Thebes: A City of Kings and Pharaohs on the Map of Ancient Egypt
Related Articles: Thebes: A City of Kings and Pharaohs on the Map of Ancient Egypt
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Thebes: A City of Kings and Pharaohs on the Map of Ancient Egypt. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Thebes: A City of Kings and Pharaohs on the Map of Ancient Egypt
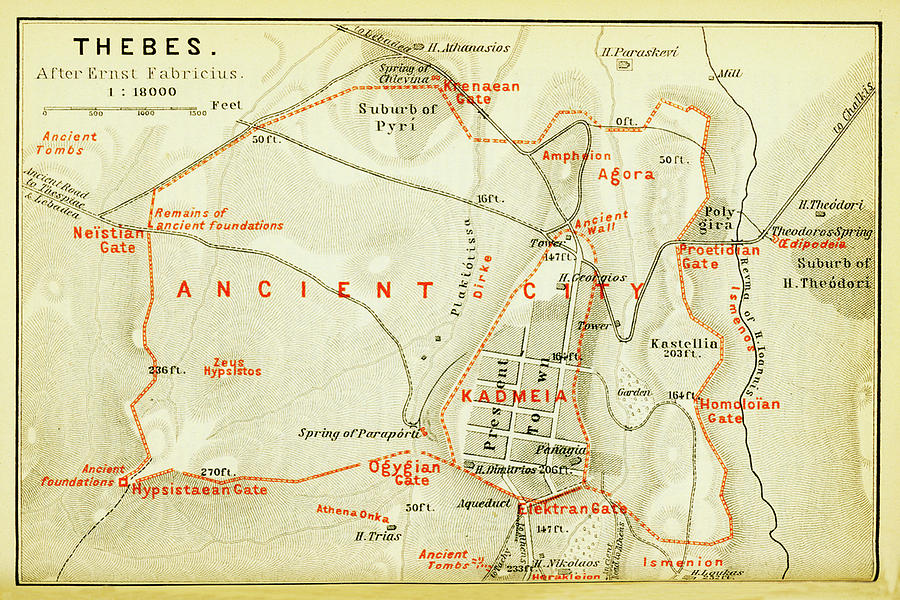
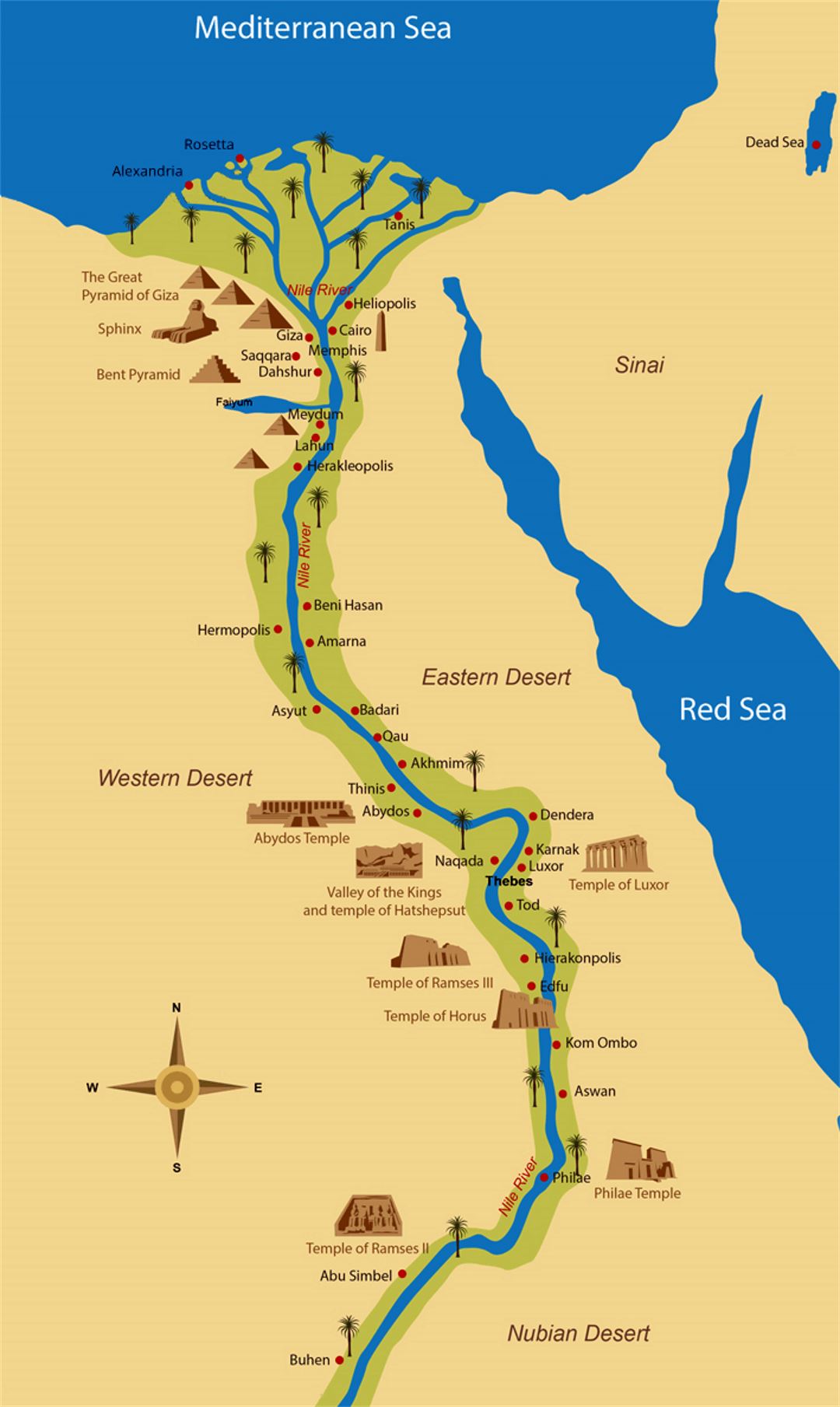
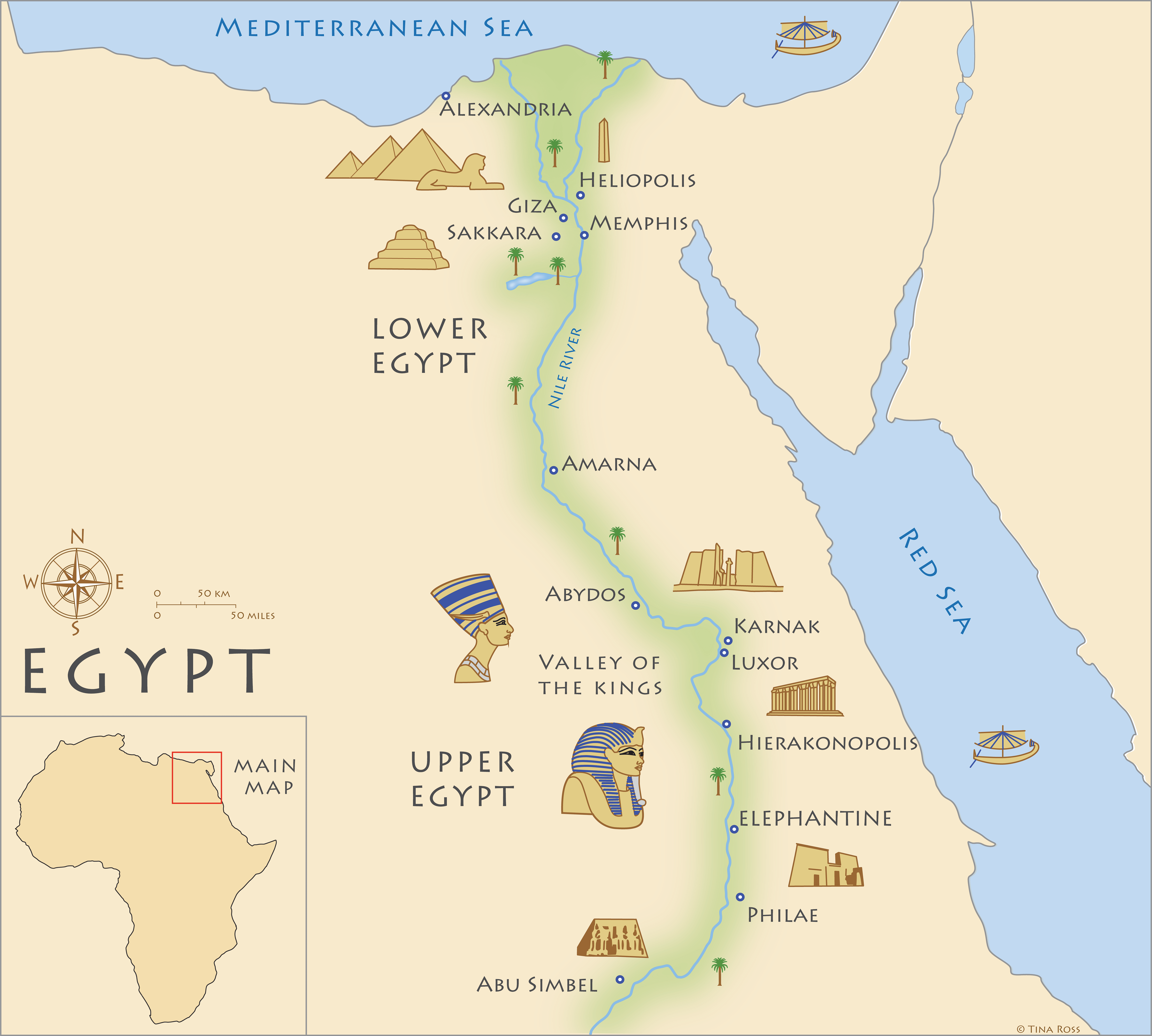
Thebes, a name synonymous with ancient Egypt’s grandeur and power, stands as a testament to a civilization that left