The Power of the Map Capital: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Related Articles: The Power of the Map Capital: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of the Map Capital: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of the Map Capital: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)

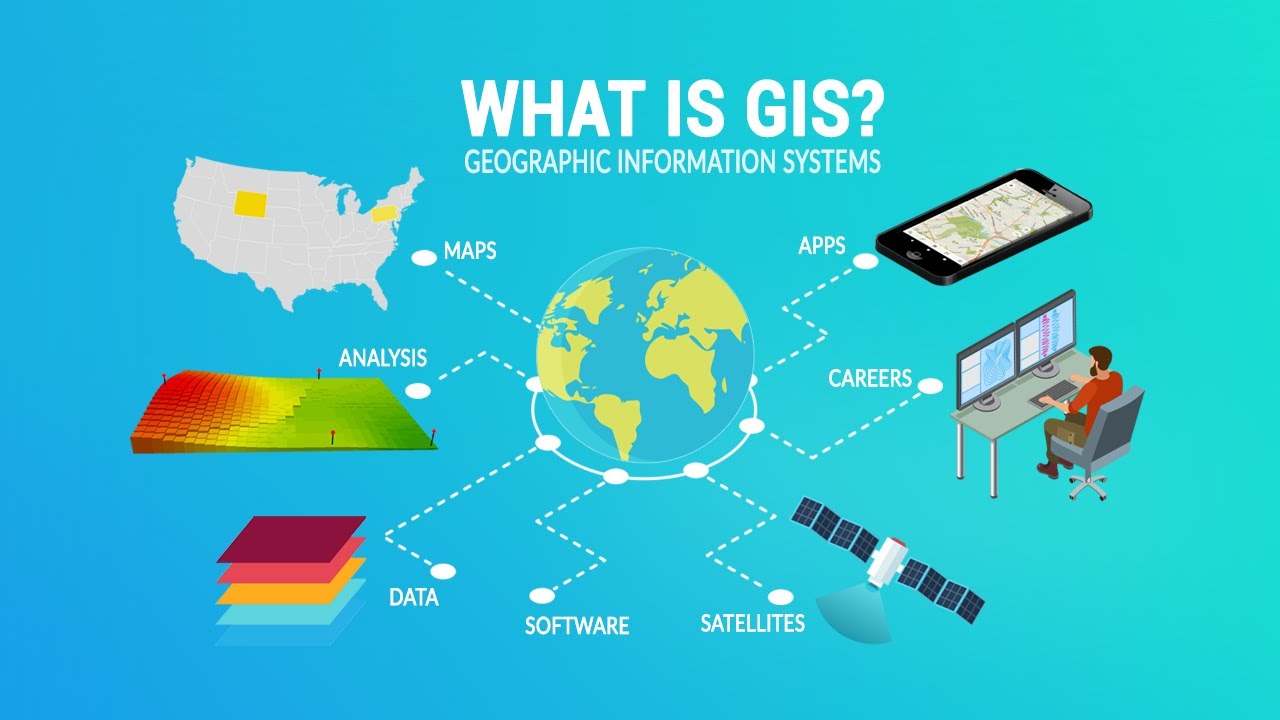
In an increasingly interconnected world, the ability to visualize, analyze, and understand spatial data is paramount. This is where Geographic Information Systems (GIS) come into play. GIS, often referred to as the "map capital," has emerged as a transformative technology with applications across various industries, from urban planning and environmental management to healthcare and disaster response.
