Thailand’s Position in the Heart of Southeast Asia: A Geographical Perspective
Related Articles: Thailand’s Position in the Heart of Southeast Asia: A Geographical Perspective
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Thailand’s Position in the Heart of Southeast Asia: A Geographical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Thailand’s Position in the Heart of Southeast Asia: A Geographical Perspective

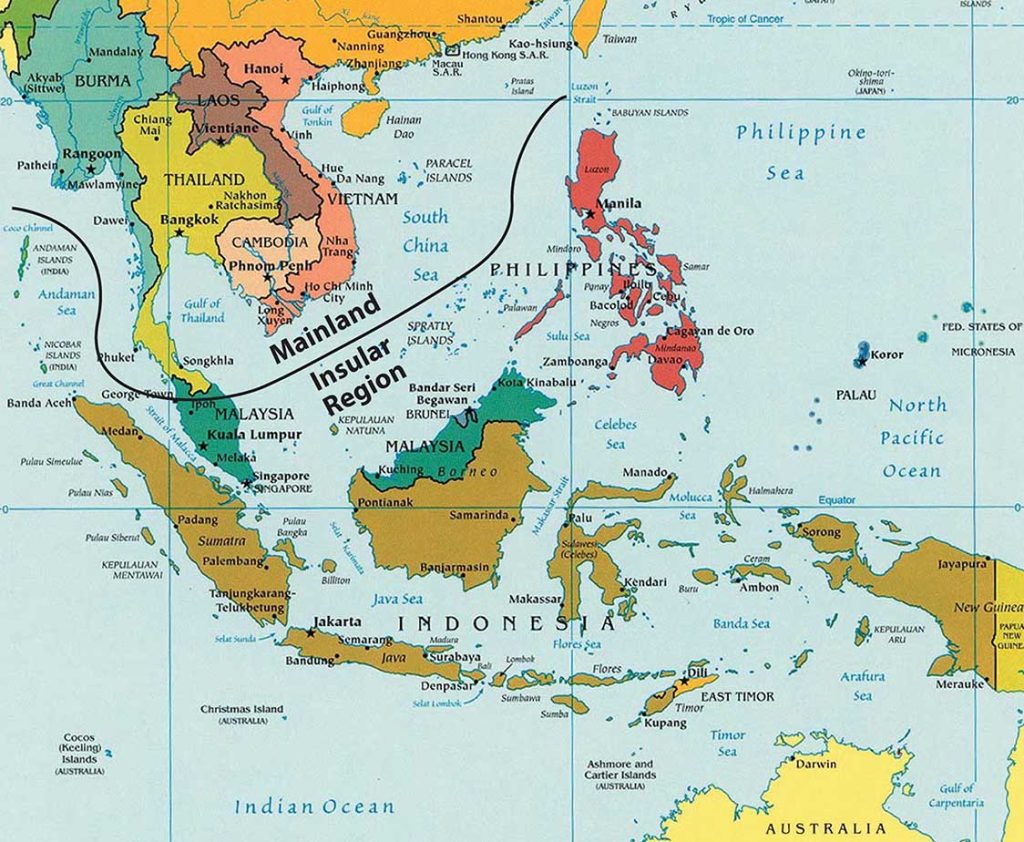
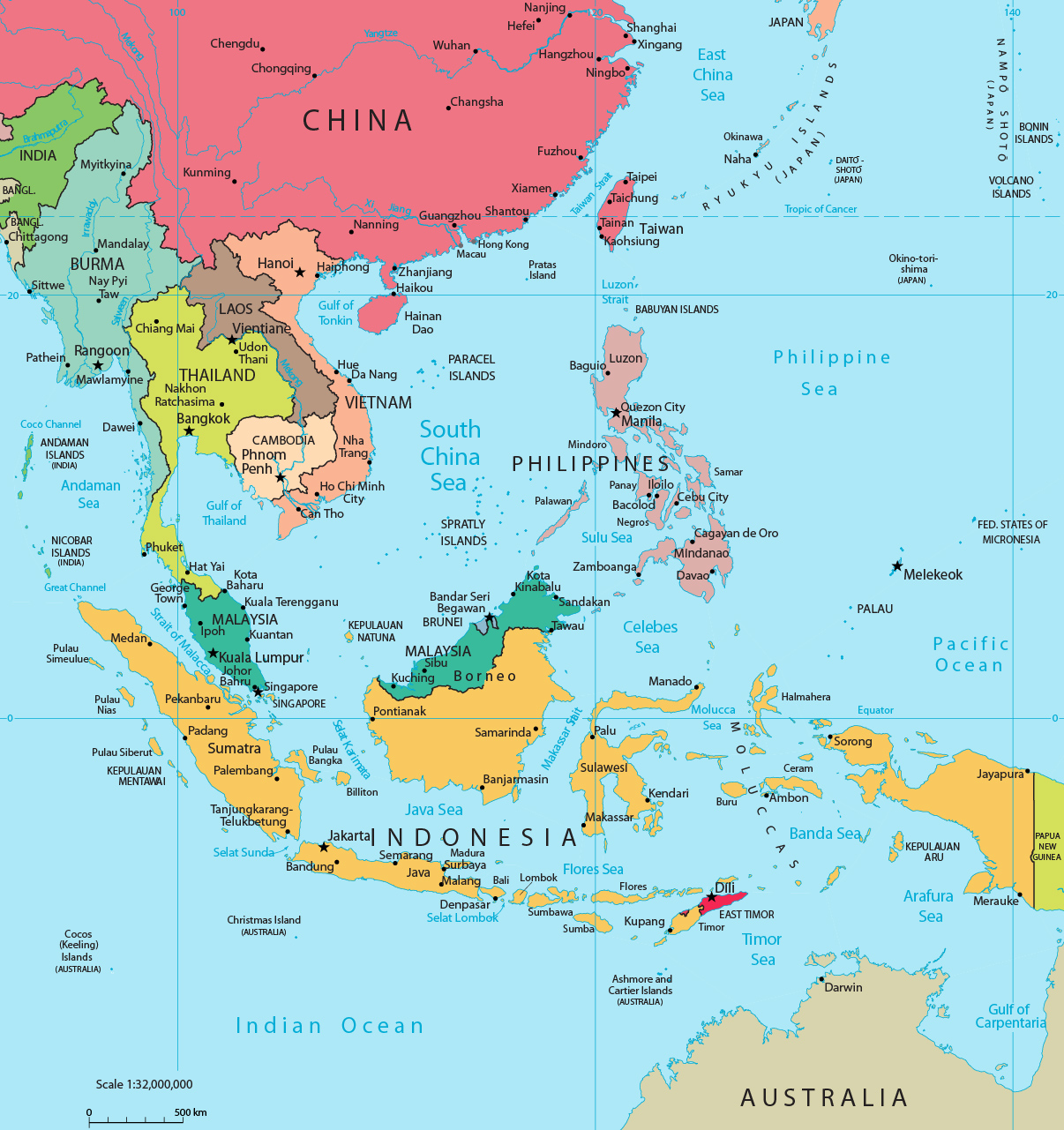
Thailand, the "Land of Smiles," occupies a strategically significant position in Southeast Asia, nestled at the geographical crossroads of the Indochinese Peninsula and the Malay