The Foundation of Development: A Deep Dive into Land Surveying Maps
Related Articles: The Foundation of Development: A Deep Dive into Land Surveying Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Foundation of Development: A Deep Dive into Land Surveying Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Foundation of Development: A Deep Dive into Land Surveying Maps
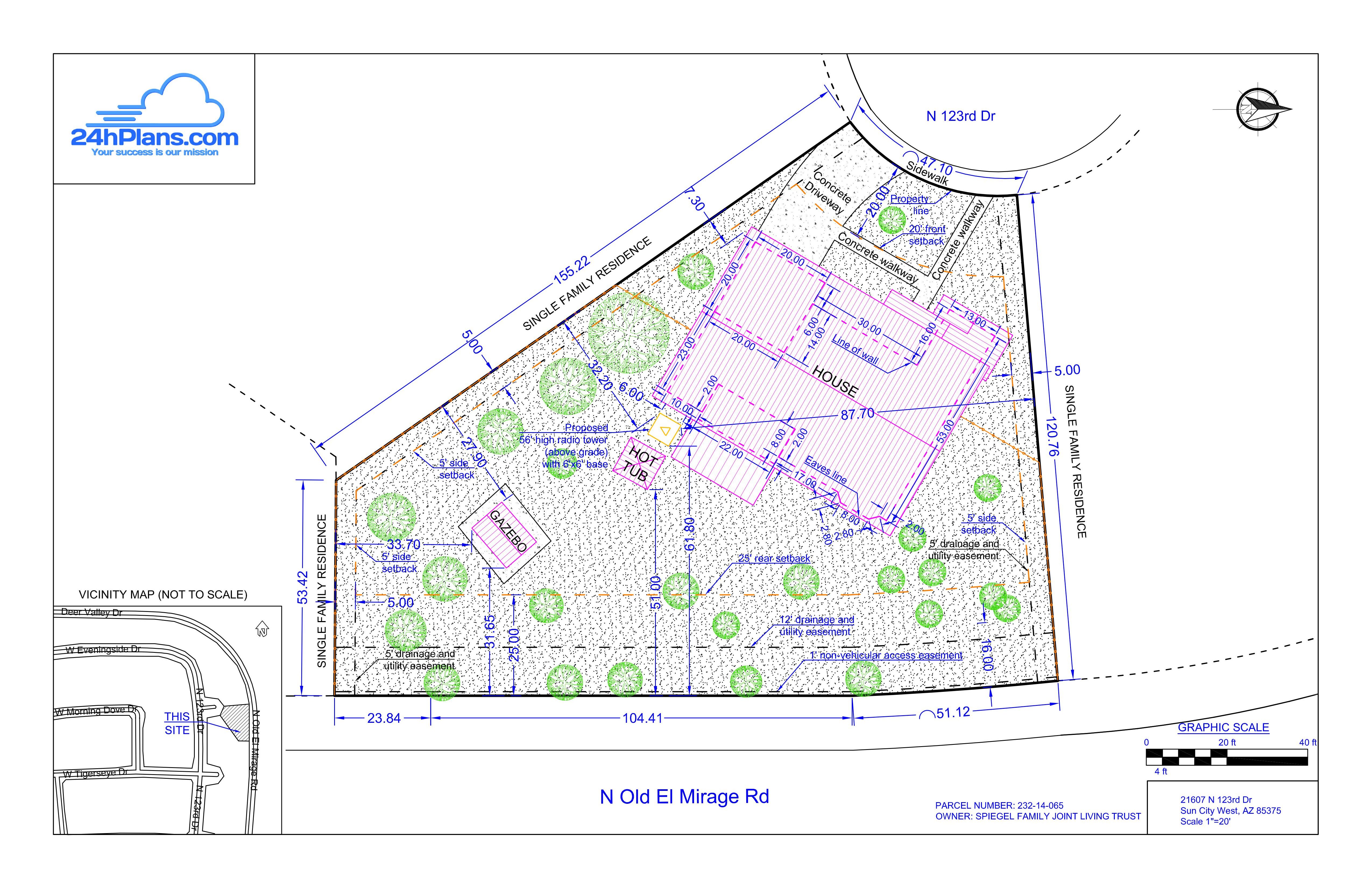
Land surveying maps, often referred to as cadastral maps, serve as the fundamental blueprint for understanding and managing the physical landscape. They are more than mere illustrations; they are meticulously crafted representations of the earth’s surface, capturing crucial information about property boundaries, topography, and infrastructure. These maps are essential tools for a wide range of applications, from urban planning and construction to environmental management and resource allocation.
