South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator
Related Articles: South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator
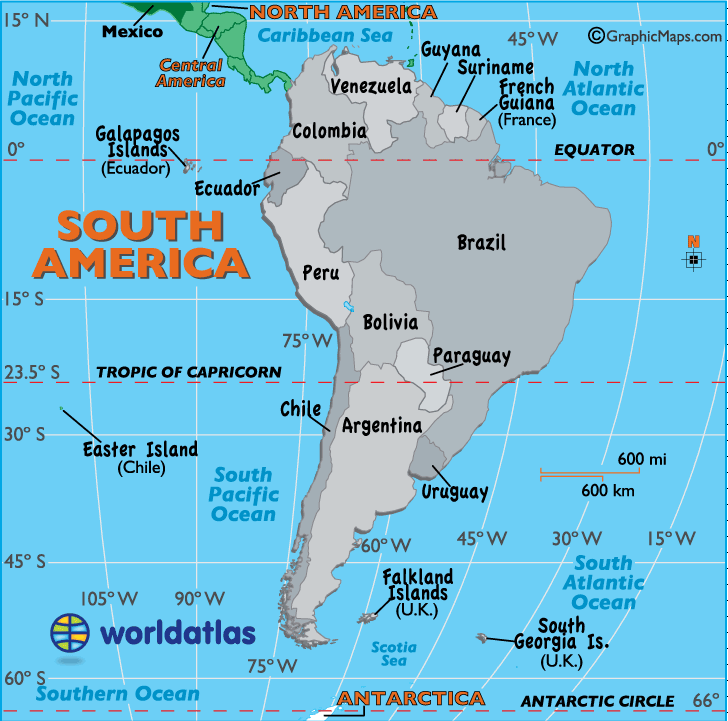
South America, the fourth largest continent, is a land of remarkable diversity, encompassing vast rainforests, towering Andes Mountains, arid deserts, and sprawling plains. A defining feature of this continent is its unique relationship with the equator, a line of latitude that circles the Earth at 0 degrees. The equator bisects South America, running through the northern portion of the continent, influencing the climate, ecosystems, and cultural landscapes of the region.
A Continent Divided by Latitude:
The equator’s passage through South America divides the continent into two distinct geographical zones:
-
North of the Equator: This region, encompassing countries like Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana, experiences a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and abundant rainfall. The Amazon rainforest, the world’s largest tropical rainforest, dominates this area, supporting an incredible biodiversity.
-
South of the Equator: This region encompasses the majority of South America, including countries like Brazil, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay. The climate in this region is more varied, ranging from tropical in the north to temperate and even cold in the south. The Andes Mountains, which run along the western edge of the continent, play a significant role in creating diverse microclimates.
The Influence of the Equator:
The equator’s influence on South America is profound:
-
Climate: The equator’s position influences the distribution of solar energy, resulting in a predominantly warm and humid climate in the northern part of the continent. The equator’s influence extends south, contributing to the tropical and subtropical climates of countries like Brazil, Ecuador, and Peru.
-
Biodiversity: The equatorial climate fosters a rich biodiversity, supporting a vast array of plant and animal life. The Amazon rainforest, located primarily north of the equator, is a global biodiversity hotspot, home to an estimated 10% of the world’s known species.
-
Culture and History: The equator has shaped the cultural landscape of South America. Indigenous cultures have thrived in the equatorial regions for centuries, developing unique traditions, languages, and ways of life adapted to the tropical environment. The equator’s influence on trade routes and colonial history is also evident, as it facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between different parts of the continent and the world.