Peninsula. Its unique location has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and economic development.
A Geographical Overview:
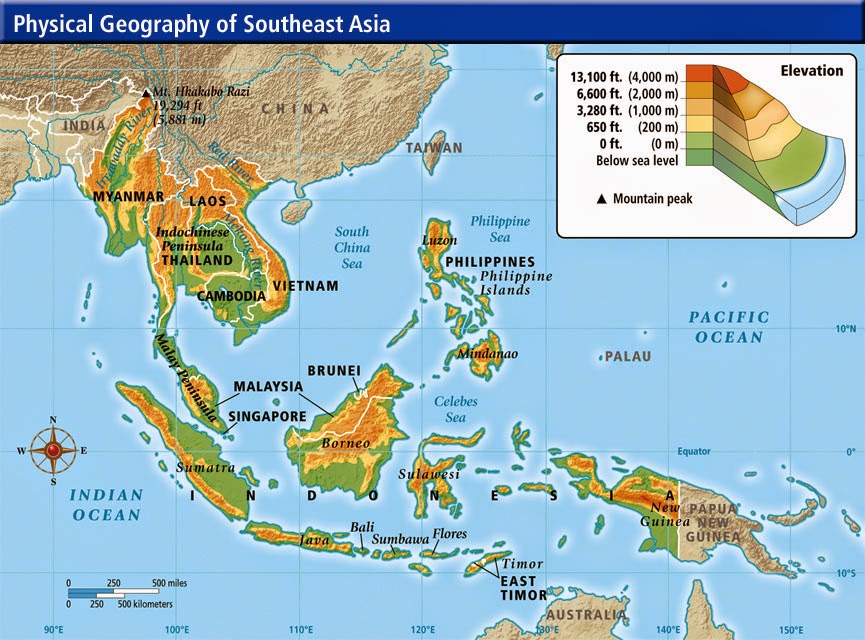
Thailand’s map reveals a country defined by its diverse landscapes. From the towering peaks of the Northern highlands to the fertile plains of the Central region, and the lush jungles of the South, Thailand’s topography is a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped the region.
- Northern Thailand: Dominated by the rugged terrain of the Shan Plateau, the North is characterized by mountainous landscapes, dense forests, and the iconic Mae Hong Son loop, a popular tourist route known for its scenic beauty.
