Navigating the World: Understanding Time Zones Through Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Time Zones Through Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Time Zones Through Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding Time Zones Through Maps
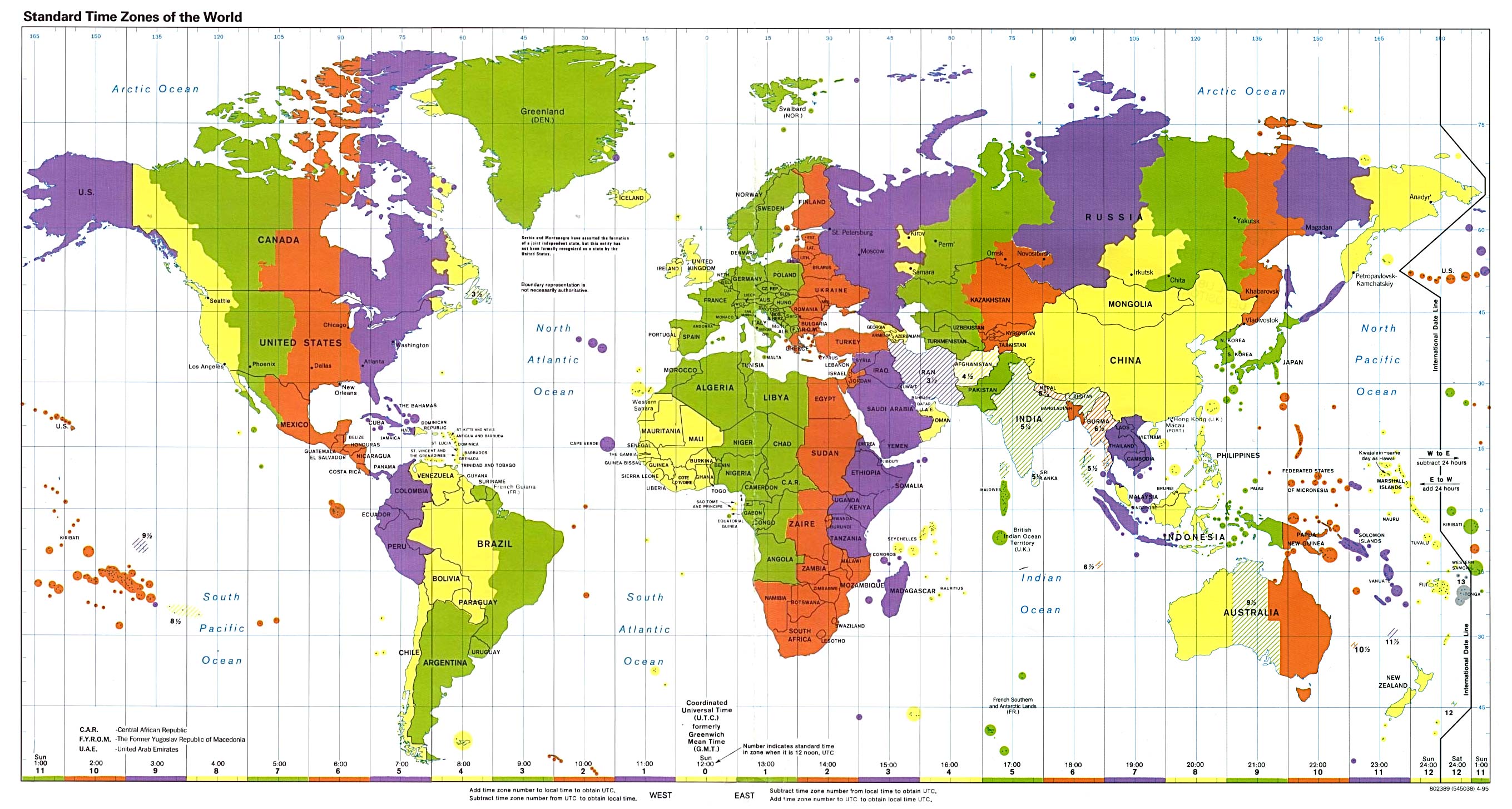
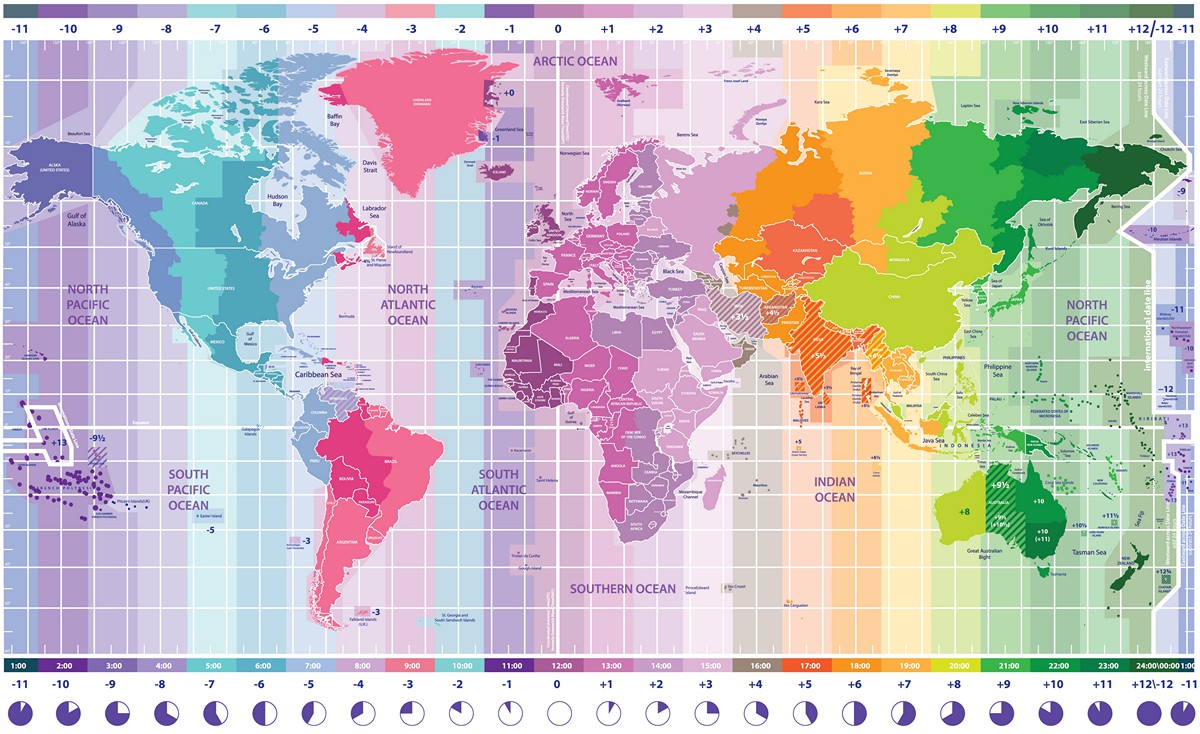
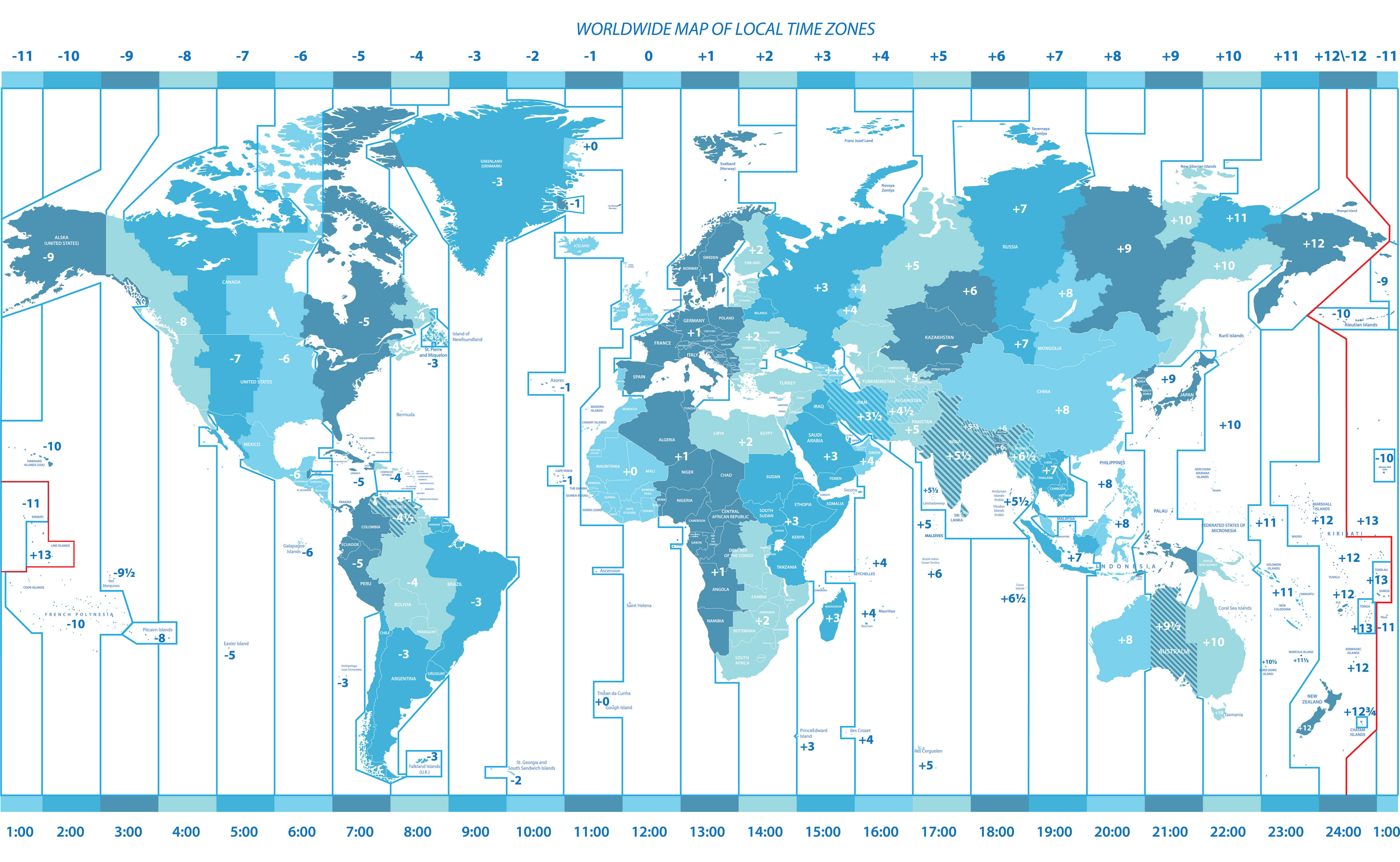
The Earth, a sphere constantly rotating on its axis, experiences the sun’s rays at different times across its surface. This simple fact gives rise to the concept of time zones, a system that divides the planet into 24 distinct regions, each with its own standard time. A map that depicts these zones is an indispensable tool for navigating the complexities of global timekeeping, facilitating communication, travel, and international business operations.
The Foundation of Time Zones:
The International Date Line, an imaginary line running roughly along the 180th meridian, serves as the dividing point between two consecutive calendar days. As one travels eastward across the Date Line, the calendar date advances by one day. Conversely, traveling westward across the line results in the calendar date moving backward.