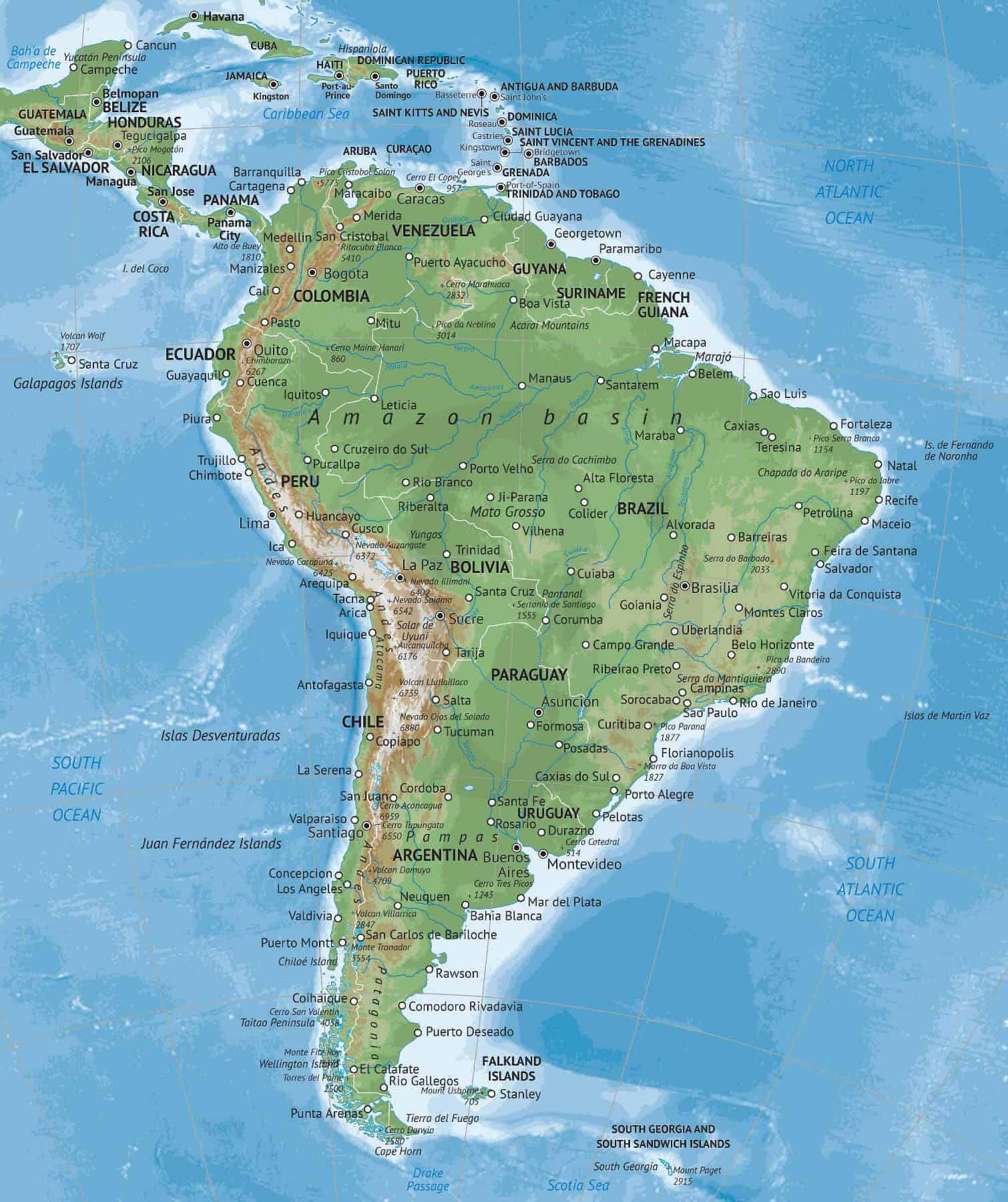
Understanding the Map:
A map of South America with the equator clearly marked is essential for understanding the continent’s geography and its relationship with the equator. Here are some key points to consider:
-
Equatorial Line: The equator is represented by a horizontal line that bisects the continent. It runs through countries like Colombia, Ecuador, and Brazil.
-
Latitude Lines: The map also shows other lines of latitude, which run parallel to the equator. These lines help to understand the location of different regions and their relative distance from the equator.
-
Longitude Lines: Longitude lines, running vertically, intersect the equator. These lines help to understand the east-west position of locations on the continent.
-
Landforms: The map should clearly depict major landforms, including the Andes Mountains, the Amazon Basin, and the vast plains of the Pampas.
