The Gulf Stream: A River in the Ocean
Related Articles: The Gulf Stream: A River in the Ocean
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Gulf Stream: A River in the Ocean. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Gulf Stream: A River in the Ocean
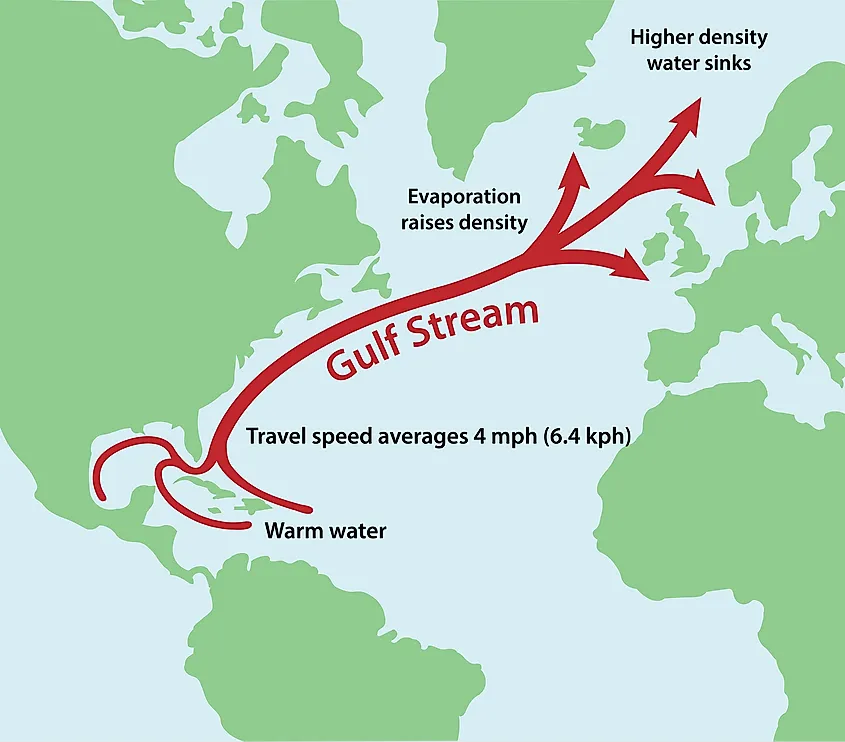
