Navigating the Pacific: A Deep Dive into Ocean Currents
Related Articles: Navigating the Pacific: A Deep Dive into Ocean Currents
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Pacific: A Deep Dive into Ocean Currents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Pacific: A Deep Dive into Ocean Currents

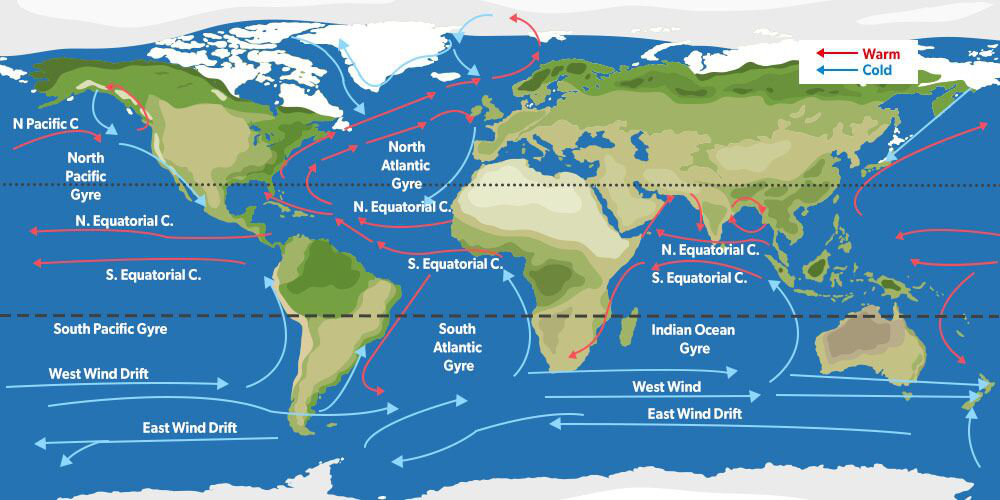
The Pacific Ocean, spanning nearly a third of the Earth’s surface, is a vast and dynamic realm. Its waters are constantly in motion, driven by a complex interplay of wind, temperature, salinity, and the Earth’s rotation. This intricate dance of currents plays a pivotal role in shaping the planet’s climate, influencing weather patterns, distributing heat, and supporting diverse marine ecosystems. Understanding the Pacific Ocean currents map is crucial for comprehending these critical functions.
A Tapestry of Currents
The Pacific Ocean currents map reveals a mesmerizing network of currents, each with its distinct characteristics and impact. These currents can be broadly categorized into two types: surface currents and deep ocean currents.
Surface Currents: The Wind-Driven Symphony
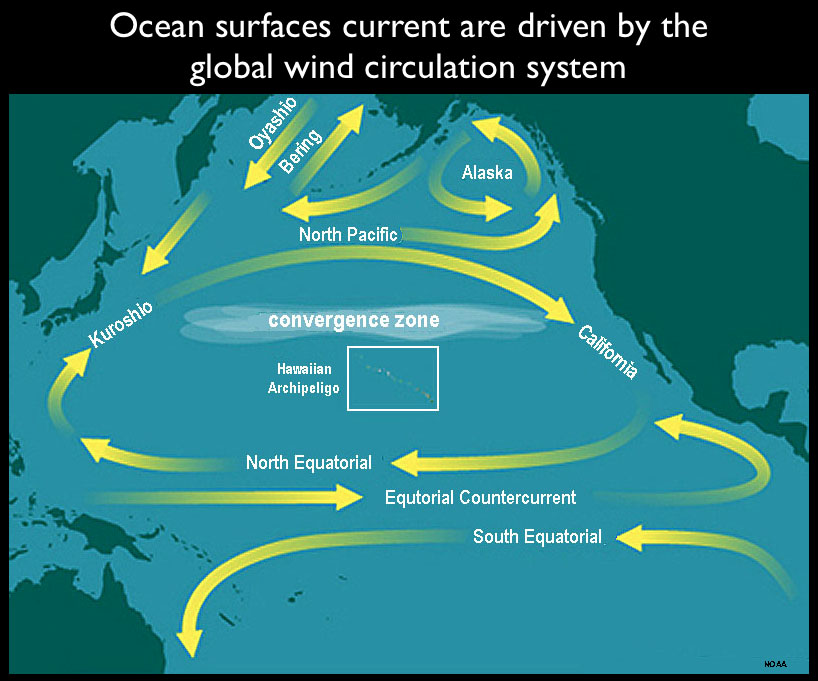
Surface currents, as their name suggests, flow near the ocean’s surface. They are primarily driven by the prevailing winds, particularly the trade winds and the westerly winds. This wind-driven motion creates a series of circular currents, known as gyres, which dominate the Pacific Ocean’s surface.
