Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Armenia: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Armenia: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Armenia: A Geographical and Historical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Armenia: A Geographical and Historical Exploration

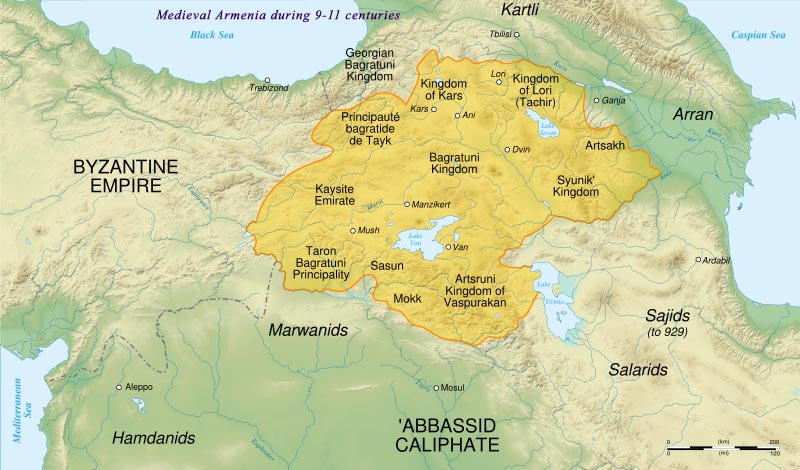
The map of ancient Armenia, a land steeped in history and culture, offers a fascinating window into a civilization that flourished for centuries. Its boundaries, though shifting over time, encompassed a strategically important region at the crossroads of major empires, shaping its destiny and leaving an indelible mark on the world.
Delving into the Geographical Tapestry:
Ancient Armenia, a landlocked region in the Caucasus, occupied a pivotal location bridging the eastern Mediterranean with the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. Its topography, characterized by high plateaus, mountain ranges, and fertile valleys, played a crucial role in its history. The Armenian Highlands, encompassing the modern-day territories of Armenia, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Iran, provided natural defenses against invaders, while its fertile valleys nurtured a vibrant agricultural economy.
Tracing the Boundaries:
The borders of ancient Armenia fluctuated throughout its history, influenced by political shifts and territorial disputes. The core region, known as "Greater Armenia," encompassed territories roughly equivalent to modern-day Armenia, eastern Turkey, and parts of Azerbaijan. During periods of expansion, the Armenian kingdom extended its reach further, incorporating territories in present-day Georgia, Syria, and northern Mesopotamia.
Key Geographical Features:
- Mount Ararat: This iconic peak, standing at 5,137 meters, holds immense cultural and religious significance for Armenians. It is believed to be the resting place of Noah’s Ark.
- Lake Van: The largest lake in Turkey, it played a vital role in Armenian culture and economy.
- The Araxes River: This major river, forming the border between Armenia and Azerbaijan, was a significant source of water and a vital trade route.
- The Euphrates River: This ancient river, flowing through modern-day Turkey and Syria, played a role in the irrigation of Armenian lands.
Historical Significance:
The map of ancient Armenia reflects a rich and complex history, shaped by the rise and fall of empires, religious transformations, and cultural exchanges.
- The Urartu Kingdom: This powerful Iron Age kingdom, centered in the Armenian Highlands, influenced the development of Armenian culture and language.
- The Armenian Kingdom: Founded in the 3rd century BC, the Armenian Kingdom established its independence and flourished for centuries, becoming a major power in the region.
- The Silk Road: Ancient Armenia lay on the Silk Road, a vital trade route connecting East and West, fostering economic prosperity and cultural exchange.
- Christianity: Armenia became the first nation to officially adopt Christianity as its state religion in the 4th century AD, marking a significant turning point in its history.
The Legacy of Ancient Armenia:
The map of ancient Armenia serves as a testament to a civilization that thrived for centuries, leaving behind a lasting legacy in art, architecture, literature, and religion.
- Monasteries and Churches: Ancient Armenian churches and monasteries, many built in remote and inaccessible locations, are renowned for their architectural beauty and historical significance.
- Art and Literature: Armenian art and literature flourished during the ancient period, showcasing a rich artistic tradition and a vibrant literary heritage.
- Cultural Identity: The map of ancient Armenia embodies a sense of national identity and cultural pride for Armenians worldwide, reminding them of their rich heritage and enduring spirit.
FAQs about the Map of Ancient Armenia:
1. What are the major regions of ancient Armenia?
Ancient Armenia encompassed several regions, including "Greater Armenia," which included modern-day Armenia, eastern Turkey, and parts of Azerbaijan. Other regions included Sophene, Commagene, and the Kingdom of Armenia Minor.
2. What was the significance of the Armenian Kingdom?
The Armenian Kingdom, founded in the 3rd century BC, established its independence and flourished for centuries, becoming a major power in the region. It played a crucial role in the defense of the Eastern Roman Empire against Persian invasions.
3. Why was Armenia important for the Silk Road?
Ancient Armenia lay on the Silk Road, a vital trade route connecting East and West. Its strategic location facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures, contributing to its economic prosperity.
4. How did Christianity impact ancient Armenia?
Armenia became the first nation to officially adopt Christianity as its state religion in the 4th century AD. This event had a profound impact on Armenian culture and identity, shaping its religious practices, art, and literature.
5. What are some of the most notable ancient Armenian sites?
Notable ancient Armenian sites include the monasteries of Tatev, Khor Virap, and Geghard, the ancient city of Ani, and the Mount Ararat, a symbol of Armenian national identity.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Ancient Armenia:
- Study the geographical features: Pay attention to the mountain ranges, rivers, and lakes that shaped the landscape and influenced the development of ancient Armenia.
- Explore the historical context: Understand the major empires and civilizations that interacted with ancient Armenia, including the Urartu Kingdom, the Armenian Kingdom, and the Roman Empire.
- Focus on the key events: Learn about the major turning points in Armenian history, such as the adoption of Christianity and the fall of the Armenian Kingdom.
- Examine the cultural legacy: Explore the art, architecture, and literature that emerged from ancient Armenia, reflecting its unique cultural heritage.
Conclusion:
The map of ancient Armenia serves as a powerful reminder of a civilization that played a significant role in shaping the history and culture of the region. Its strategic location, diverse landscapes, and rich cultural heritage continue to inspire and fascinate scholars and travelers alike. Studying the map of ancient Armenia offers a unique opportunity to understand the complex interplay of geography, history, and culture that shaped this remarkable civilization.




/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/89/8a/898a9e8c-059e-4860-8ac0-b12ff03e41a8/armenia1.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Armenia: A Geographical and Historical Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!