- Central Thailand: The heartland of the country, the Central region encompasses the Chao Phraya River Delta, a fertile plain where rice cultivation has been the cornerstone of the economy for centuries. Bangkok, the capital city, is situated here, a bustling metropolis and a crucial economic hub.
- Northeastern Thailand: Known as Isan, this region is characterized by the Khorat Plateau, a vast expanse of relatively flat terrain with a distinctive cultural identity.
- Southern Thailand: Comprised of the Malay Peninsula, the South boasts a coastline along the Andaman Sea and the Gulf of Thailand, dotted with pristine beaches, islands, and lush mangrove forests.
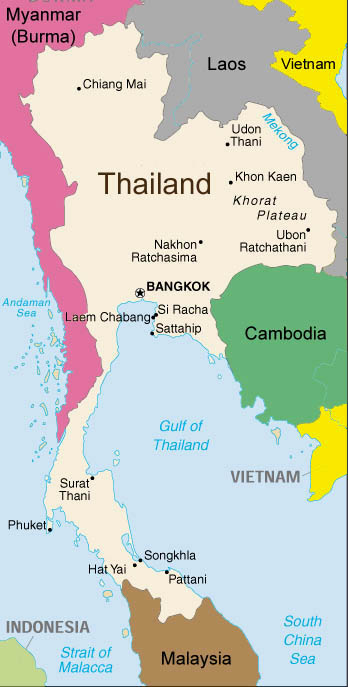
Navigating Thailand’s Borders:
Thailand shares borders with five countries, each contributing to its unique cultural and economic tapestry:
- Myanmar (Burma): To the west, Thailand shares a long border with Myanmar, a relationship marked by historical ties and cultural exchange.
- Laos: The Mekong River forms a natural border between Thailand and Laos, fostering cross-border trade and cultural connections.
- Cambodia: The eastern border with Cambodia holds historical significance, with both countries sharing a rich cultural heritage.
- Malaysia: The southern border with Malaysia marks the transition from the Malay Peninsula to the island of Borneo, a region known for its diverse flora and fauna.
- The Gulf of Thailand: This body of water separates Thailand from Vietnam and Cambodia, providing access to international trade routes.
Strategic Significance:
Thailand’s strategic location has made it a key player in Southeast Asian politics and economics. Its position as a land bridge between mainland Southeast Asia and the Malay Peninsula has facilitated trade and cultural exchange for centuries.
- Trade and Commerce: Thailand’s central location has made it a hub for trade, particularly in agricultural products, textiles, and manufactured goods. Its proximity to major shipping routes and its well-developed infrastructure have contributed to its economic success.
- Regional Cooperation: Thailand plays a significant role in regional organizations such as ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations), promoting cooperation and economic integration in the region.
- Tourism: Thailand’s diverse landscapes, rich culture, and friendly people have made it a top tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors annually.
FAQs about Thailand’s Geography:
1. What are the major geographic features of Thailand?
Thailand’s geography is characterized by its diverse landscapes, including mountainous highlands, fertile plains, and coastal regions. The Chao Phraya River Delta in the Central region plays a crucial role in agriculture and transportation.
2. What countries border Thailand?
Thailand shares borders with Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, and Malaysia. It also shares a maritime border with Vietnam and Cambodia through the Gulf of Thailand.
3. What is the significance of Thailand’s location?
Thailand’s strategic location at the crossroads of the Indochinese Peninsula and the Malay Peninsula has facilitated trade, cultural exchange, and regional cooperation. Its position as a land bridge has connected Southeast Asia with the rest of the world.
4. How does Thailand’s geography influence its culture and economy?
Thailand’s diverse landscapes have fostered distinct regional cultures and economic activities. The fertile plains of the Central region have made rice cultivation a cornerstone of the economy, while the mountainous regions have supported unique ethnic communities.
5. What are some of the major cities in Thailand?
Bangkok, the capital city, is the largest and most important urban center. Other major cities include Chiang Mai in the North, Phuket in the South, and Khon Kaen in the Northeast.
Tips for Understanding Thailand’s Geography:
- Utilize online maps: Interactive maps can provide detailed information about Thailand’s geography, including its topography, cities, and major landmarks.
- Explore different regions: Each region of Thailand offers a unique cultural and geographical experience.
- Read about Thailand’s history: Understanding the historical context can provide insights into how Thailand’s geography has shaped its development.
- Engage with local communities: Interacting with local people can offer firsthand knowledge of the region’s culture and geography.
Conclusion:
Thailand’s map is a testament to the country’s rich diversity and strategic significance in Southeast Asia. Its diverse landscapes, rich culture, and strategic location have made it a vibrant hub for trade, tourism, and regional cooperation. Understanding Thailand’s geography is crucial for appreciating its unique cultural heritage and its role in the global community.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Thailand’s Position in the Heart of Southeast Asia: A Geographical Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!