Unmasking the Heat: Understanding Heat Zones Maps and Their Significance
Related Articles: Unmasking the Heat: Understanding Heat Zones Maps and Their Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unmasking the Heat: Understanding Heat Zones Maps and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unmasking the Heat: Understanding Heat Zones Maps and Their Significance

Heat zones maps, also known as heat maps, are visual representations that depict the intensity of a particular phenomenon across a defined area. They use color gradients, typically ranging from cool colors (blue, green) for low intensity to warm colors (yellow, red) for high intensity, to illustrate the distribution and concentration of the phenomenon being analyzed.
These maps are not limited to depicting heat, but can be used to visualize a wide range of data including:
- Population density: Identifying areas with high concentrations of people.
- Traffic congestion: Highlighting areas with heavy traffic flow.
- Crime rates: Pinpointing locations with elevated crime activity.
- Sales performance: Revealing areas with strong sales figures.
- Website traffic: Identifying areas on a website with the most user engagement.
The versatility of heat zones maps makes them a powerful tool for various applications across diverse fields, ranging from urban planning and public safety to marketing and business analysis.
Deciphering the Colors: Interpreting Heat Zones Maps
The core strength of heat zones maps lies in their ability to visually communicate complex data in an easily digestible format. By employing color gradients, they effectively translate numerical data into a readily understandable visual representation.
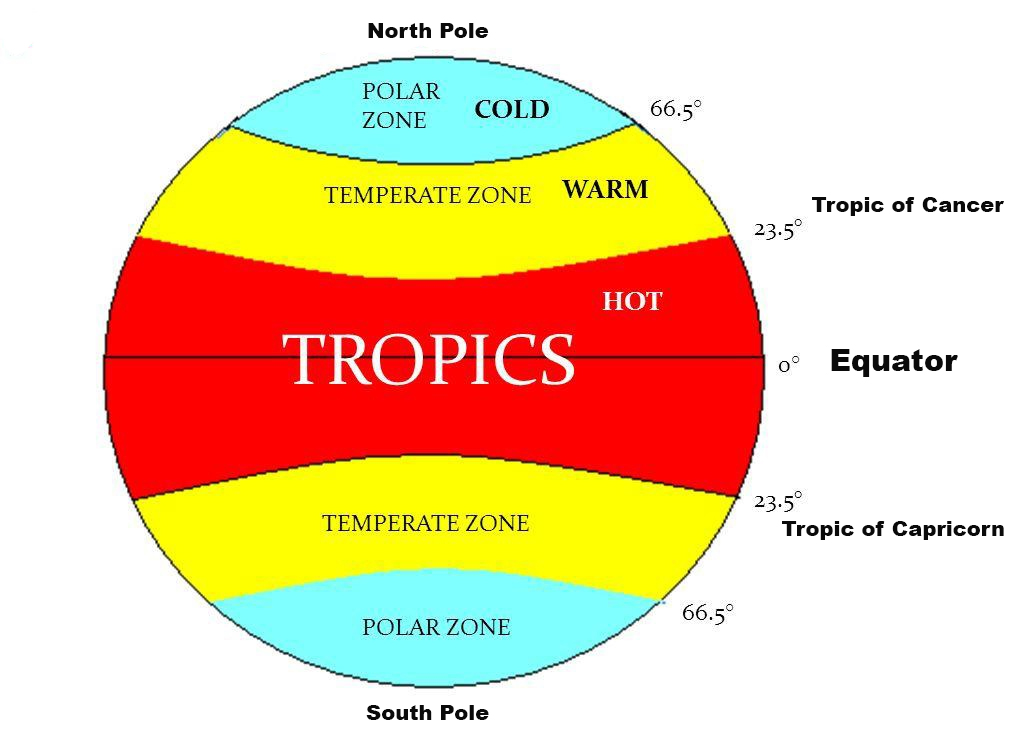
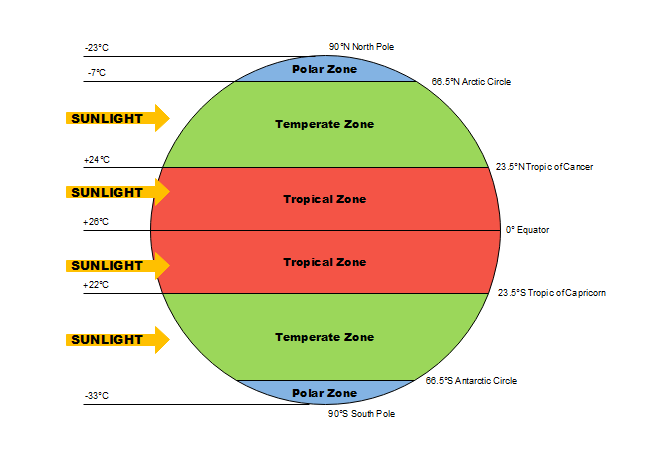
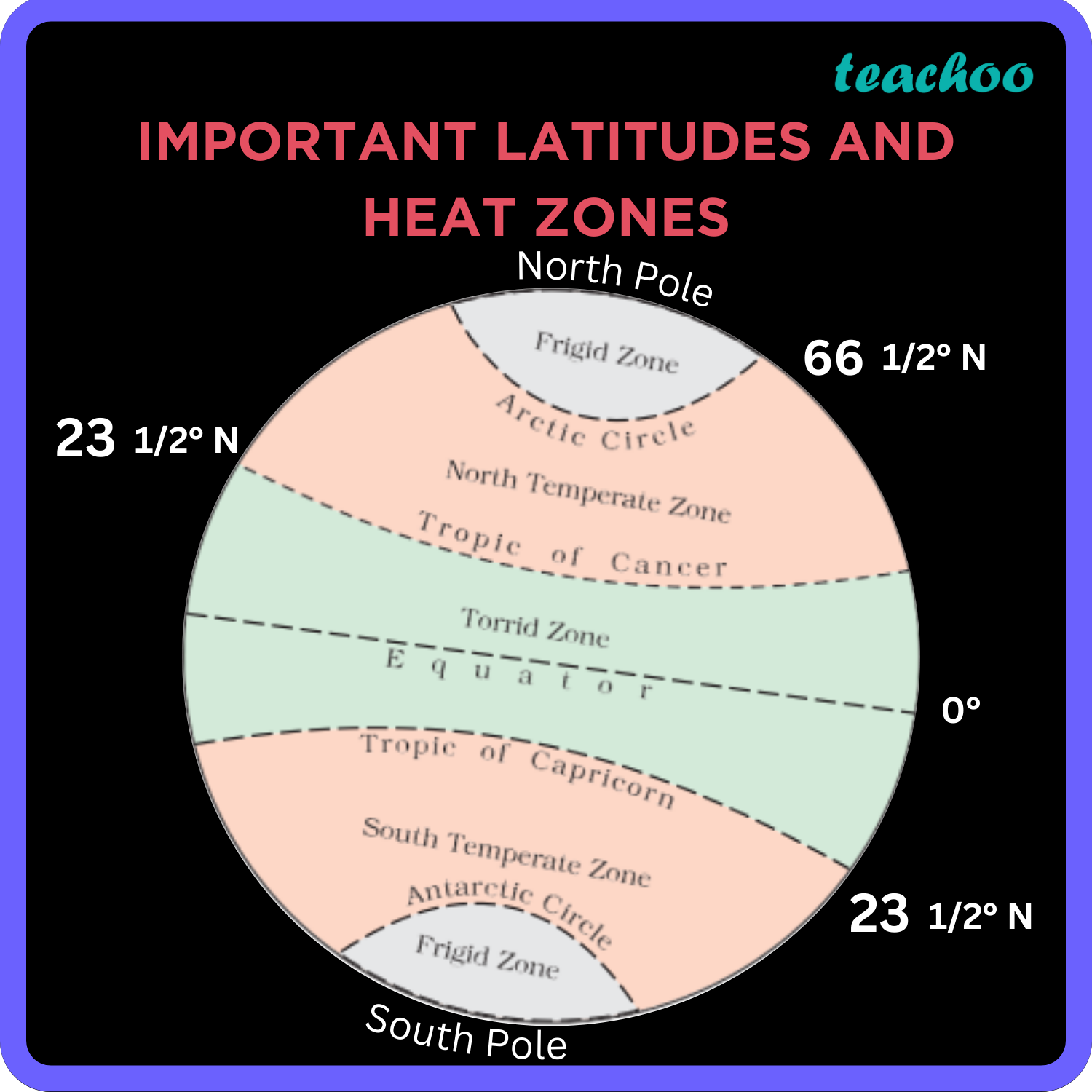
- Red: Signifies the highest intensity of the phenomenon being analyzed. This could represent areas with the highest population density, the heaviest traffic flow, or the most significant crime rates, depending on the specific data being visualized.