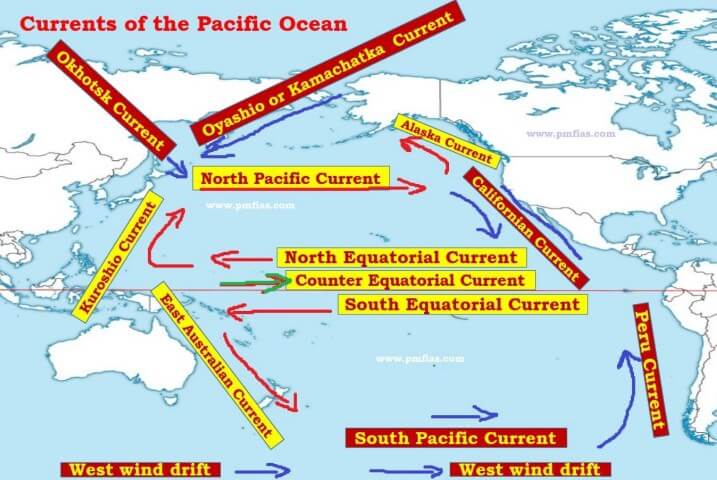
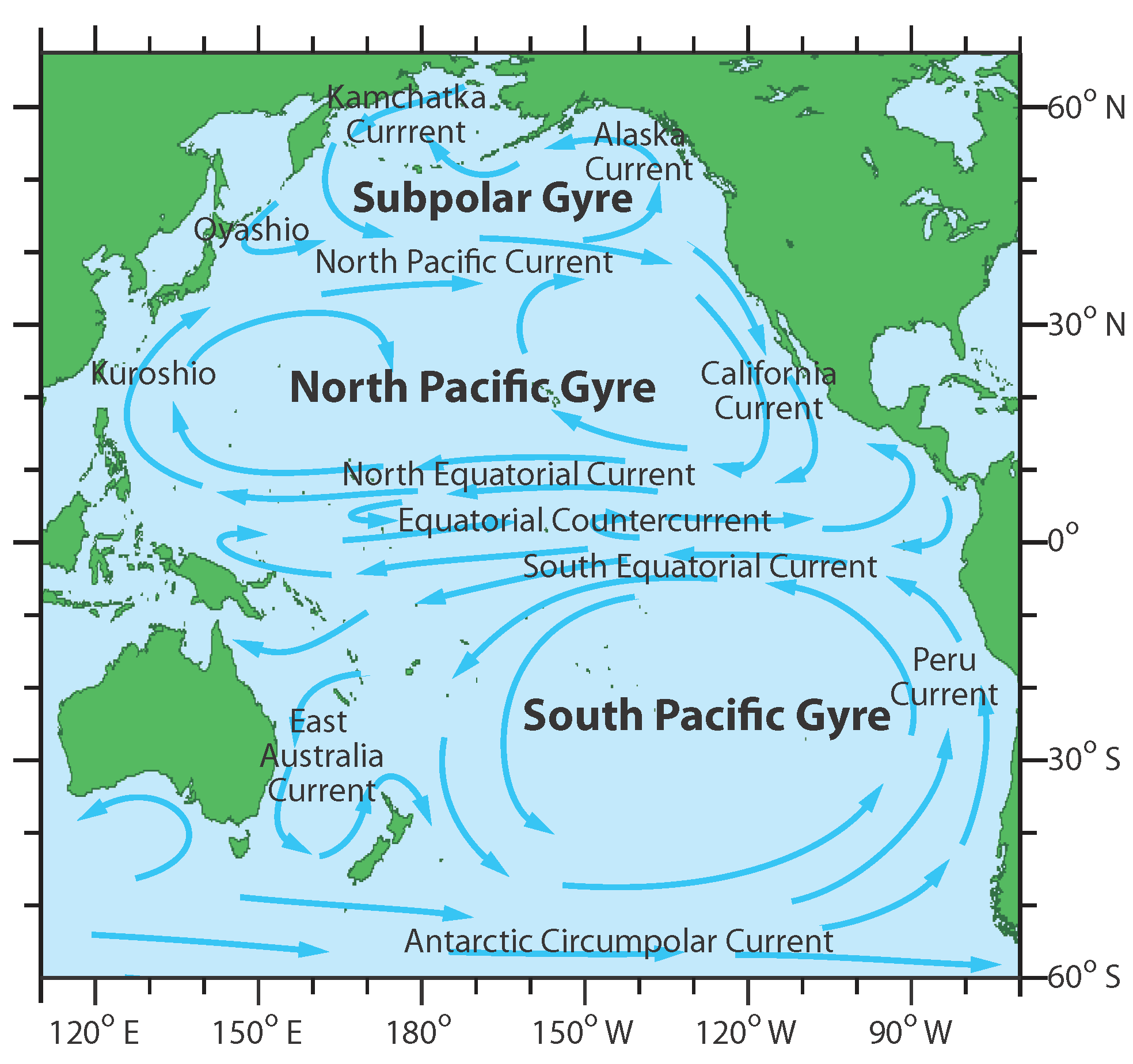
- The North Pacific Gyre: This clockwise gyre encompasses the North Pacific Ocean, driven by the trade winds in the east and the westerly winds in the west. The North Pacific Current, the Kuroshio Current (Japan Current), the California Current, and the North Equatorial Current are key components of this gyre.
- The South Pacific Gyre: This counter-clockwise gyre dominates the South Pacific, driven by the trade winds in the east and the westerly winds in the west. The South Equatorial Current, the East Australian Current, the Peru Current (Humboldt Current), and the South Pacific Current are the main components of this gyre.
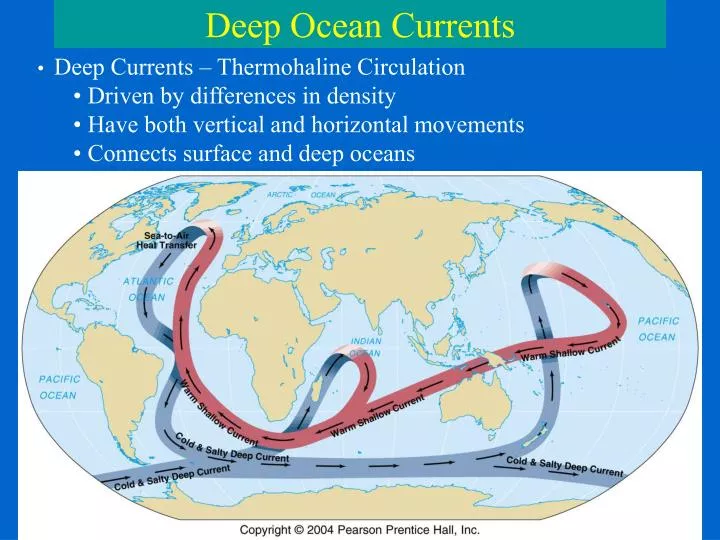
Deep Ocean Currents: The Thermohaline Conveyor Belt
Deep ocean currents, also known as thermohaline currents, are driven by differences in temperature and salinity. Cold, salty water is denser than warm, less salty water. This density difference creates a slow but powerful circulation system that transports water throughout the global ocean.
- The Pacific Deep Water Formation: Cold, salty water sinks in the North Atlantic, forming the North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW). This water mass then flows south, eventually entering the Pacific Ocean as a deep current.
- The Pacific Bottom Water: Formed in the Southern Ocean, this cold, dense water flows northward along the bottom of the Pacific Ocean, contributing to the global thermohaline circulation.