an indelible mark on history. Its sprawling ruins, nestled along the fertile banks of the Nile River in Upper Egypt, offer a glimpse into a bygone era of pharaohs, temples, and magnificent monuments. Today, the ancient city of Thebes, known to the Egyptians as Waset, is a UNESCO World Heritage site, drawing visitors from across the globe to marvel at its remnants of a civilization that flourished for millennia.
A City of Many Names and Many Faces:
Thebes, a name derived from the Greek word "Thebai," was known to the Egyptians as Waset, meaning "scepter." This name reflects the city’s significance as the capital of Upper Egypt during the Middle Kingdom and the New Kingdom periods. Throughout its history, Thebes evolved from a regional center to a dominant force in Egyptian politics, religion, and culture.
A Strategic Location:
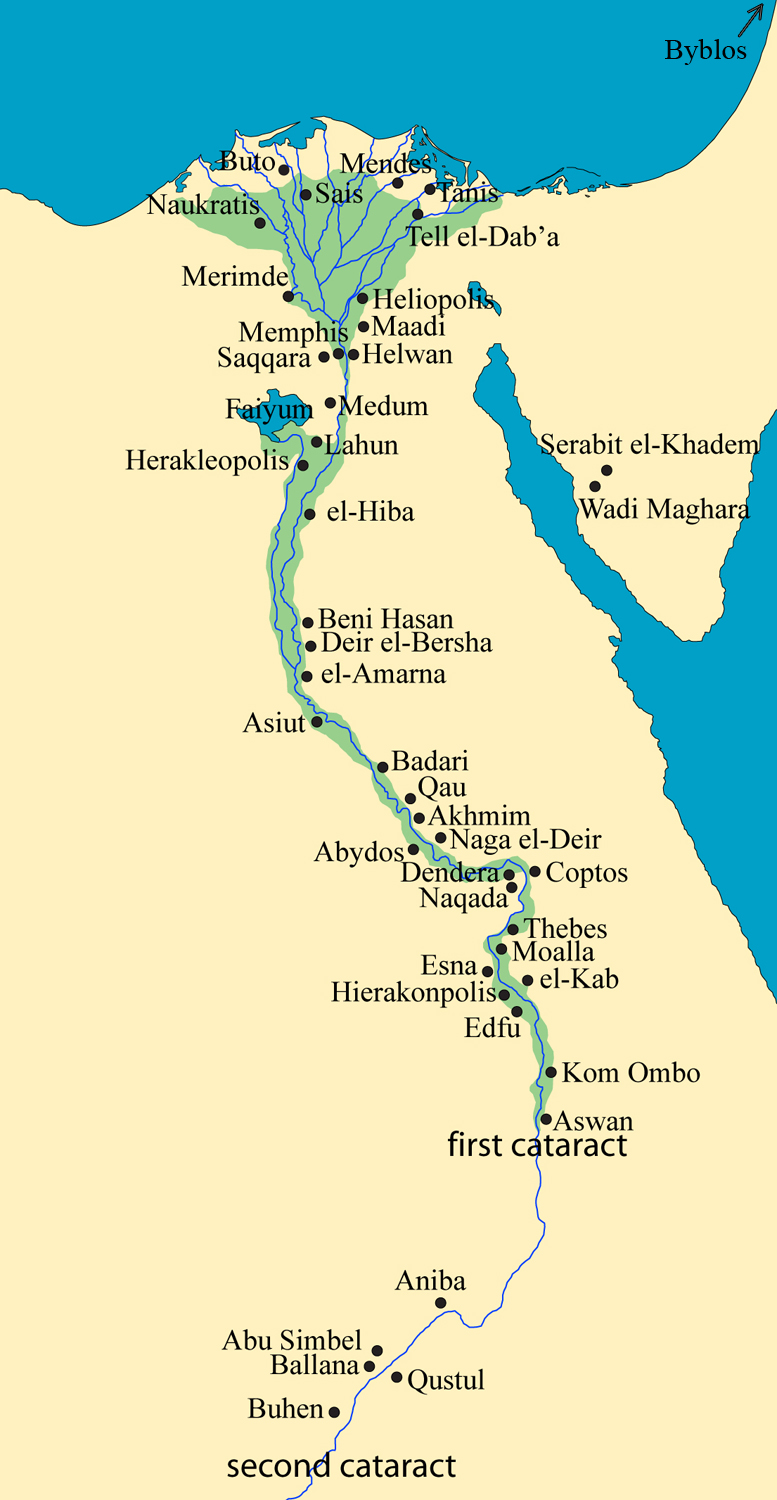
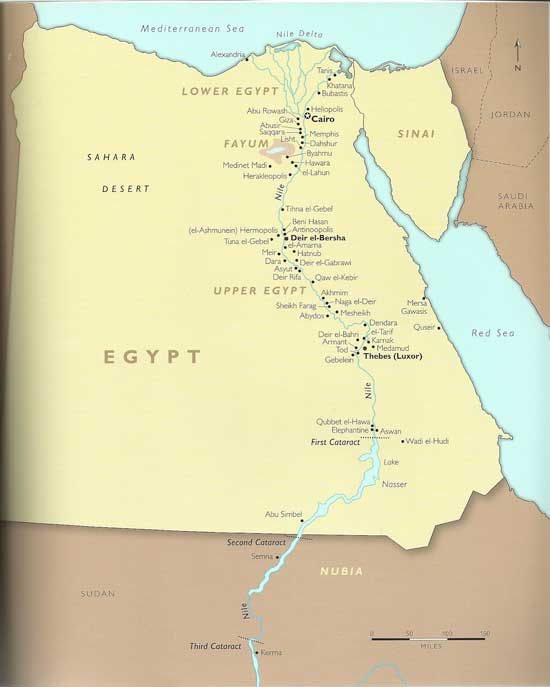
Thebes’ strategic location on the Nile River, the lifeblood of ancient Egypt, contributed significantly to its rise to prominence. Situated at the intersection of trade routes connecting Upper and Lower Egypt, Thebes became a crucial hub for commerce and transportation. The Nile’s fertile banks provided fertile land for agriculture, ensuring the city’s prosperity and its ability to sustain a large population.