Unveiling the Essence of Land Surveying Maps
At its core, land surveying is the science of accurately measuring and defining the earth’s surface. Land surveying maps translate these measurements into visual representations, providing a comprehensive overview of the land’s features. This process involves:
- Boundary Determination: Precisely defining the limits of property ownership, ensuring clear and unambiguous legal definitions.
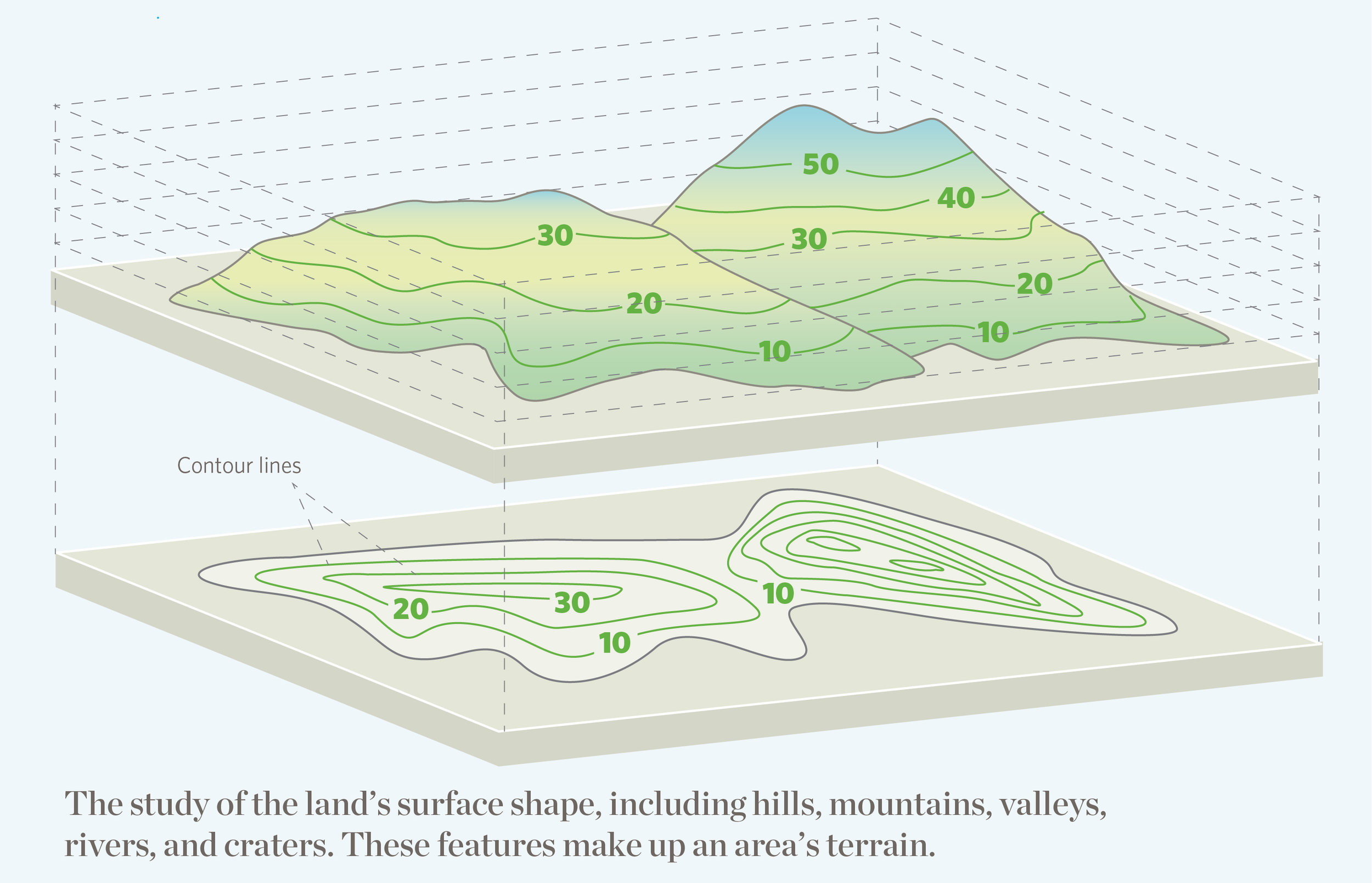
- Topographic Mapping: Depicting the land’s elevation, slopes, and other surface features, crucial for construction, infrastructure development, and environmental studies.