The Importance of Pacific Ocean Currents
The Pacific Ocean currents map unveils the intricate web of forces that shape the planet’s climate and ecosystems. Understanding these currents is crucial for various reasons:
- Climate Regulation: Ocean currents act as a massive heat transfer system, distributing heat from the tropics towards the poles. This process moderates global temperatures, preventing extreme variations in climate.
- Weather Patterns: The Pacific Ocean currents influence weather patterns across the globe. For example, the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon, characterized by shifts in the Pacific Ocean currents, can cause significant weather disruptions in various regions.
- Marine Life and Ecosystems: Ocean currents transport nutrients, oxygen, and larvae, supporting diverse marine ecosystems. They also influence the distribution of marine species, creating unique habitats.
- Navigation and Shipping: Understanding ocean currents is essential for navigation and shipping. Sailors have long utilized currents to their advantage, leveraging their direction and speed to optimize their voyages.
- Resource Management: Ocean currents influence the distribution of marine resources, such as fish stocks. Understanding these currents is crucial for sustainable management of fisheries and other marine resources.
Navigating the FAQs: A Deeper Look
Q: How do ocean currents impact weather patterns?
A: Ocean currents play a significant role in shaping weather patterns. They transport heat from the tropics towards the poles, influencing the distribution of temperature and precipitation. For example, the warm Kuroshio Current brings mild temperatures to Japan, while the cold California Current contributes to the cool, dry climate of the California coast.
Q: What is the significance of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO)?
A: ENSO is a natural climate pattern that involves fluctuations in sea surface temperatures and atmospheric pressure in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. During El Niño events, the trade winds weaken, allowing warm water to flow eastward, causing warmer than average temperatures in the eastern Pacific. This shift can disrupt weather patterns globally, leading to increased rainfall in some regions and droughts in others. La Niña, the opposite phase of ENSO, involves stronger trade winds and cooler than average temperatures in the eastern Pacific.
Q: How do ocean currents affect marine ecosystems?
A: Ocean currents are vital for marine ecosystems, acting as conveyor belts for nutrients, oxygen, and larvae. They support the growth of phytoplankton, the base of the marine food web, and influence the distribution of marine species. For example, the cold, nutrient-rich waters of the Humboldt Current support a rich ecosystem, including large populations of anchovies, which are a key food source for seabirds and other marine animals.
Q: How can we use ocean currents for navigation and shipping?
A: Sailors have long used ocean currents to their advantage. By understanding the direction and speed of currents, they can optimize their routes, reducing travel time and fuel consumption. Modern shipping vessels also use this knowledge to plan their voyages, taking advantage of favorable currents to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Q: What are the challenges associated with ocean currents?
A: While ocean currents provide numerous benefits, they also pose some challenges. Changes in ocean currents, such as those associated with climate change, can disrupt marine ecosystems, affect weather patterns, and impact coastal communities. Additionally, marine pollution, such as plastic debris, can be transported by ocean currents, leading to environmental damage.
Tips for Navigating the Pacific Ocean Currents Map
- Visualize the Currents: Use online maps and interactive tools to visualize the flow of ocean currents. This will provide a better understanding of their direction, speed, and patterns.
- Study the Gyres: Familiarize yourself with the major gyres in the Pacific Ocean, including their direction of rotation and the currents that comprise them.
- Understand the Drivers: Learn about the factors that drive ocean currents, such as wind, temperature, and salinity. This will help you understand the forces behind their movement.
- Explore the Impacts: Investigate the effects of ocean currents on climate, weather, marine life, and human activities. This will provide a comprehensive understanding of their importance.
Conclusion: A Symphony of Motion
The Pacific Ocean currents map reveals a dynamic and intricate web of forces that shape our planet. These currents, driven by wind, temperature, and salinity, play a critical role in climate regulation, weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and human activities. Understanding this complex symphony of motion is crucial for navigating the challenges of a changing world and ensuring the health of our oceans for generations to come. By studying the Pacific Ocean currents map, we gain valuable insights into the interconnectedness of our planet and the importance of preserving its delicate balance.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Pacific: A Deep Dive into Ocean Currents. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!