Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the British Rail Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the British Rail Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the British Rail Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the British Rail Map
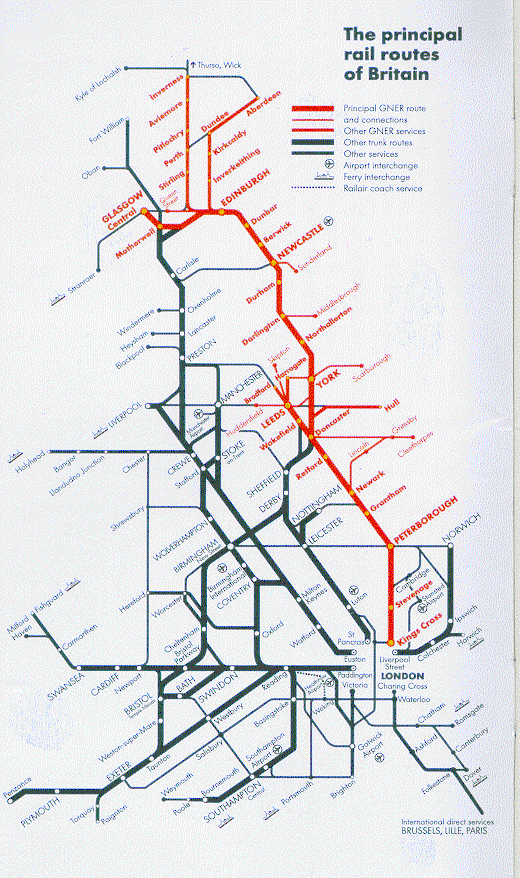
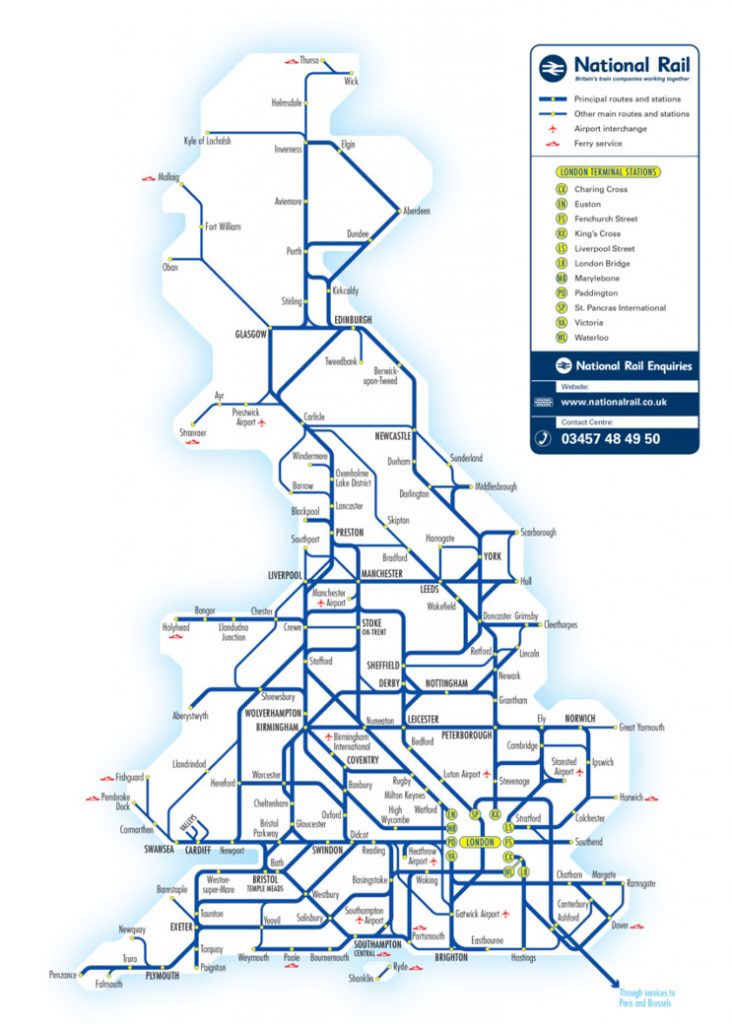
The British rail network, a sprawling tapestry of lines and stations, is a vital artery for travel and commerce across the United Kingdom. Understanding its intricate map is essential for anyone seeking to navigate this system efficiently. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the British rail map, exploring its history, key features, and practical applications.