The Gulf Stream, a powerful, warm ocean current flowing northward along the eastern coast of North America, is a vital component of the global ocean circulation system. Its influence extends far beyond its physical boundaries, impacting weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and even human activities.
A River of Warmth:
The Gulf Stream originates in the Gulf of Mexico, where warm, tropical waters are heated by the sun. This warm water, less dense than colder water, is pushed northward by prevailing winds and the Earth’s rotation, creating a swift, meandering river within the vast ocean. As it flows along the eastern coast of North America, the Gulf Stream carries an immense amount of heat, significantly influencing the climates of North America and Western Europe.
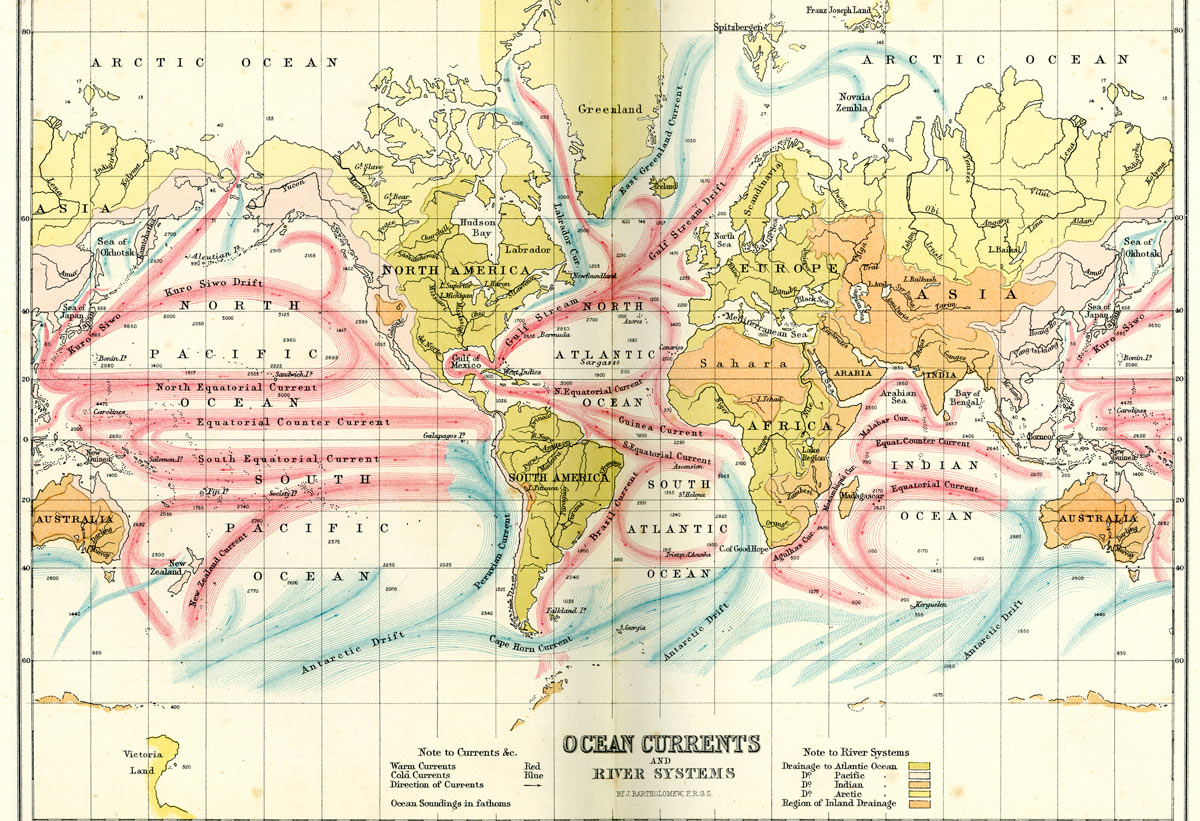
Mapping the Flow:
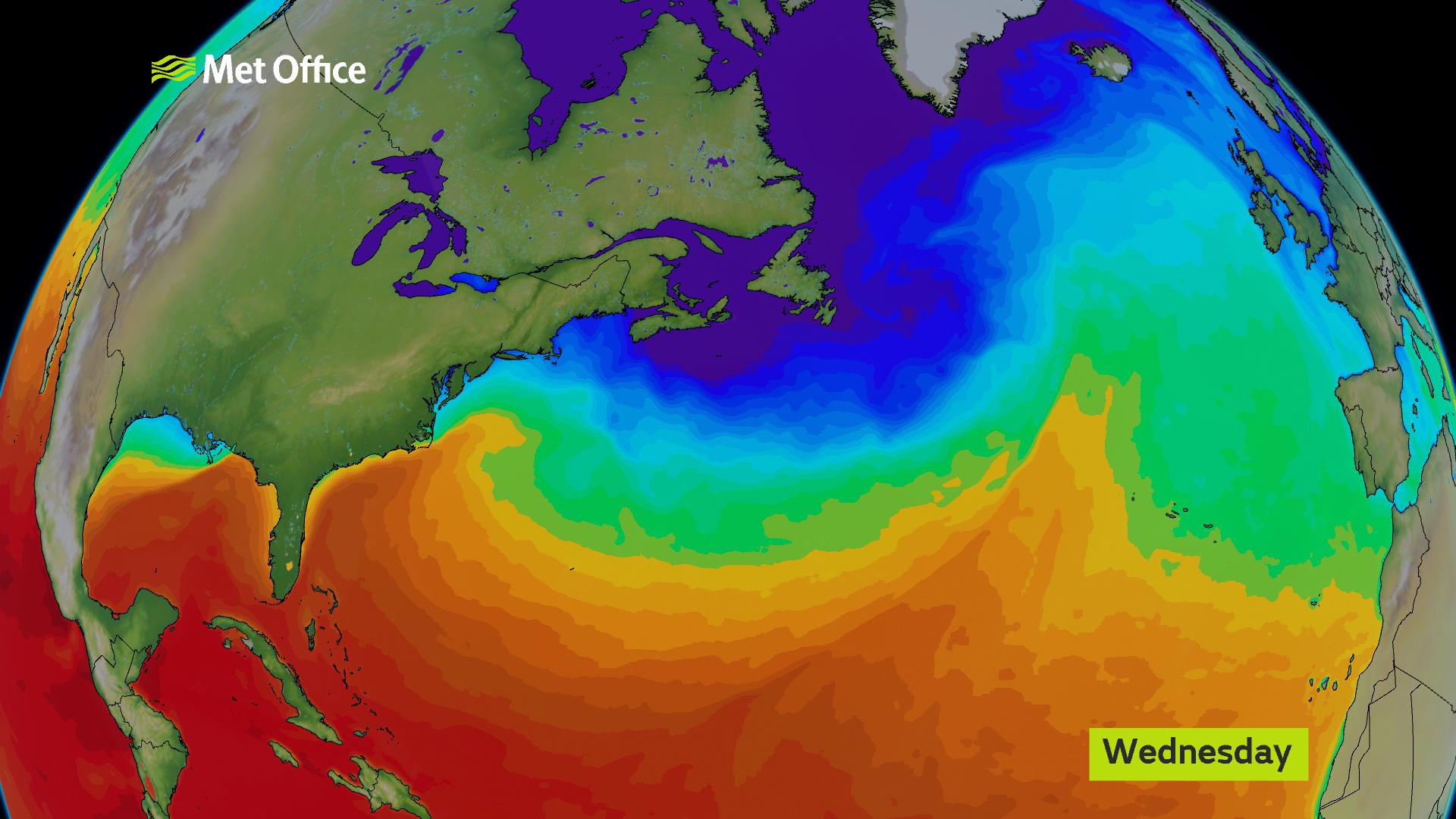
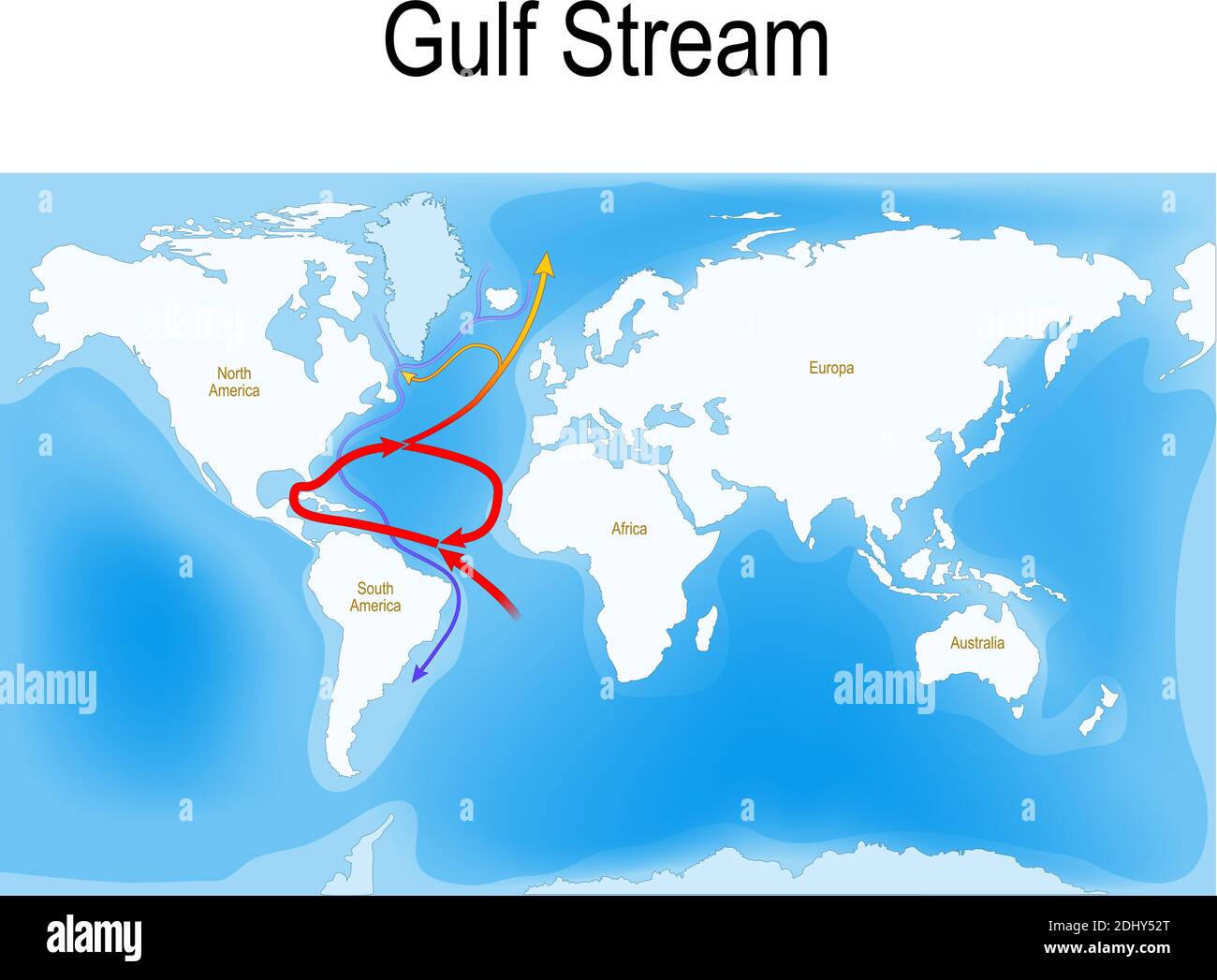
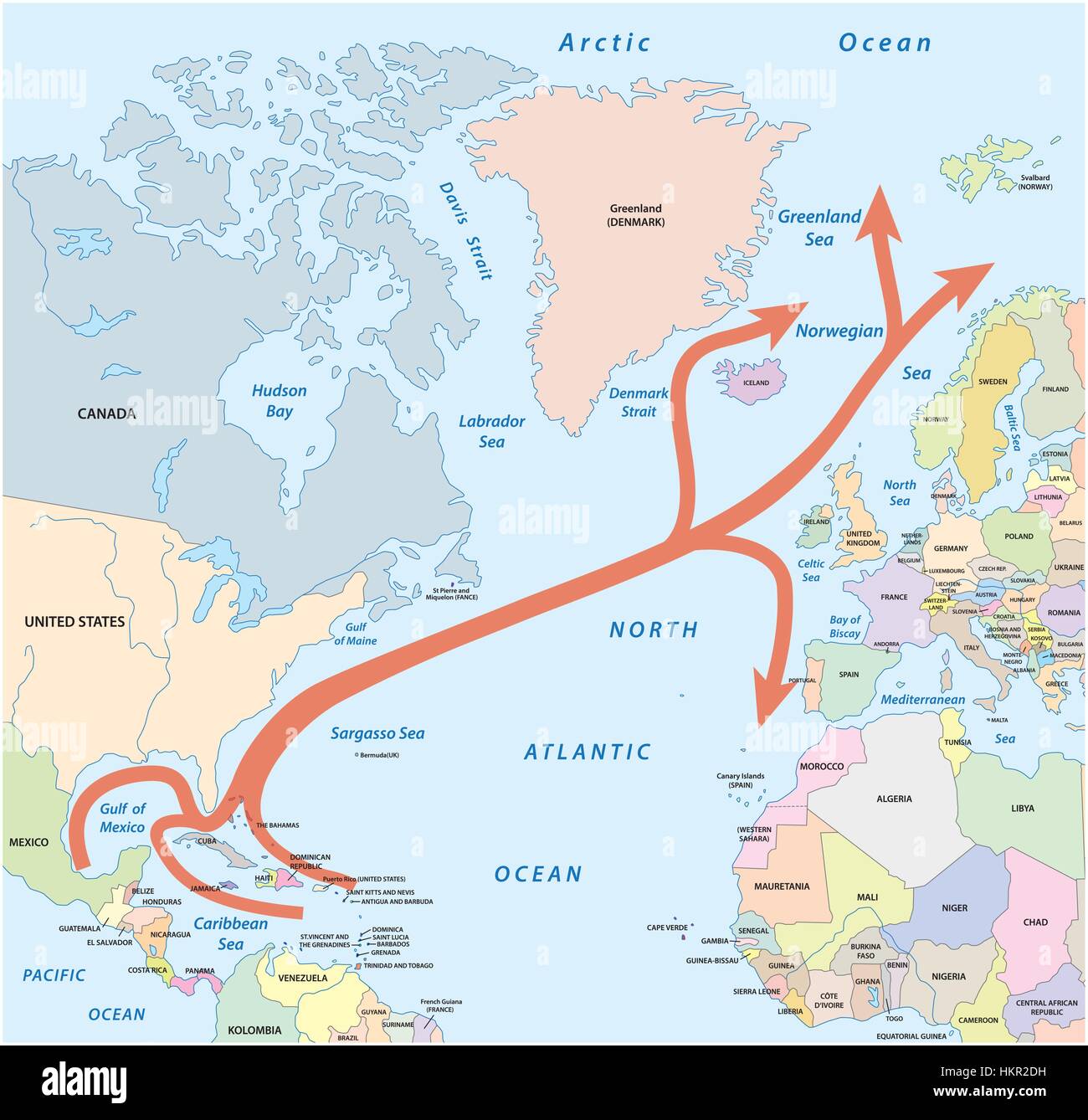
Visualizing the Gulf Stream’s path is essential to understanding its impact. Maps depicting the current’s trajectory reveal its remarkable journey.
