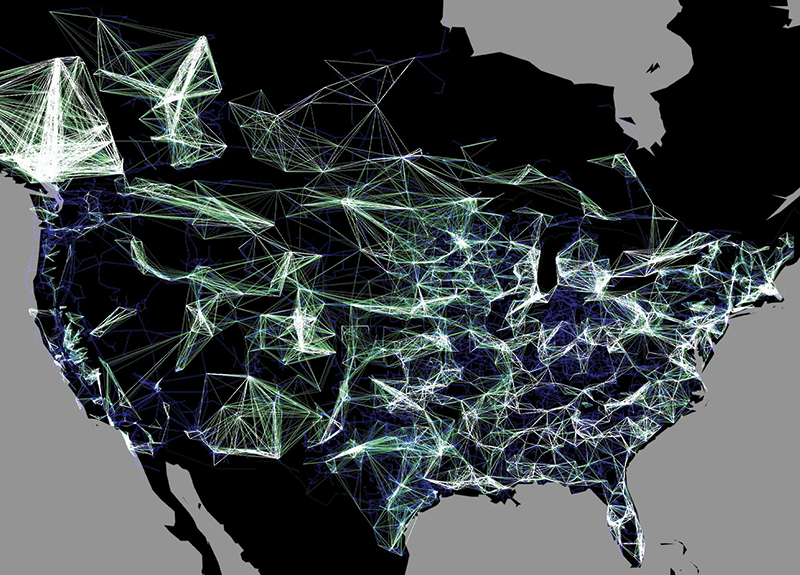
The world is a tapestry of interconnected data points, a complex web of relationships waiting to be unraveled. Maps, traditionally used for navigation, have evolved into powerful tools for visualizing and understanding this data. Map visualizations, by transforming data into geographically-grounded representations, offer a unique lens for exploring patterns, trends, and insights that might remain hidden in raw data sets.
Understanding the Essence of Map Visualizations
At its core, map visualization involves translating numerical or categorical data onto a geographical framework. This seemingly simple act unlocks a powerful potential for revealing spatial relationships, geographical variations, and the distribution of phenomena across space. By visually representing data on a map, we can:
- Identify Spatial Clusters: Spotting areas with high concentrations of specific data points, such as crime rates, disease outbreaks, or population density.
- Uncover Geographic Trends: Revealing how data values change across regions, such as the spread of poverty, the growth of industries, or the impact of climate change.
- Analyze Relationships: Understanding the correlation between different data sets, such as the relationship between pollution levels and proximity to industrial zones, or the impact of infrastructure on economic development.
- Communicate Insights Effectively: Presenting complex data in a readily understandable format, making it accessible to a wider audience and facilitating informed decision-making.
The Versatility of Map Visualizations
The applications of map visualizations span diverse fields, encompassing:
- Business Intelligence: Analyzing customer demographics, market trends, and competitor locations to optimize business strategies.
- Urban Planning: Visualizing population density, traffic flow, and access to services to design efficient and sustainable urban environments.
- Environmental Monitoring: Tracking pollution levels, deforestation rates, and natural resource depletion to inform environmental conservation efforts.
- Public Health: Mapping disease outbreaks, identifying high-risk areas, and monitoring the effectiveness of public health interventions.
- Social Sciences: Analyzing migration patterns, social inequalities, and the impact of political events on population distribution.
- Disaster Management: Visualizing disaster-affected areas, predicting potential risks, and coordinating relief efforts.
Types of Map Visualizations
The world of map visualizations offers a diverse toolkit, each type serving a specific purpose:
- Choropleth Maps: Using color gradients to represent data values across geographical regions, highlighting areas with high or low concentrations.
- Dot Density Maps: Employing dots to represent data points, with the density of dots reflecting the magnitude of the phenomenon.
- Proportional Symbol Maps: Utilizing symbols of varying sizes to represent data values, with larger symbols indicating higher values.
- Flow Maps: Depicting movement patterns, such as migration flows, trade routes, or transportation networks.
- Heatmaps: Using color gradients to represent data density, highlighting areas with high concentrations of data points.
- Cartograms: Distorting geographical boundaries to represent data values, emphasizing areas with high or low values.
Beyond Static Representations: Interactive Map Visualizations
While static maps provide a snapshot of data, interactive map visualizations offer a dynamic and immersive experience. By incorporating features like:
- Zooming and Panning: Allowing users to explore specific areas of interest in detail.
- Data Filtering and Selection: Enabling users to isolate and analyze specific data sets.
- Data Aggregation and Disaggregation: Providing options to view data at different levels of granularity.
- Time-Series Analysis: Tracking changes in data values over time, revealing trends and patterns.
Interactive map visualizations empower users to actively engage with the data, discover hidden insights, and make informed decisions based on the visualized information.
FAQs About Map Visualizations
Q: What are the benefits of using map visualizations?
A: Map visualizations offer several advantages:
- Enhanced Understanding: Presenting complex data in a visually intuitive format, making it easier to grasp and interpret.
- Improved Decision-Making: Providing a spatial context for data analysis, enabling informed decisions based on geographical patterns and relationships.
- Effective Communication: Communicating data insights to a wider audience, including those with limited technical expertise.
- Data Exploration and Discovery: Facilitating the exploration of data, revealing patterns and trends that might otherwise remain hidden.
Q: What are the limitations of map visualizations?
A: While powerful, map visualizations also have limitations:
- Data Bias: The accuracy and validity of map visualizations depend on the quality and completeness of the underlying data.
- Visual Distortions: Map projections and data aggregation methods can introduce visual distortions, potentially affecting the interpretation of data.
- Oversimplification: Map visualizations can simplify complex data, potentially omitting important nuances and details.
Q: What are some tips for creating effective map visualizations?
A: Creating effective map visualizations requires careful consideration:
- Choose the Right Map Type: Select a map type that best suits the data and the intended message.
- Use Clear and Consistent Visuals: Employ colors, symbols, and legends effectively to convey information clearly.
- Minimize Visual Clutter: Avoid excessive use of colors, symbols, or labels that can obscure data patterns.
- Provide Context and Explanation: Include relevant information, such as a legend, scale, and data sources to aid interpretation.
Conclusion: The Evolving Landscape of Map Visualizations
Map visualizations have emerged as a crucial tool for understanding the spatial dimensions of data, enabling us to explore patterns, trends, and relationships that might remain hidden in raw data sets. As technology continues to advance, map visualizations are becoming increasingly sophisticated, incorporating interactive elements, advanced data analysis techniques, and immersive experiences. The future of map visualizations holds immense potential, promising to unlock new insights, empower informed decision-making, and foster a deeper understanding of our interconnected world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Patterns: The Power of Map Visualizations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!