A History of Connection: The Evolution of the British Rail Map
The origins of the British rail map can be traced back to the early 19th century, when the Industrial Revolution sparked a boom in railway construction. Initially, various independent companies built and operated their own lines, resulting in a fragmented network. This period saw the emergence of iconic lines like the Great Western Railway and the London and North Western Railway, each with its unique character and route map.
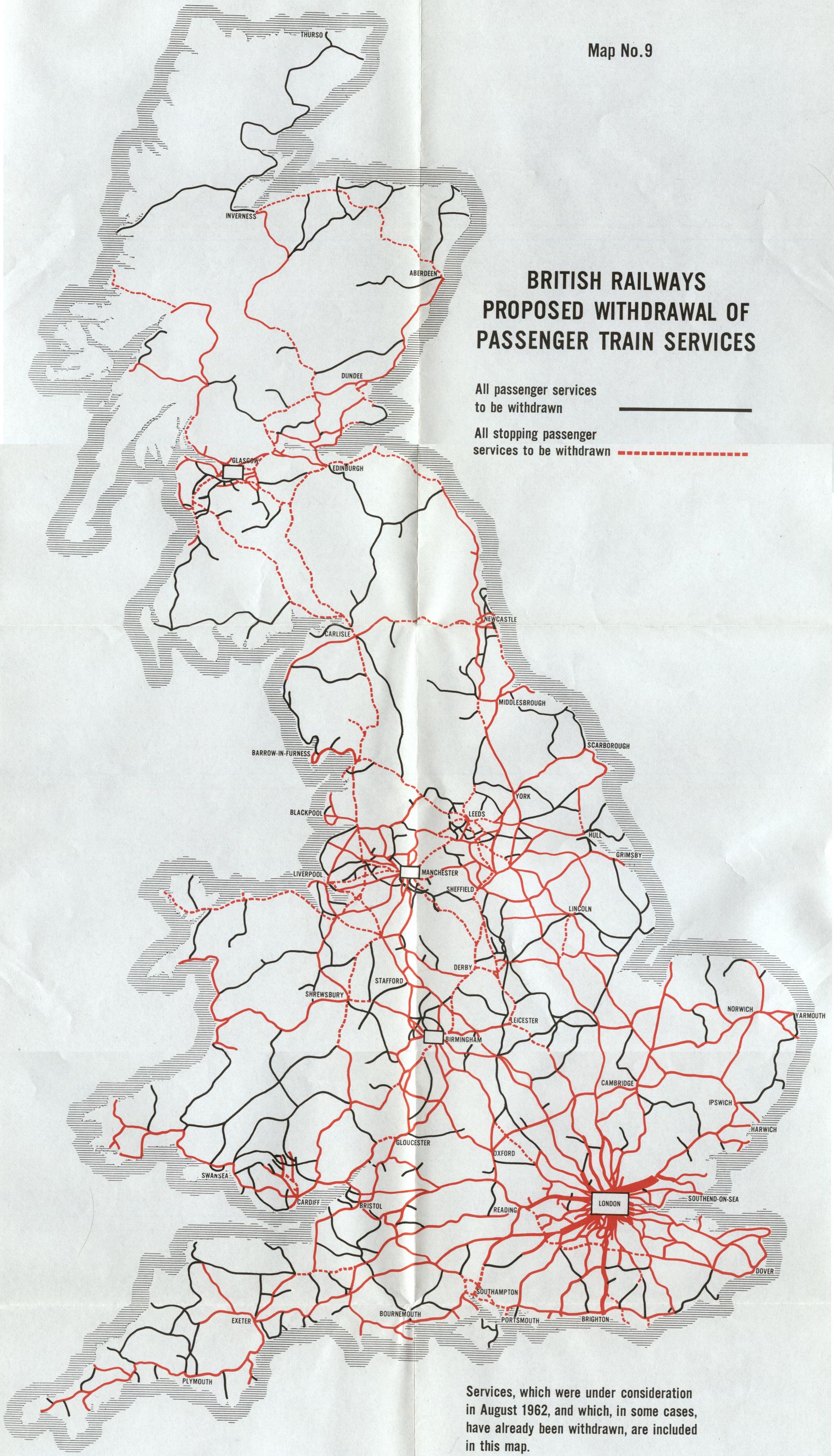
The 20th century witnessed a gradual consolidation of the railway network under nationalization. The formation of British Rail in 1948 brought about a unified system, with a standardized map and fare structure. The subsequent decades saw further developments, including the introduction of high-speed lines and the modernization of infrastructure.