- Infrastructure Mapping: Representing existing and planned infrastructure, including roads, utilities, and buildings, aiding in planning and development projects.
- Resource Mapping: Identifying and mapping natural resources, such as water bodies, forests, and mineral deposits, facilitating resource management and conservation efforts.
The Importance of Accuracy and Precision
The value of land surveying maps lies in their accuracy and precision. These maps are not mere sketches; they are meticulously created using advanced surveying techniques and technologies, ensuring that the information they convey is reliable and dependable. This accuracy is paramount for various reasons:
- Legal Clarity: Land surveying maps provide the legal framework for property ownership, resolving disputes and ensuring fair and equitable distribution of land.
- Planning and Development: Accurate maps are essential for urban planning, infrastructure development, and construction projects, enabling informed decision-making and minimizing costly errors.
- Environmental Management: Land surveying maps contribute to environmental conservation by providing detailed information about sensitive ecosystems, water resources, and geological formations.
- Resource Allocation: By mapping natural resources, these maps guide efficient resource allocation, maximizing utilization and ensuring sustainable practices.
Types of Land Surveying Maps
Land surveying maps are not a one-size-fits-all solution; they are tailored to specific purposes and applications. Some common types include:
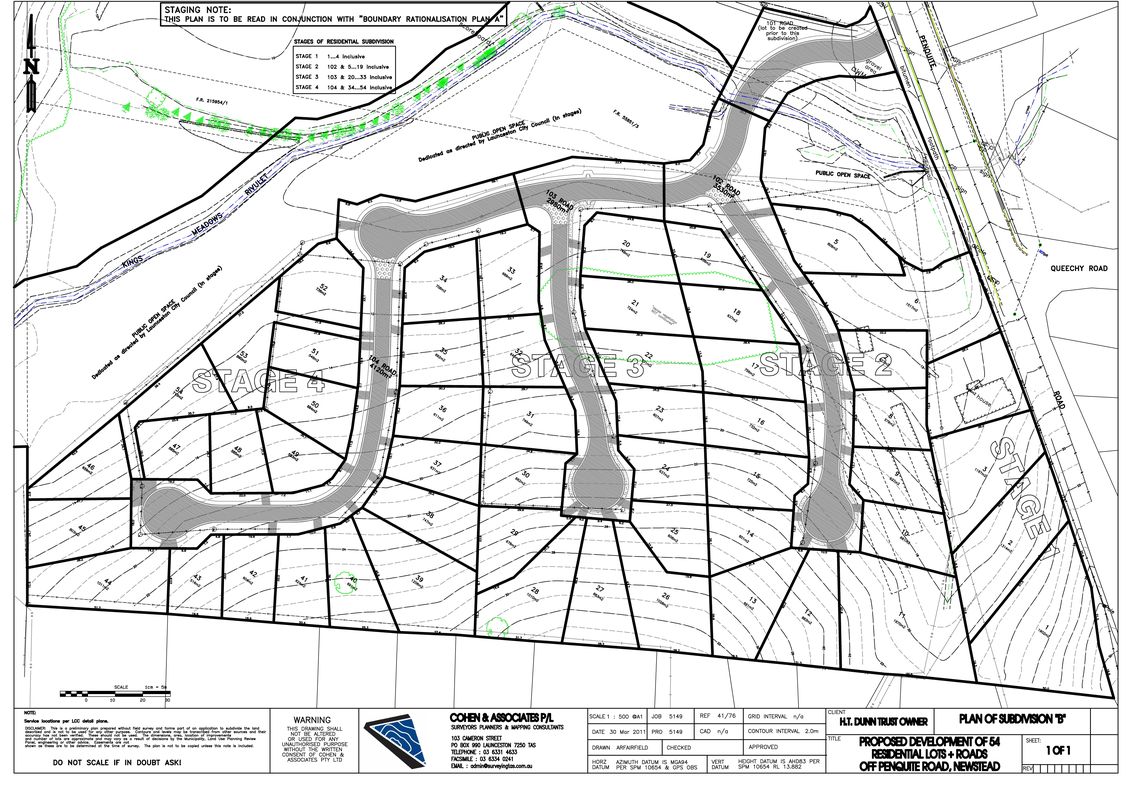
- Cadastral Maps: Focus on property boundaries and ownership, providing a detailed record of land parcels and their legal status.