Thebes: A City of Temples and Tombs:
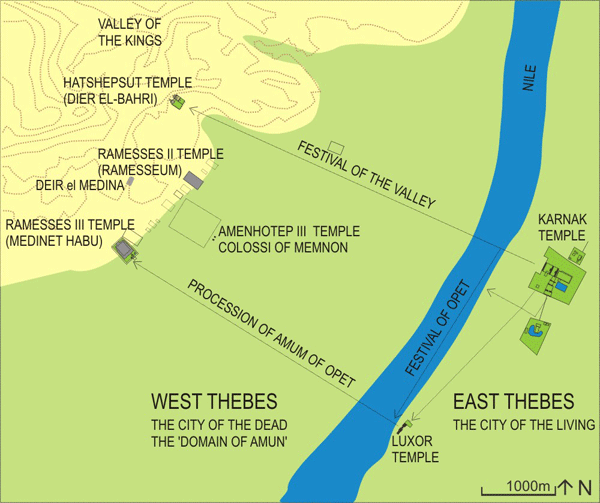
Thebes is renowned for its impressive collection of temples and tombs, showcasing the architectural prowess and artistic brilliance of the ancient Egyptians. The city’s most prominent temple, the Karnak Temple Complex, is a sprawling collection of sanctuaries, chapels, and pylons dedicated to various deities. The Luxor Temple, located on the east bank of the Nile, served as the ceremonial center of the city and was connected to Karnak by an avenue of sphinxes.