Decoding the Map: Key Features and Terminology
The British rail map, in its modern form, is a complex yet intuitive visual representation of the network. Understanding its key features and terminology is crucial for effective navigation.
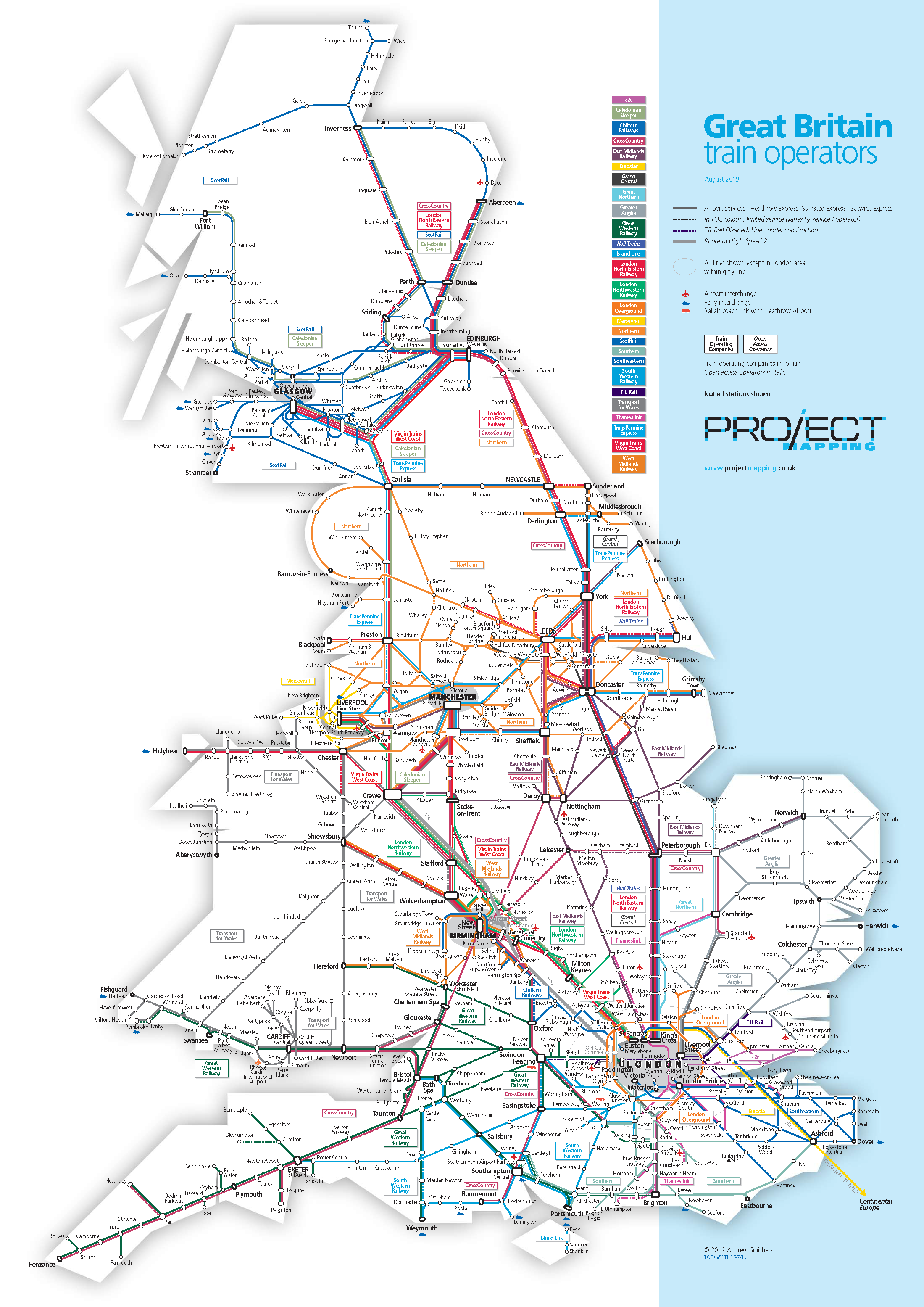
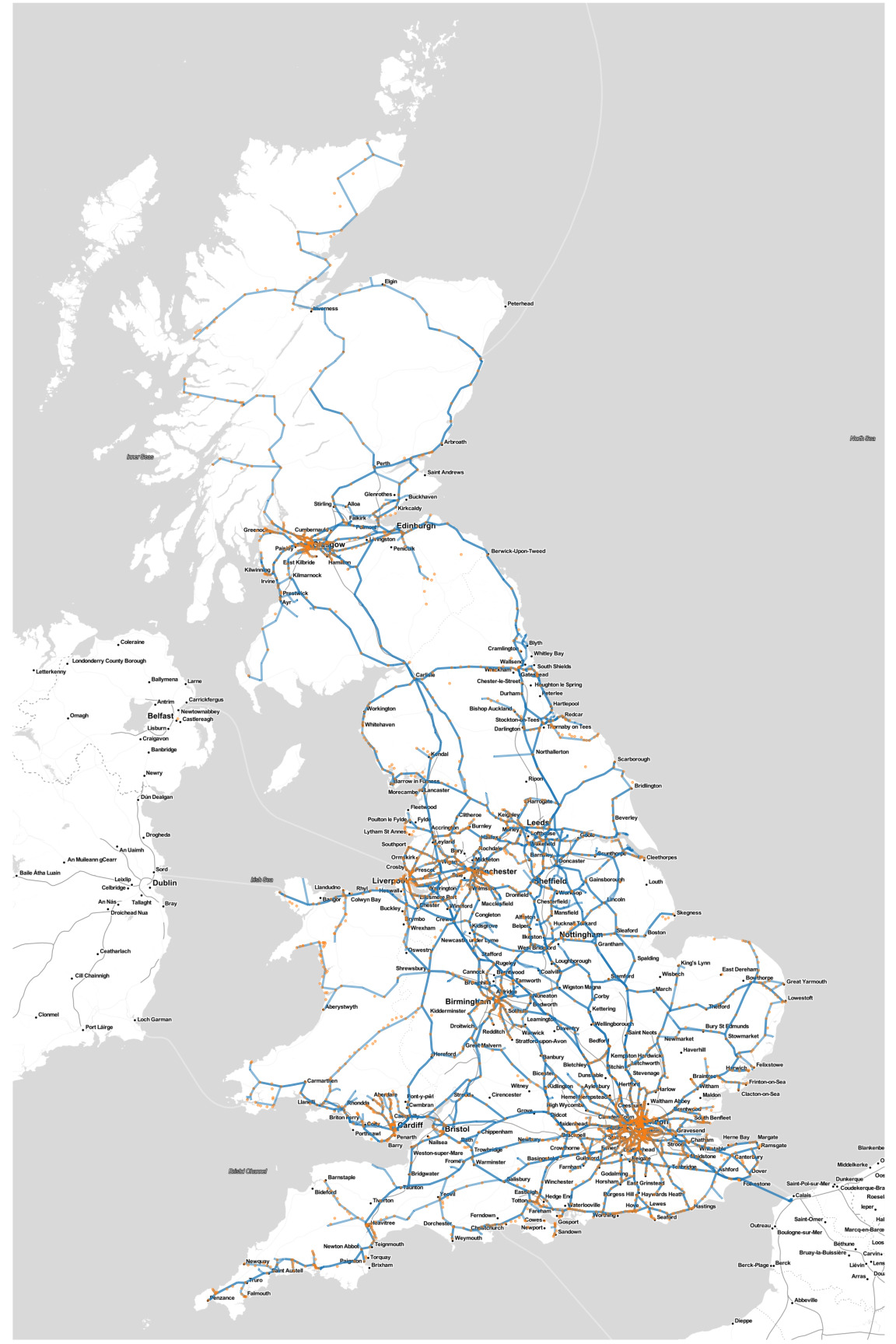
1. Lines and Stations: The map depicts numerous lines, each representing a specific route. Lines are often color-coded to distinguish them, with key lines like the East Coast Main Line or the West Coast Main Line clearly marked. Stations, represented by dots or squares, are the points where passengers board and disembark trains.