Understanding GIS: Beyond the Map
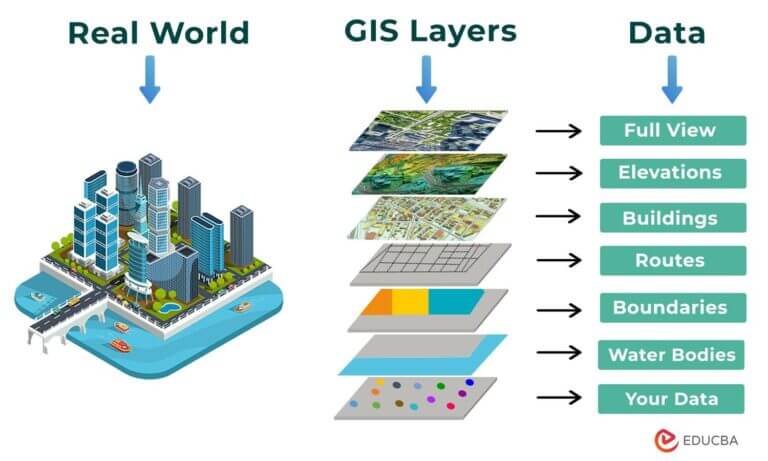
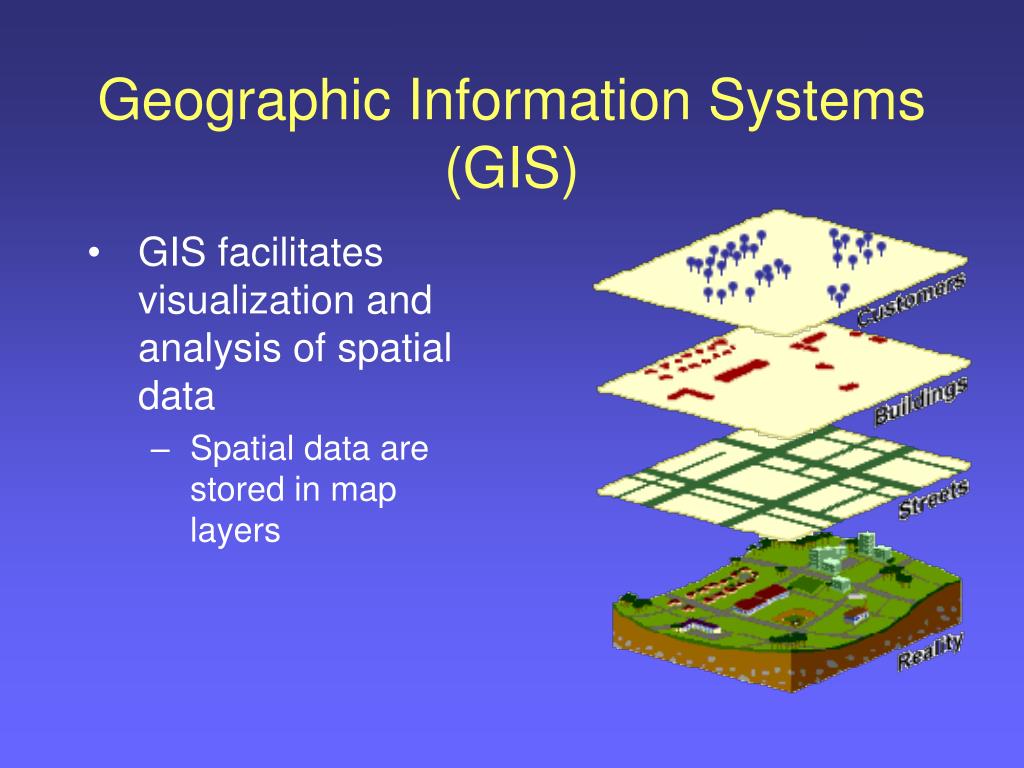
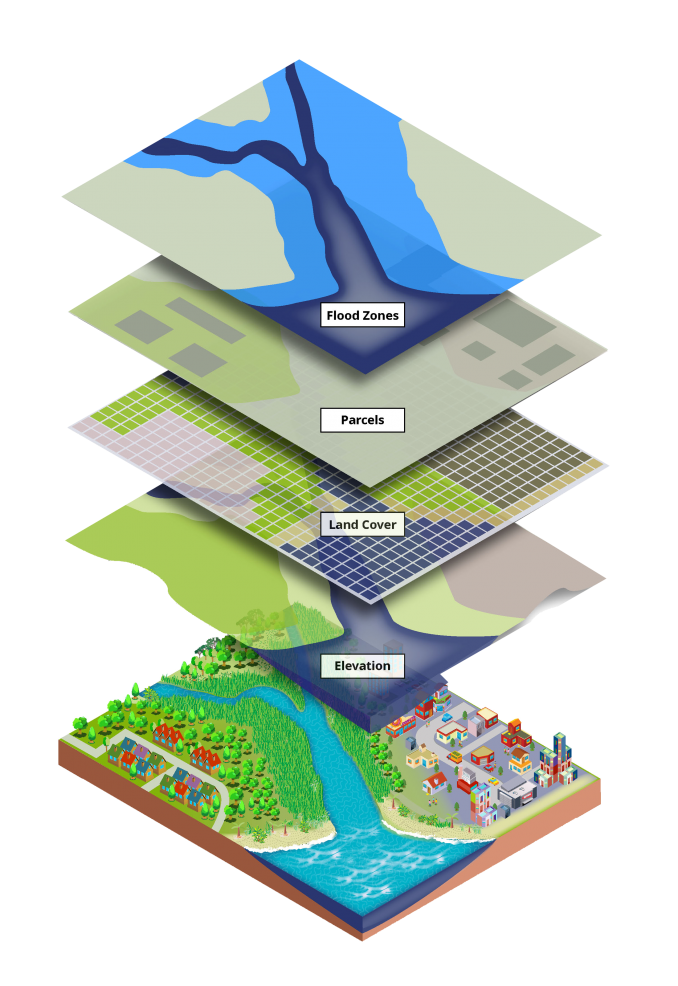
GIS is more than just making pretty maps. It’s a powerful tool that combines data from various sources – geographic coordinates, demographics, environmental factors, and more – to create interactive maps that reveal patterns, relationships, and insights. This capability stems from the core principles of GIS:
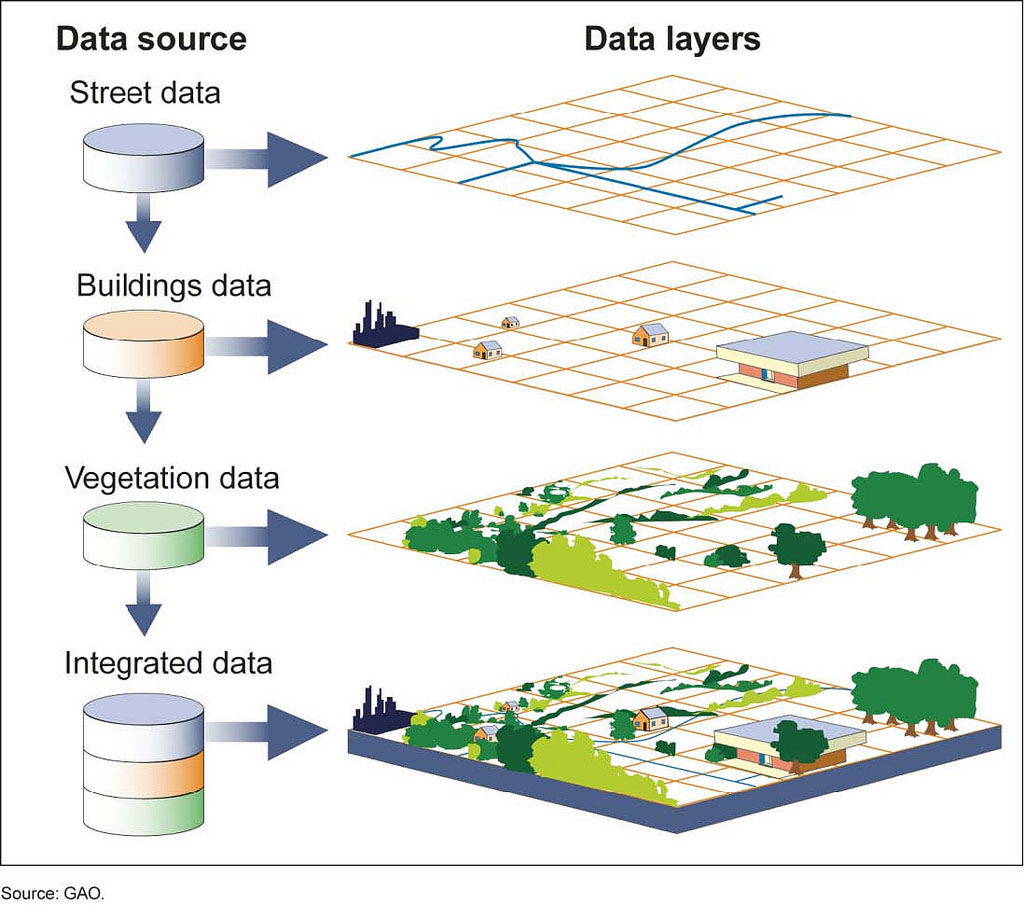
- Spatial Data: GIS utilizes data that has a geographic location associated with it. This location can be a point, line, polygon, or a combination of these, allowing for the representation of various features like buildings, roads, or environmental zones.
- Geographic Analysis: GIS enables the analysis of spatial relationships and patterns. For instance, identifying areas at risk of flooding, analyzing the distribution of diseases, or optimizing delivery routes.
- Visualization and Communication: GIS transforms complex data into visually compelling maps and charts, making it easier to understand and communicate insights to a wider audience.
The Benefits of Embracing the Map Capital
The adoption of GIS offers numerous benefits for individuals, organizations, and society as a whole:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: GIS provides a comprehensive spatial understanding of data, empowering informed decision-making across various sectors.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: By optimizing workflows and resource allocation, GIS contributes to greater efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced Costs: GIS can help identify cost-effective solutions, reduce redundancies, and optimize resource utilization.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability: GIS provides a transparent platform for data visualization and analysis, promoting accountability and public engagement.