-
Political Boundaries: Political boundaries of different countries are essential for understanding the continent’s political landscape.
FAQs About South America and the Equator:
Q: What is the significance of the equator passing through South America?
A: The equator’s passage through South America significantly influences the continent’s climate, biodiversity, and cultural landscape. It creates distinct geographical zones, fosters a rich ecosystem, and has shaped the development of indigenous cultures and trade routes.
Q: What are the main climatic zones in South America influenced by the equator?
A: South America experiences a range of climates, influenced by the equator. The northern part of the continent experiences a tropical climate, while the southern part exhibits a diverse range of climates, from tropical to temperate and even cold.
Q: What are some of the key cultural impacts of the equator on South America?
A: The equator has profoundly influenced the cultural landscape of South America. Indigenous cultures have thrived in the equatorial regions, developing unique traditions, languages, and ways of life. The equator’s influence on trade routes and colonial history is also evident, as it facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between different parts of the continent and the world.
Q: How does the equator affect the biodiversity of South America?
A: The equatorial climate fosters a rich biodiversity, supporting a vast array of plant and animal life. The Amazon rainforest, located primarily north of the equator, is a global biodiversity hotspot, home to an estimated 10% of the world’s known species.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by countries located on the equator in South America?
A: Countries located on the equator in South America face challenges related to climate change, deforestation, and the preservation of biodiversity. These challenges require sustainable development strategies and international cooperation to ensure the long-term well-being of the region.