2. Interchanges: These are crucial points where multiple lines converge, allowing for easy transfers between different routes. Major interchanges like London Euston or Birmingham New Street are essential hubs within the network.
3. Train Types: The map often indicates different train types, such as high-speed trains, commuter trains, or regional services. Each type typically has its own distinct route and frequency.
4. Timetables: While not always directly depicted on the map, timetables are integral to understanding the network’s operation. They provide detailed information on train schedules, journey times, and fare structures.
5. Zones and Fares: The British rail network is divided into zones, with fares varying based on the distance traveled. The map may not always explicitly show these zones, but they are crucial for determining the cost of travel.
Practical Applications of the British Rail Map
The British rail map serves as an invaluable tool for various purposes:
1. Journey Planning: The map allows for efficient planning of train journeys, enabling users to identify the optimal route, potential interchanges, and estimated journey times.
2. Exploring Destinations: The map can inspire travel by showcasing the extensive network and the diverse destinations it connects. Passengers can readily discover new places and plan trips based on their interests.
3. Understanding the Network: The map provides a comprehensive overview of the rail network, highlighting its key lines, stations, and interchanges. This knowledge can be useful for understanding the broader context of travel within the UK.
4. Supporting Local Communities: The rail network plays a vital role in connecting communities and supporting local economies. The map helps visualize the importance of rail infrastructure and its contribution to regional development.
5. Promoting Sustainable Travel: By showcasing the extensive reach of the rail network, the map encourages the use of public transportation, promoting sustainable travel and reducing reliance on cars.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I find the best route for my journey?
Several online tools and apps, such as National Rail Enquiries or Trainline, allow you to input your starting and destination points and retrieve the most efficient route, including journey times and fare options.
2. How do I understand the different train types?
The map often uses icons or labels to distinguish train types. Alternatively, websites like National Rail Enquiries provide detailed information on train types, including their amenities and operating schedules.
3. How do I purchase tickets?
Tickets can be purchased online, at train stations, or through mobile apps. It is generally cheaper to book tickets in advance, especially for long-distance journeys.
4. What are the different fare types?
Fares vary based on factors such as the distance traveled, time of travel, and type of ticket. Advance purchase tickets are typically cheaper than standard tickets.
5. What happens if my train is delayed or cancelled?
National Rail Enquiries provides real-time information on train delays and cancellations. In case of disruption, passengers are entitled to compensation depending on the severity of the delay.
Tips for Using the British Rail Map
1. Familiarize yourself with key lines and stations: Understanding the major routes and interchanges will enhance your navigation abilities.
2. Utilize online tools and apps: Websites like National Rail Enquiries and apps like Trainline provide comprehensive information on routes, timetables, and fares.
3. Plan ahead: Book tickets in advance, especially for long-distance journeys, and allow sufficient time for travel, especially during peak hours.
4. Check for updates and disruptions: Stay informed about potential delays or cancellations by checking National Rail Enquiries or other reliable sources.
5. Consider alternative routes: If your preferred route is disrupted, explore alternative options using the map and online tools.
Conclusion
The British rail map is an essential tool for navigating the extensive network of lines and stations across the UK. It provides a visual representation of the system, allowing for efficient journey planning, exploration of destinations, and understanding of the network’s broader context. By familiarizing oneself with the map’s key features and utilizing available resources, travelers can enhance their experience and navigate the British rail network with ease.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the British Rail Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!