- Sustainable Development: GIS plays a crucial role in environmental monitoring, resource management, and sustainable urban planning.
Applications of GIS: Shaping the World Around Us
The versatility of GIS extends to numerous fields, making it an indispensable tool in modern society:
- Urban Planning: GIS assists in urban planning by analyzing population density, traffic patterns, and infrastructure needs, enabling informed decisions regarding development, transportation, and resource allocation.
- Environmental Management: GIS is crucial for monitoring environmental conditions, managing natural resources, and mitigating environmental hazards. It allows for the analysis of deforestation patterns, pollution levels, and climate change impacts.
- Agriculture: GIS helps optimize agricultural practices by analyzing soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop yields, contributing to increased productivity and sustainability.
- Healthcare: GIS facilitates disease surveillance, identifying areas with high disease prevalence and guiding resource allocation for public health initiatives.
- Disaster Response: GIS is vital for emergency response, providing real-time information on disaster impacts, facilitating rescue operations, and aiding in post-disaster recovery efforts.
- Transportation: GIS optimizes transportation networks by analyzing traffic flow, identifying bottlenecks, and planning efficient routes for public transit and logistics.
- Business and Marketing: GIS assists businesses in analyzing customer demographics, identifying potential markets, and optimizing supply chains for increased profitability.
Exploring the Future of GIS
The evolution of GIS continues with advancements in technology and data availability:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Integration of AI algorithms into GIS enhances automated data analysis, pattern recognition, and predictive modeling, enabling more sophisticated spatial insights.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based GIS platforms offer scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, allowing for collaborative data management and analysis.
- Big Data: GIS is increasingly equipped to handle massive datasets, enabling the analysis of complex spatial patterns and trends.
- Mobile GIS: Mobile GIS applications extend the power of spatial analysis to smartphones and tablets, facilitating real-time data collection and analysis in the field.
FAQs about GIS: Demystifying the Map Capital
Q: What are the essential components of a GIS?
A: A GIS typically comprises hardware, software, data, and human expertise. Hardware includes computers and specialized devices for data acquisition and processing. Software provides tools for data management, analysis, and visualization. Data encompasses geographic information in various formats, such as maps, satellite imagery, and sensor data. Human expertise is vital for data interpretation, analysis, and application of GIS solutions.
Q: What are the different types of GIS data?
A: GIS data can be categorized into three main types:
- Vector Data: Represents geographic features as points, lines, and polygons. Examples include buildings, roads, and rivers.
- Raster Data: Represents geographic information as a grid of cells, each containing a value representing a specific attribute, such as elevation, temperature, or land cover.
- Attribute Data: Non-spatial information associated with geographic features, such as population density, land use, or property values.
Q: What are some of the popular GIS software packages?
A: Several widely used GIS software packages exist, including:
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive GIS platform developed by Esri, offering a wide range of tools for data management, analysis, and visualization.
- QGIS: An open-source GIS software, providing powerful capabilities for data analysis and map creation.
- Google Earth Pro: A popular tool for visualizing and exploring geographic data, offering interactive 3D maps and satellite imagery.
Q: How can I learn more about GIS?
A: Several resources are available for learning about GIS, including:
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and edX offer comprehensive GIS courses for beginners and advanced users.
- University Programs: Many universities offer undergraduate and graduate degrees in GIS, providing in-depth knowledge and practical skills.
- Professional Organizations: Organizations like the Association for Geographic Information Systems (AGIS) and the Urban and Regional Information Systems Association (URISA) offer resources, networking opportunities, and professional development programs.
Tips for Utilizing GIS Effectively
- Clearly Define Your Objectives: Before embarking on a GIS project, define your goals and objectives to ensure the chosen tools and data align with your needs.
- Data Quality is Paramount: Ensure the accuracy and reliability of your data sources, as data quality directly impacts the validity of your analysis and conclusions.
- Explore Different Data Sources: Utilize a variety of data sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon you are studying.
- Leverage Visualization Tools: Utilize GIS tools for creating clear and informative maps and charts to effectively communicate your findings.
- Collaborate with Experts: Seek guidance from GIS professionals for complex projects and data analysis to ensure accurate and reliable results.
Conclusion: The Map Capital as a Catalyst for Progress
GIS has emerged as a powerful tool for understanding and shaping our world. Its ability to analyze spatial data, reveal patterns, and empower informed decision-making makes it an indispensable asset across various sectors. By embracing the "map capital," we unlock a wealth of possibilities for achieving greater efficiency, sustainability, and progress in a rapidly changing world. As technology continues to evolve, GIS will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in addressing global challenges and shaping a more sustainable and equitable future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of the Map Capital: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS). We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!