- Yellow: Indicates a moderately high intensity of the phenomenon.
- Green: Represents areas with a moderate intensity.
- Blue: Signifies the lowest intensity of the phenomenon.
The specific color gradient used may vary depending on the software or platform being used to create the map. However, the general principle of using a spectrum of colors to depict intensity remains consistent.
Beyond Visualization: The Benefits of Heat Zones Maps
Heat zones maps offer more than just visual clarity. They serve as valuable tools for:
- Identifying trends: They allow for the identification of patterns and trends within the data. For example, a heat map visualizing crime rates could reveal areas with consistent high crime activity, allowing law enforcement to allocate resources effectively.
- Making informed decisions: The insights gleaned from heat zones maps can inform decision-making in various domains. Urban planners can use heat maps of population density to optimize infrastructure development, while marketers can use heat maps of website traffic to understand user behavior and improve website design.
- Optimizing resources: By highlighting areas of high concentration, heat zones maps facilitate the efficient allocation of resources. For example, a heat map showing traffic congestion can help transportation authorities identify bottlenecks and implement solutions to improve traffic flow.
- Improving efficiency: Heat zones maps can be used to streamline processes and improve efficiency. For example, a sales team can use a heat map of sales performance to identify high-performing territories and allocate resources accordingly.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Heat Zones Maps
1. What types of data can be visualized using heat zones maps?
Heat zones maps can be used to visualize a wide range of data, including but not limited to:
- Quantitative data: Data that can be measured numerically, such as population density, traffic flow, crime rates, sales figures, and website traffic.
- Qualitative data: Data that describes qualities or characteristics, such as customer satisfaction ratings, product reviews, and social media sentiment.
2. How are heat zones maps created?
Heat zones maps are typically created using specialized software or online platforms. These tools allow users to upload data and specify the area to be visualized. The software then automatically generates the heat map based on the user’s input.
3. What are the limitations of heat zones maps?
While heat zones maps are powerful tools, they do have limitations:
- Oversimplification: They can oversimplify complex data, potentially leading to misinterpretations.
- Bias: The data used to create heat zones maps can be biased, leading to inaccurate representations.
- Context: It’s important to consider the context of the data being visualized. For example, a heat map of crime rates may not accurately reflect the true situation if the data is not adjusted for population density.
4. What are some real-world applications of heat zones maps?
Heat zones maps find applications in various fields:
- Urban planning: For analyzing population density, identifying areas requiring infrastructure development, and planning public transportation routes.
- Public safety: For analyzing crime rates, identifying high-risk areas, and deploying resources effectively.
- Marketing: For understanding website traffic, identifying user behavior, and optimizing marketing campaigns.
- Business analysis: For analyzing sales performance, identifying profitable territories, and allocating resources efficiently.
Tips for Creating Effective Heat Zones Maps
- Choose the right data: Select data that is relevant to the question being asked and ensures an accurate representation of the phenomenon being visualized.
- Use appropriate color gradients: Select colors that are visually appealing and clearly convey the intensity of the phenomenon being analyzed.
- Provide clear labels and legends: Include labels and legends to explain the data being visualized and the color gradient used.
- Consider the audience: Tailor the map to the specific audience, using language and visuals they will understand.
- Use appropriate tools: Select software or online platforms that are capable of creating high-quality heat zones maps.
Conclusion: The Power of Visual Insights
Heat zones maps are powerful tools for visualizing data and extracting valuable insights. By using color gradients to represent intensity, they effectively communicate complex information in a readily understandable format. Their applications span diverse fields, offering a wealth of benefits ranging from improved decision-making and optimized resource allocation to enhanced efficiency and a deeper understanding of trends and patterns. As data becomes increasingly ubiquitous, heat zones maps will continue to play a crucial role in enabling data-driven insights and informed decision-making across various sectors.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unmasking the Heat: Understanding Heat Zones Maps and Their Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!