- Topographic Maps: Depict the land’s elevation, slopes, and contours, often used for construction, engineering, and environmental studies.
- Planimetric Maps: Show horizontal features, such as roads, buildings, and utilities, without depicting elevation changes.
- Hydrographic Maps: Focus on water bodies, including rivers, lakes, and coastlines, providing information about depths, currents, and other aquatic features.
The Evolution of Land Surveying Maps
Historically, land surveying relied on manual methods, using instruments like theodolites and chains. However, the advent of technology has revolutionized the field, introducing advanced tools and techniques. Modern land surveying maps utilize:
- Global Positioning Systems (GPS): Satellite-based technology for precise location determination, significantly improving accuracy and efficiency.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Powerful software for managing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data, enabling complex mapping and analysis.
- Remote Sensing: Techniques like aerial photography and satellite imagery provide a broader perspective, capturing vast areas and generating detailed maps.
The Future of Land Surveying Maps
The future of land surveying maps is intertwined with advancements in technology. Emerging technologies like:
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): Drones equipped with cameras and sensors provide high-resolution imagery, enabling efficient and cost-effective mapping.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): A remote sensing technique that measures distances using laser pulses, providing detailed 3D models of the terrain.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered algorithms can automate data analysis and interpretation, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in map creation.
These advancements are transforming land surveying maps into even more powerful tools, enabling more comprehensive and accurate representations of the earth’s surface.
FAQs about Land Surveying Maps
1. What is the difference between a land surveying map and a regular map?
Land surveying maps focus on legal property boundaries and detailed physical features, while regular maps typically depict broader geographical areas and emphasize general features.
2. How are land surveying maps used in real estate transactions?
Land surveying maps provide the legal framework for property ownership, ensuring clear and accurate boundaries, which is essential for property transactions.
3. Can I access land surveying maps for my property?
Publicly available cadastral maps can be accessed online or through local government offices. Private land surveying maps are typically held by the property owner or the surveyor who created them.
4. What are the benefits of using a professional land surveyor?
Professional surveyors possess the expertise, equipment, and legal knowledge to ensure accurate and reliable land surveying maps, minimizing potential legal disputes and costly errors.
5. How often should land surveying maps be updated?
The frequency of updates depends on factors like property changes, infrastructure development, and legal requirements. Regular updates ensure the accuracy and relevance of the maps.
Tips for Understanding and Using Land Surveying Maps
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend: Understand the symbols and abbreviations used to represent different features.
- Pay attention to the scale: The scale indicates the relationship between the map’s dimensions and the actual size of the land.
- Consider the map’s purpose: Understand the intended use of the map and its limitations.
- Consult with a professional surveyor: For complex projects or legal matters, seek guidance from a qualified surveyor.
Conclusion
Land surveying maps are not merely static representations; they are dynamic tools that underpin our understanding of the land and guide our interactions with it. Their accuracy and precision are crucial for ensuring legal clarity, facilitating efficient planning and development, and supporting sustainable resource management. As technology continues to advance, land surveying maps will evolve, offering even greater insights and contributing to a more informed and responsible approach to land use and development.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Foundation of Development: A Deep Dive into Land Surveying Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!