Understanding Body Map Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Body Map Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Body Map Pain: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Body Map Pain: A Comprehensive Guide

Pain, a ubiquitous human experience, often manifests in complex ways, defying simple explanations. While traditional pain management focuses on identifying the source of discomfort, a growing body of research emphasizes the importance of understanding the neural pathways and psychological factors that influence our perception of pain. This is where the concept of body map pain emerges, offering a nuanced perspective on how our brain interprets and processes pain signals.
Body map pain refers to the internal representation of our bodies, a mental map that reflects our physical structure and the location of pain. This map is not static; it is constantly being shaped by our experiences, emotions, and even our cultural beliefs. It is a dynamic representation of our physical self, influenced by a complex interplay of sensory input, memory, and emotional processing.
The Neurological Basis of Body Map Pain:
Our perception of pain originates from the somatosensory cortex, a region in the brain responsible for processing sensory information, including touch, temperature, and pain. The somatosensory homunculus, a distorted representation of the human body within this cortex, illustrates how different parts of the body are mapped onto the brain. Areas with a higher density of sensory receptors, like the fingertips and lips, occupy a larger space on the homunculus, reflecting their heightened sensitivity.
The body map, however, is not simply a passive reflection of physical reality. It is an active construction, constantly being updated based on our experiences. When we experience pain, the brain receives signals from the affected area, activating specific regions within the somatosensory cortex. These activations, over time, shape our internal representation of the body, influencing how we perceive and respond to pain.
Factors Influencing Body Map Pain:
Beyond the neurological pathways, several factors contribute to our body map pain:
- Past Experiences: Previous pain experiences, even those seemingly unrelated to the current discomfort, can influence our perception of pain. This is due to the brain’s tendency to create associations between pain and specific body regions.
- Emotional State: Stress, anxiety, and depression can amplify pain perception. Emotional distress can alter the brain’s processing of pain signals, leading to increased sensitivity and a heightened awareness of pain.
- Cultural Beliefs: Cultural beliefs and societal norms can also influence how we interpret and express pain. Some cultures encourage stoicism, while others emphasize vocalization of pain. These beliefs can shape our body map pain, influencing our pain threshold and how we communicate our discomfort.
- Attention and Focus: Our attention and focus can significantly impact pain perception. Focusing on the pain can amplify its intensity, while diverting attention can help reduce its impact.
The Importance of Understanding Body Map Pain:
Recognizing the dynamic nature of body map pain offers valuable insights into pain management and treatment. By understanding the factors that influence our perception of pain, we can:
- Identify and Address Underlying Factors: Understanding the role of past experiences, emotions, and cultural beliefs can help identify and address the root causes of chronic pain.
- Develop Personalized Treatment Plans: A personalized approach to pain management considers the individual’s unique body map pain, taking into account their specific experiences, emotional state, and cultural context.
- Utilize Cognitive Behavioral Techniques: Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness techniques can help individuals reframe their thoughts and beliefs about pain, reducing its perceived intensity and impact.
- Improve Communication with Healthcare Providers: A clear understanding of body map pain allows individuals to communicate their experiences more effectively with healthcare providers, leading to more accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
FAQs about Body Map Pain:
Q: How is body map pain different from traditional pain assessment?
A: Traditional pain assessment often relies on objective measures, such as physical examination and imaging tests. Body map pain considers the subjective experience of pain, recognizing that it is influenced by a complex interplay of neurological, psychological, and social factors.
Q: Can body map pain be changed?
A: Yes, body map pain is dynamic and can be influenced by various factors. By addressing underlying emotional issues, changing negative thought patterns, and engaging in mindfulness practices, individuals can modify their body map pain and reduce their perception of pain.
Q: How can I use body map pain to manage my own pain?
A: By understanding the factors that influence your body map pain, you can develop strategies to manage your discomfort. This might involve addressing underlying emotional issues, practicing mindfulness, or engaging in activities that shift your attention away from the pain.