Tips for Studying the Map of South America with the Equator:
-
Use a physical map: A physical map provides a more accurate representation of the continent’s landforms and elevation, helping you visualize the influence of the equator on the terrain.
-
Identify key locations: Mark the equator on the map and identify major cities, rivers, and mountains. This will help you understand the geographical context of the continent.
-
Research the climate zones: Use the map to identify the different climate zones in South America, and research the characteristics of each zone. This will help you understand how the equator influences the climate of the continent.
-
Explore the cultural diversity: The map can be used to explore the cultural diversity of South America. Research the indigenous cultures of different regions and their relationship with the equatorial environment.
-
Consider the environmental challenges: The map can help you understand the environmental challenges faced by South America, such as deforestation, climate change, and biodiversity loss. Research the causes of these challenges and the efforts being made to address them.
Conclusion:
The equator’s passage through South America is a defining feature of the continent, influencing its climate, biodiversity, and cultural landscape. Understanding the relationship between South America and the equator is crucial for appreciating the continent’s remarkable diversity and the challenges it faces. By studying a map of South America with the equator clearly marked, we can gain a deeper insight into the continent’s geography, history, and culture, fostering a greater appreciation for this fascinating and complex region of the world.
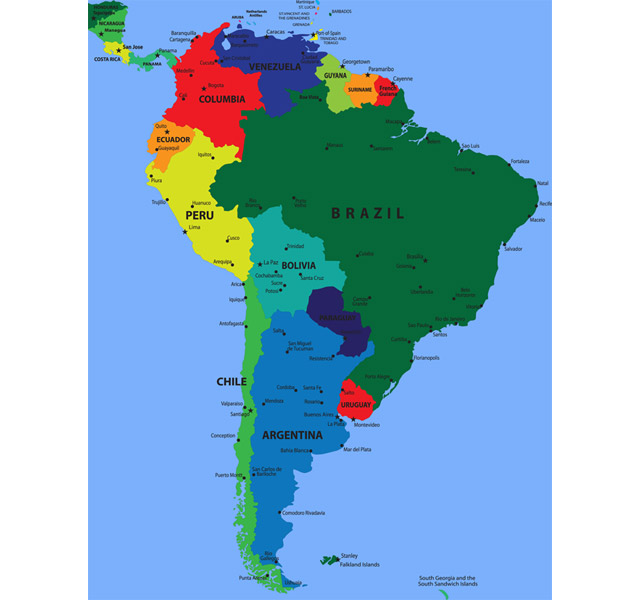



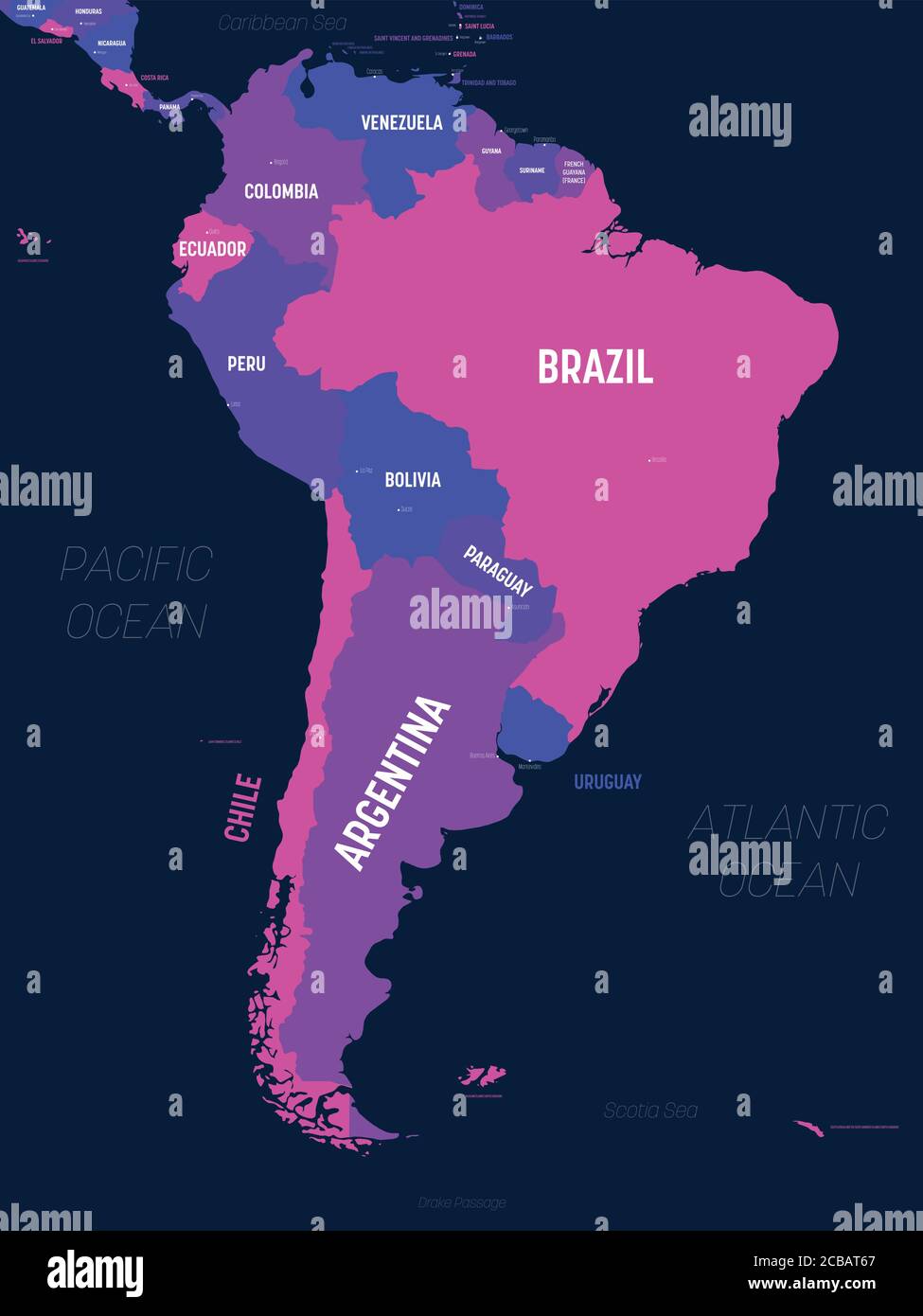
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/countries-that-lie-on-the-equator-1435319_V2-01-28e48f27870147d3a00edc1505f55770.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into South America: A Continent Straddling the Equator. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!