- Origin: The Gulf Stream originates in the Gulf of Mexico, where warm, tropical waters gather.
- Northward Flow: The current flows northward along the eastern coast of North America, hugging the coastline.
- The Loop Current: A branch of the Gulf Stream, known as the Loop Current, detaches from the main stream and circles counterclockwise in the Gulf of Mexico, before rejoining the main flow.
- Across the Atlantic: The Gulf Stream then crosses the Atlantic Ocean, heading towards Western Europe.
- North Atlantic Current: As it moves eastward, the Gulf Stream merges with other currents, forming the North Atlantic Current, which continues to carry warmth towards Northern Europe.
A Balancing Act:
The Gulf Stream plays a crucial role in regulating global climate by transporting heat from the tropics towards the poles. This heat transfer helps moderate temperatures, preventing extreme variations in weather patterns. Without the Gulf Stream, Western Europe would experience much colder temperatures, significantly impacting its climate and ecosystems.
Life in the Stream:
The Gulf Stream also supports a diverse marine ecosystem. Its warm waters provide habitat for various species of fish, sea turtles, and marine mammals. The current’s flow also facilitates nutrient transport, fueling the growth of phytoplankton, the base of the marine food web.
Human Impact:
The Gulf Stream also plays a significant role in human activities. Its powerful currents influence shipping routes, reducing travel times and facilitating trade. However, human activities also impact the Gulf Stream. Climate change, pollution, and overfishing can alter the current’s strength, direction, and overall health, potentially impacting global climate and marine ecosystems.
FAQs about the Gulf Stream:
1. How fast does the Gulf Stream flow?
The Gulf Stream’s speed varies depending on location and depth. On average, it flows at speeds of 2-4 miles per hour.
2. What are the effects of the Gulf Stream on climate?
The Gulf Stream moderates temperatures in North America and Western Europe, preventing extreme weather variations.
3. How does the Gulf Stream impact marine life?
The Gulf Stream supports a diverse marine ecosystem by providing warm waters and facilitating nutrient transport.
4. How is the Gulf Stream affected by climate change?
Climate change can alter the Gulf Stream’s strength, direction, and overall health, potentially impacting global climate and marine ecosystems.
5. What measures can be taken to protect the Gulf Stream?
Addressing climate change, reducing pollution, and implementing sustainable fishing practices are crucial for protecting the Gulf Stream and its vital role in the global ecosystem.
Tips for Understanding the Gulf Stream:
- Visualize the flow: Use maps and online resources to visualize the Gulf Stream’s path and understand its impact on different regions.
- Explore its influence on climate: Research the Gulf Stream’s role in regulating global temperatures and how it affects weather patterns.
- Learn about its impact on marine life: Discover the diverse ecosystem supported by the Gulf Stream and the threats it faces.
- Stay informed about climate change: Understand how climate change affects the Gulf Stream and the potential consequences for global climate and marine ecosystems.
- Support sustainable practices: Encourage efforts to reduce pollution, promote sustainable fishing, and address climate change to protect the Gulf Stream and its vital role in the global ecosystem.
Conclusion:
The Gulf Stream, a powerful, warm ocean current, plays a critical role in regulating global climate, supporting marine ecosystems, and influencing human activities. Understanding its dynamics and impact is crucial for appreciating its vital role in the global ecosystem and for developing strategies to protect it from the threats posed by climate change and human activities. By fostering awareness and promoting sustainable practices, we can ensure the continued health and vitality of this vital ocean current.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Gulf Stream: A River in the Ocean. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!