Understanding California’s Fault Lines: A Map to Seismic Safety
Related Articles: Understanding California’s Fault Lines: A Map to Seismic Safety
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding California’s Fault Lines: A Map to Seismic Safety. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding California’s Fault Lines: A Map to Seismic Safety
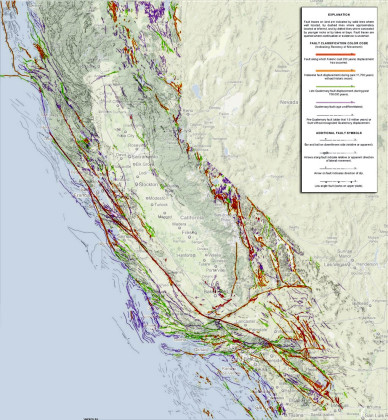
California is renowned for its stunning landscapes, vibrant cities, and thriving industries. However, beneath this surface of beauty and dynamism lies a complex network of geological features that make the state one of the most seismically active regions on Earth. These features, known as fault lines, are the scars of tectonic plate interactions, and they represent the potential for powerful earthquakes. Understanding the location and behavior of these faults is crucial for mitigating seismic risk and ensuring the safety of California’s residents and infrastructure.
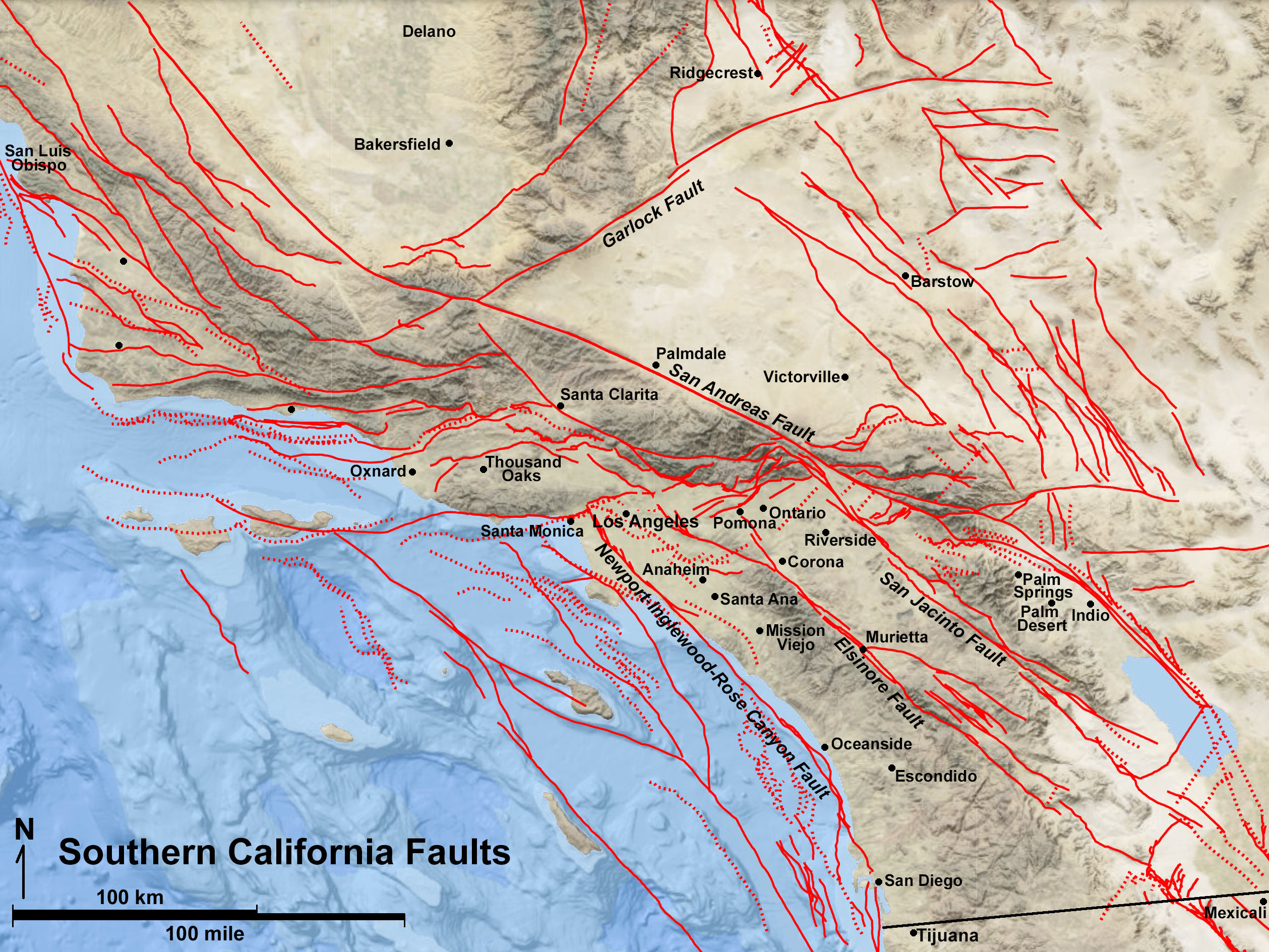
California’s Seismic Landscape: A Tapestry of Faults
The state’s earthquake vulnerability stems from its position at the boundary of two major tectonic plates: the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. These plates are constantly moving, grinding against each other, and building up immense pressure. This pressure is released periodically in the form of earthquakes, with the fault lines acting as the conduits for these seismic events.