The Theban Necropolis, located on the west bank of the Nile, is home to a vast array of royal and private tombs. The Valley of the Kings, a secluded valley nestled in the cliffs, houses the tombs of many powerful pharaohs, including Tutankhamun, Ramses II, and Seti I. The Valley of the Queens, located nearby, contains the tombs of royal consorts and other prominent figures.
Thebes: A Cultural and Religious Center:
Beyond its architectural marvels, Thebes was a vibrant center of Egyptian culture and religion. The city was home to numerous religious festivals, including the annual Opet Festival, which celebrated the divine union of Amun-Re, the king of the gods, and Mut, the goddess of motherhood. Thebes also served as the center of the Amun cult, with the god Amun-Re being worshipped at the Karnak Temple Complex.
The city’s cultural influence extended beyond its religious practices. Thebes was renowned for its skilled artisans, who produced exquisite jewelry, pottery, and other artifacts. The city’s wealth and power attracted artists, scholars, and intellectuals from across Egypt, fostering a vibrant intellectual and artistic environment.
Thebes: A City in Decline:
Despite its long period of prosperity, Thebes eventually declined in power and influence. The decline began in the Late Period, as Egypt faced challenges from foreign invaders and internal instability. The city’s once-powerful pharaohs were replaced by weaker rulers, and the religious and cultural practices that had once defined Thebes began to fade.
Thebes: A Legacy that Endures:
Despite its decline, Thebes’ legacy continues to inspire awe and wonder. The city’s magnificent ruins stand as a testament to the achievements of ancient Egyptian civilization. The temples, tombs, and artifacts unearthed from Thebes offer invaluable insights into the lives, beliefs, and practices of the ancient Egyptians.
FAQs about Thebes:
Q: What is the best time to visit Thebes?
A: The best time to visit Thebes is during the cooler months, from October to April, when the weather is pleasant and the crowds are smaller.
Q: How long does it take to explore Thebes?
A: To fully explore the city’s major sites, including the Karnak Temple Complex, Luxor Temple, and Theban Necropolis, you should allocate at least three days.
Q: What are the must-see attractions in Thebes?
A: Some of the must-see attractions in Thebes include:
- Karnak Temple Complex: A sprawling complex of temples, chapels, and pylons dedicated to various deities.
- Luxor Temple: A magnificent temple located on the east bank of the Nile, connected to Karnak by an avenue of sphinxes.
- Valley of the Kings: A secluded valley containing the tombs of many powerful pharaohs.
- Valley of the Queens: A valley containing the tombs of royal consorts and other prominent figures.
- Hatshepsut’s Temple: A stunning temple dedicated to the female pharaoh Hatshepsut, carved into the cliffs of the Theban Necropolis.
- Medinet Habu Temple: A large temple complex dedicated to the god Amun-Re, built by Ramses III.
Q: What are the best ways to get around Thebes?
A: The best way to get around Thebes is by taxi or by hiring a private tour guide. You can also explore the city on foot, but be aware that the distances between attractions can be significant.
Tips for Visiting Thebes:
- Plan your visit in advance: Book your flights, accommodation, and tours in advance, especially if you are traveling during peak season.
- Wear comfortable shoes: You will be doing a lot of walking, so comfortable shoes are essential.
- Bring a hat and sunscreen: The sun can be intense, so protect yourself from the heat.
- Bring plenty of water: Stay hydrated, especially if you are visiting during the warmer months.
- Hire a guide: A knowledgeable guide can enhance your experience and provide valuable insights into the history and culture of Thebes.
- Respect the sites: Be mindful of the ancient ruins and treat them with respect.
Conclusion:
Thebes, a city of kings and pharaohs, stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of ancient Egyptian civilization. Its magnificent temples, tombs, and artifacts offer a glimpse into a bygone era of grandeur, power, and innovation. Visiting Thebes is an unforgettable experience, offering a unique opportunity to connect with a civilization that has captivated the world for centuries.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Thebes: A City of Kings and Pharaohs on the Map of Ancient Egypt. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!