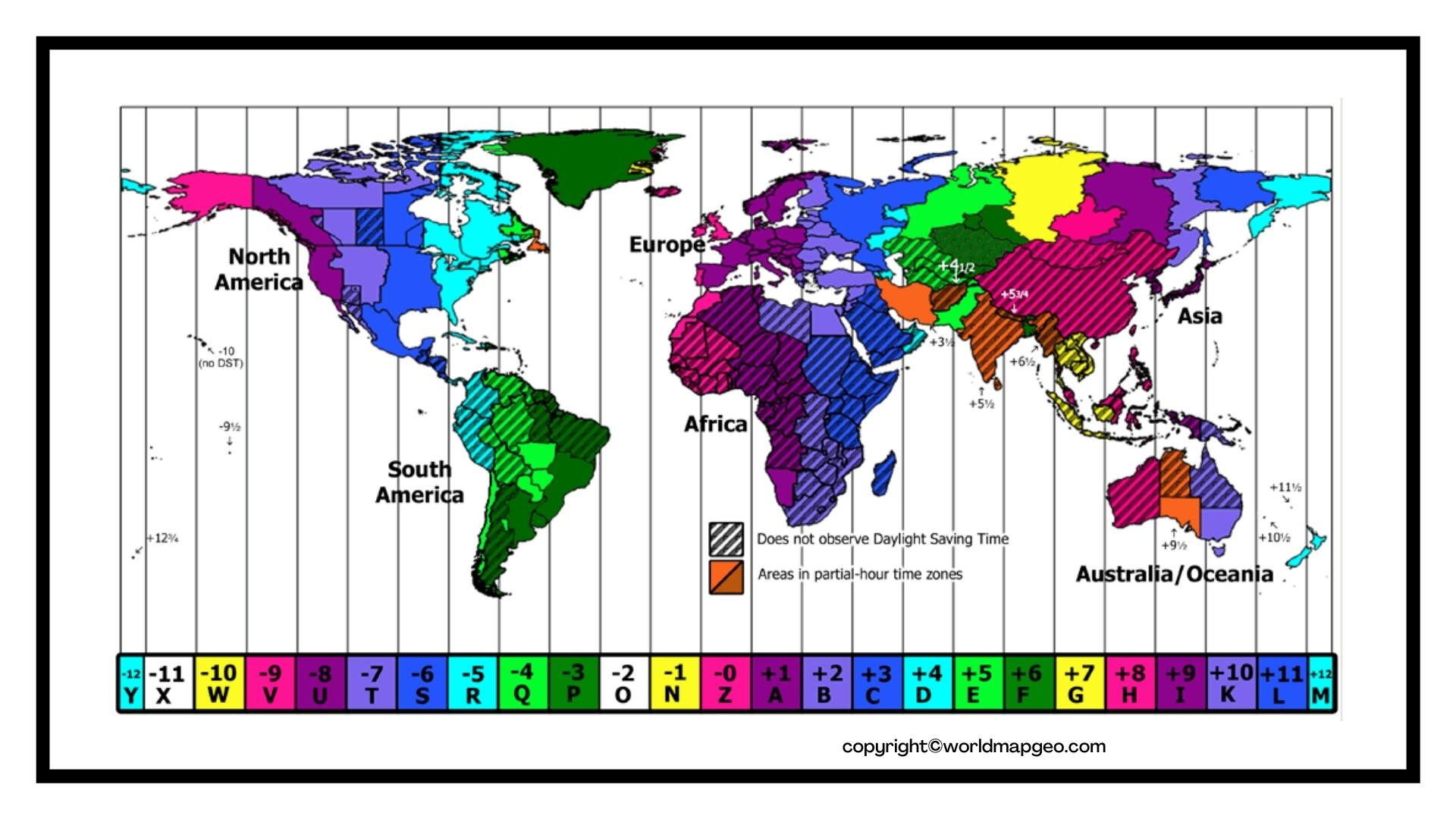
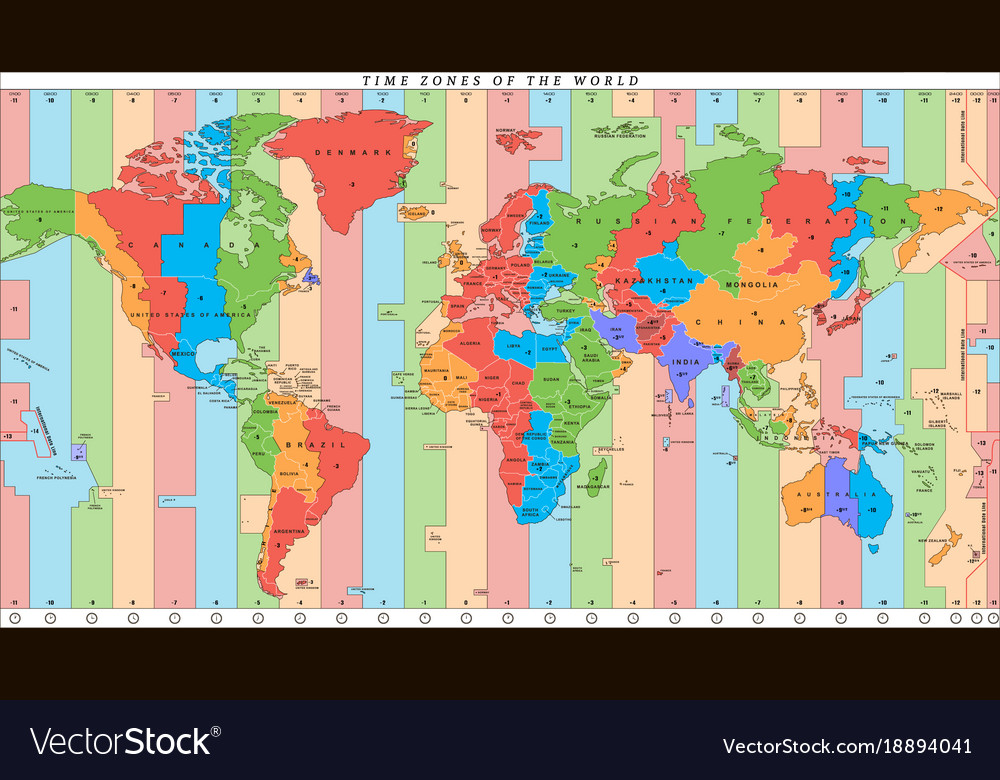
The Map as a Visual Guide:
A time zone map, often featuring vibrant colors to distinguish each zone, provides a visual representation of this global time system. Each zone is typically assigned a specific time offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), also known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), which is the standard reference time for the world.
Understanding the Map’s Key Features:
- Time Zone Boundaries: The map clearly depicts the boundaries between adjacent time zones, which are often irregular due to geographical factors and political considerations.
- Time Offsets: Each zone is labeled with its specific time offset from UTC. For instance, Eastern Standard Time (EST) in North America is five hours behind UTC (UTC-5).
- Daylight Saving Time: Many regions implement Daylight Saving Time (DST) during certain months, shifting their clocks forward by an hour. The map may indicate these regions with distinct markings or colors.
- Special Cases: Some areas may have unique time zone configurations, such as fractional time zones or areas with multiple time zones within a single country. The map provides visual cues for these exceptions.
The Importance of Time Zone Maps:
Time zone maps are vital for numerous reasons:
- Global Communication: Understanding time differences is crucial for scheduling phone calls, video conferences, and other forms of communication across different time zones.
- International Travel: Travelers rely on time zone maps to adjust their watches and internal clocks for smooth transitions between locations.
- Business Operations: Businesses with global operations need to coordinate schedules, manage logistics, and ensure efficient communication across time zones.
- Scientific Research: Scientists use time zone maps to track astronomical events, analyze geophysical data, and conduct research that involves time-sensitive observations.
FAQs About Time Zone Maps:
1. Why are time zone boundaries not perfectly straight lines?