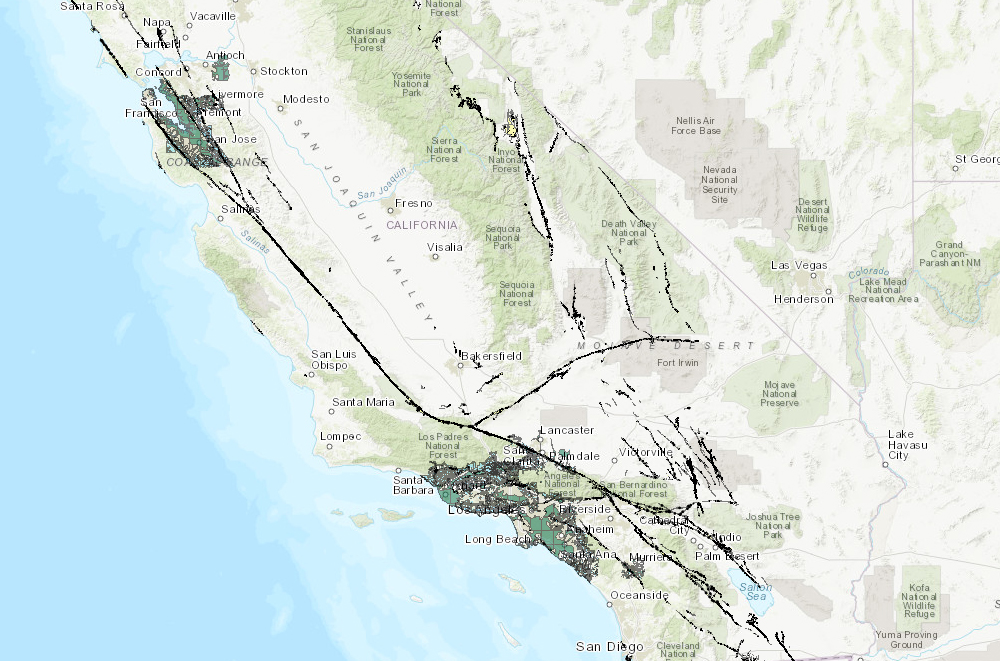
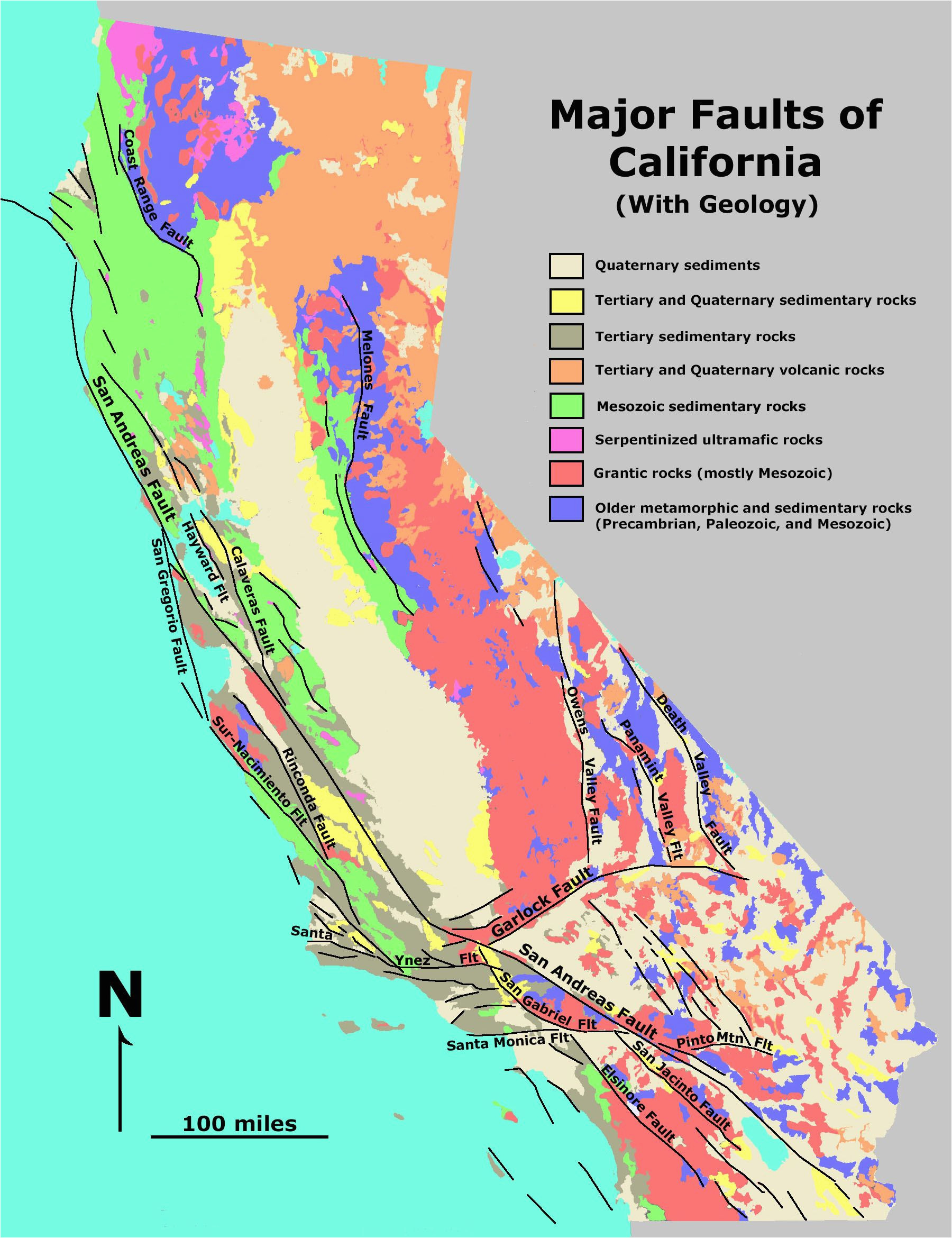
The San Andreas Fault, arguably the most famous fault in the world, bisects California from north to south, stretching over 800 miles. It represents the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. The San Andreas Fault is a strike-slip fault, meaning that the plates slide horizontally past each other. This movement is responsible for the majority of California’s significant earthquakes, including the devastating 1906 San Francisco earthquake.
Beyond the San Andreas Fault, California is crisscrossed by a network of other significant faults, each with its own unique characteristics and potential for generating earthquakes. These include:
- The Hayward Fault: This fault runs parallel to the San Andreas Fault, passing through the East Bay region and posing a serious threat to the densely populated San Francisco Bay Area.
- The Calaveras Fault: This fault branches off the San Andreas Fault near Hollister and extends north through the Diablo Range. It is known for its potential to generate significant earthquakes.
- The San Jacinto Fault: This fault runs parallel to the San Andreas Fault in Southern California and is considered one of the most active faults in the state.
- The Elsinore Fault: This fault stretches from the Salton Sea to the Pacific Ocean and is known for its complex structure and potential for generating large earthquakes.
The Importance of Understanding Fault Lines
A comprehensive understanding of California’s fault lines is paramount for several reasons:
- Earthquake Prediction and Mitigation: By studying fault lines, seismologists can gain insights into the frequency, magnitude, and potential impact of future earthquakes. This knowledge allows for the development of early warning systems, improved building codes, and effective disaster preparedness plans.
- Infrastructure Design and Development: Understanding the location and characteristics of fault lines is crucial for the safe design and construction of critical infrastructure, including buildings, bridges, dams, and power lines. This knowledge helps engineers incorporate seismic resilience into their designs, minimizing potential damage and disruption during earthquakes.
- Land Use Planning and Development: By mapping out fault zones, authorities can guide land use planning, ensuring that high-risk areas are not designated for development that could lead to significant casualties and economic losses in the event of an earthquake.
- Public Awareness and Education: A clear understanding of fault lines and their associated risks empowers the public to make informed decisions about their safety and preparedness. This includes understanding the importance of earthquake drills, having emergency supplies, and knowing evacuation routes.