Tips for Managing Body Map Pain:
- Practice Mindfulness: Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help shift attention away from pain and reduce its perceived intensity.
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: Identify and challenge negative thoughts about pain, reframing them with more realistic and positive perspectives.
- Engage in Physical Activity: Regular exercise can release endorphins, natural pain relievers, and improve overall well-being, potentially reducing pain perception.
- Seek Professional Help: If you are struggling to manage chronic pain, seek professional guidance from a healthcare provider or a pain management specialist.
Conclusion:
Body map pain offers a valuable lens through which to understand the complex nature of pain. By recognizing the dynamic interplay of neurological, psychological, and social factors that influence our perception of pain, we can develop more comprehensive and personalized approaches to pain management. Understanding the body map pain allows us to move beyond simply addressing the physical source of discomfort and instead focus on the individual’s unique experience, leading to more effective and holistic pain relief.



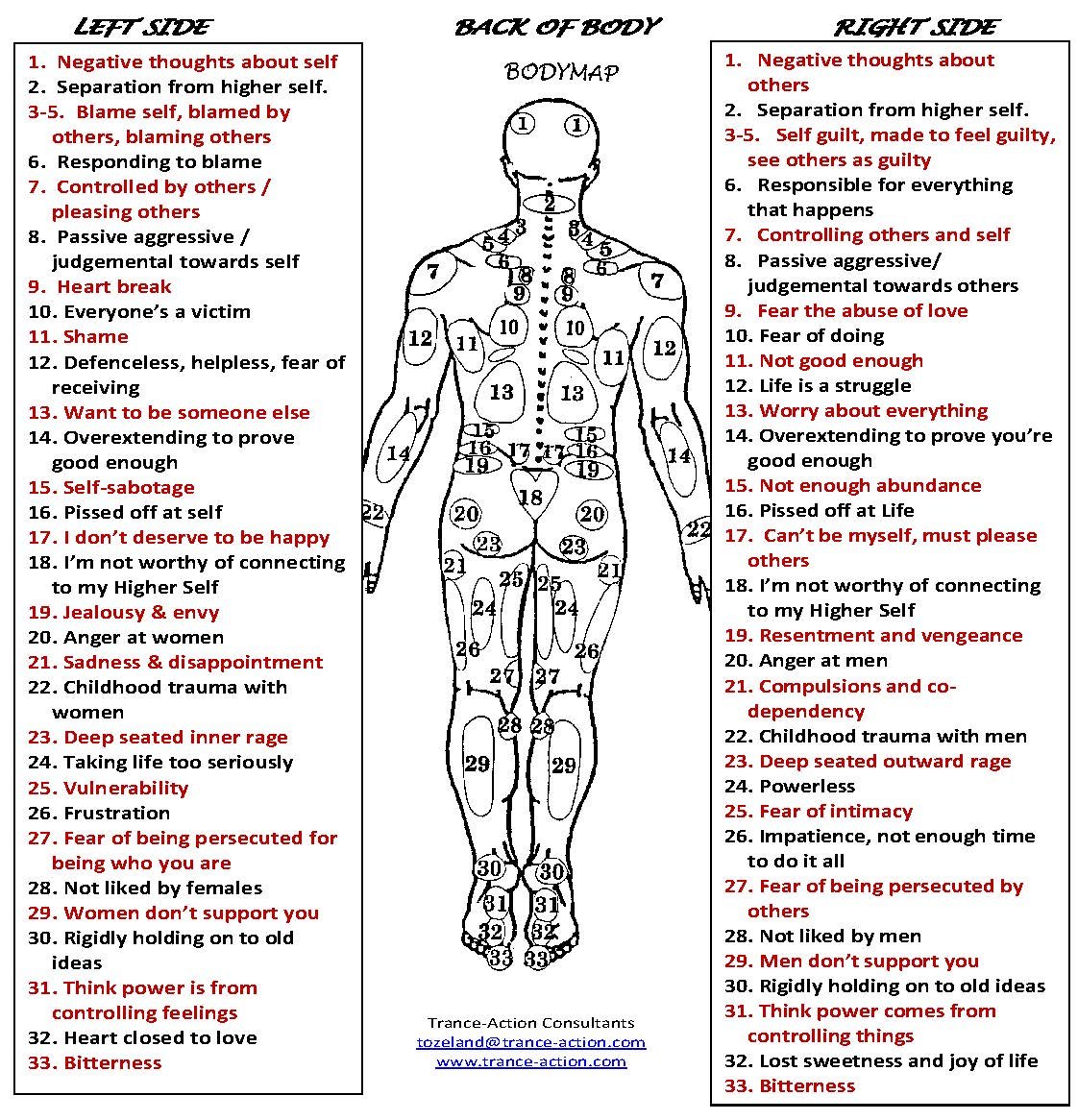

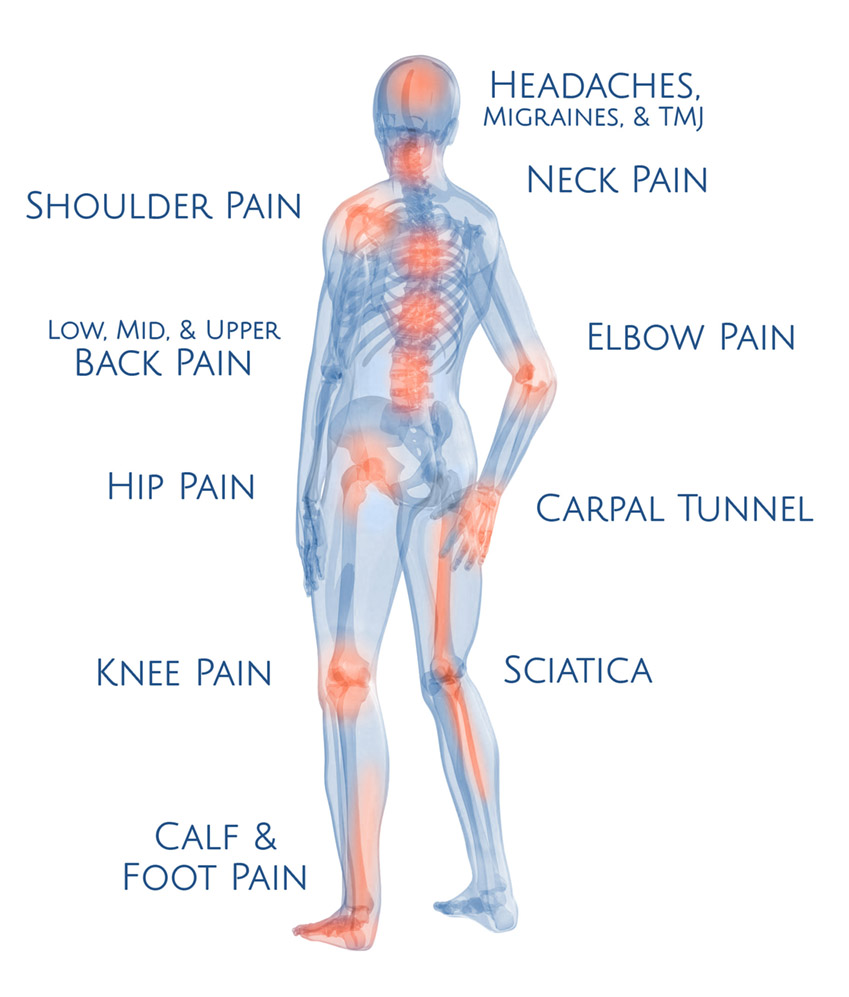

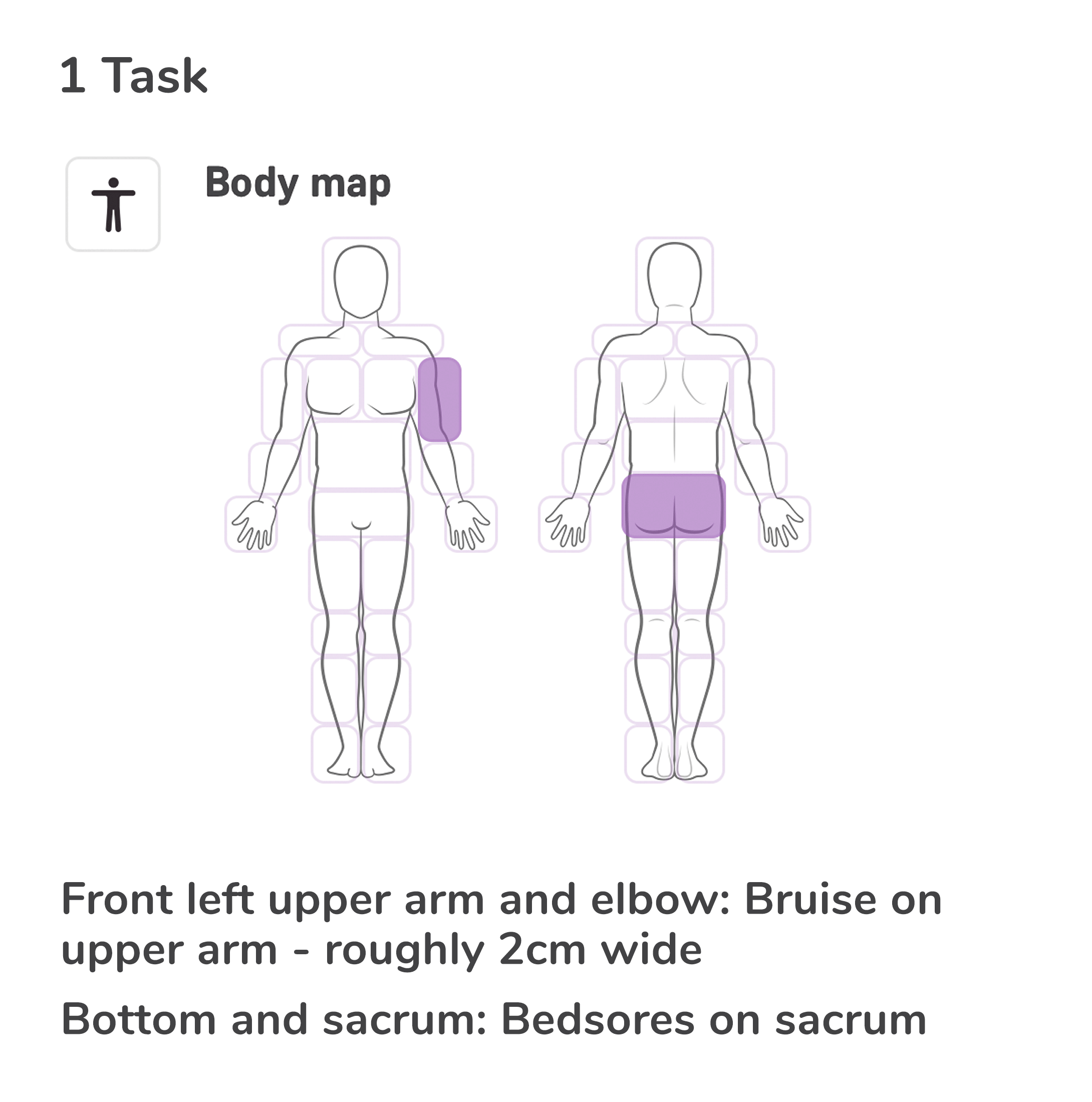
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Body Map Pain: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!