Time zone boundaries are often irregular due to geographical factors, such as mountain ranges, bodies of water, and political considerations. They are designed to minimize the number of people within a single country having to adjust their time by more than an hour.
2. How do I determine the current time in another time zone?
By using a time zone map, you can identify the time offset of a specific location from UTC. Then, add or subtract the offset from the current UTC time to determine the local time.
3. What is the purpose of Daylight Saving Time?
Daylight Saving Time aims to make better use of daylight hours by shifting clocks forward by an hour during certain months. This can save energy and reduce traffic accidents.
4. How do I find the time zone of a specific location?
Many online tools and mobile apps allow you to search for a specific location and retrieve its corresponding time zone.
5. Why are there multiple time zones within some countries?
Countries with large geographical areas or diverse populations may adopt multiple time zones to account for the varying lengths of daylight hours across their territories.
Tips for Using Time Zone Maps:
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend and symbols.
- Use online tools and mobile apps to search for specific locations and time zones.
- Consider the time difference when scheduling international calls or meetings.
- Adjust your watch and internal clock when traveling across time zones.
- Stay informed about any changes to Daylight Saving Time regulations.
Conclusion:
A time zone map serves as a vital tool for navigating the complexities of global timekeeping. It enables individuals, businesses, and organizations to effectively communicate, travel, and conduct operations across different time zones. By understanding the map’s features and utilizing its information wisely, we can navigate the world with greater efficiency and accuracy.


![Free Large World Time Zone Map Printable [PDF]](https://worldmapswithcountries.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Printable-World-Time-Zone-Map.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Time Zones Through Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!