FAQs about California’s Fault Lines
1. How often do earthquakes occur in California?
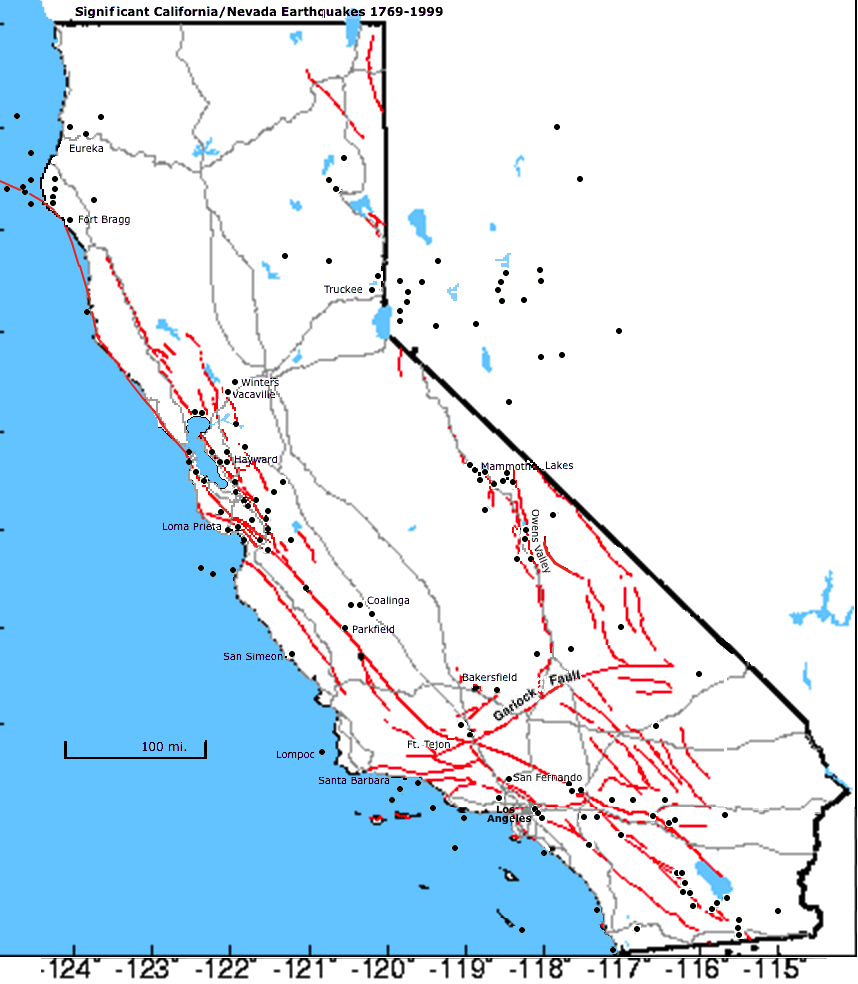
California experiences thousands of earthquakes every year, most of which are too small to be felt. However, significant earthquakes, those with magnitudes of 5.0 or greater, occur on average every few years.
2. What is the biggest earthquake recorded in California?
The largest earthquake ever recorded in California was the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, estimated at a magnitude of 7.8.
3. Can we predict earthquakes?
While we cannot predict the exact time and location of an earthquake, we can use scientific methods to assess the likelihood of earthquakes occurring in specific areas and to estimate their potential magnitude.
4. How can I prepare for an earthquake?
Preparing for an earthquake involves several steps:
- Secure your home: Anchor heavy furniture and appliances to prevent them from falling during shaking.
- Create an emergency kit: Include food, water, first-aid supplies, a flashlight, a radio, and other essential items.
- Develop an evacuation plan: Identify safe areas in your home and establish a meeting point for your family.
- Stay informed: Subscribe to emergency alerts and stay updated on earthquake-related news.
5. What should I do during an earthquake?
During an earthquake, it is important to:
- Drop, cover, and hold on: Find cover under a sturdy piece of furniture and hold on until the shaking stops.
- Stay away from windows and other potential hazards: Falling objects can cause serious injuries.
- If you are outdoors, move away from buildings and power lines: These structures pose a risk of collapse or falling debris.
Tips for Staying Safe in Earthquake-Prone Areas
- Know your risk: Identify the potential hazards in your area and learn about the earthquake risks specific to your home or workplace.
- Participate in earthquake drills: Regular practice helps you react calmly and effectively during an actual earthquake.
- Secure your home and belongings: Take steps to prevent damage and injuries by securing furniture, appliances, and other items.
- Stay informed: Subscribe to emergency alerts and stay updated on earthquake-related news and information.
- Be prepared to evacuate: Know the evacuation routes for your neighborhood and have a plan for where to go if you need to leave your home.
Conclusion
California’s fault lines are a constant reminder of the state’s seismic vulnerability. While earthquakes cannot be prevented, understanding these geological features, their behavior, and their potential impact is crucial for mitigating risk and ensuring the safety of California’s residents and infrastructure. By embracing a culture of preparedness, investing in earthquake-resistant infrastructure, and promoting public awareness, California can navigate its seismic future with greater resilience and minimize the potential for devastating consequences.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding California’s Fault Lines: A Map to Seismic Safety. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!