Navigating the Celestial Highway: Understanding Satellite Orbit Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Celestial Highway: Understanding Satellite Orbit Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Celestial Highway: Understanding Satellite Orbit Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Celestial Highway: Understanding Satellite Orbit Maps

The vast expanse of space, once a realm of mystery, is now crisscrossed by a network of artificial objects: satellites. These silent sentinels, orbiting our planet, serve a myriad of purposes, from broadcasting television signals to monitoring weather patterns and even guiding our navigation systems. To comprehend the intricate dance of these celestial bodies, we turn to satellite orbit maps.
A Visual Representation of the Celestial Network
A satellite orbit map is a visual representation of the trajectories of satellites orbiting Earth. These maps provide a comprehensive overview of the distribution, altitude, and inclination of satellites, offering valuable insights into the global network of space-based technology.
Key Elements of a Satellite Orbit Map
-
Orbit Type: Satellite orbits are classified based on their shape and inclination. Common types include:
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO): Satellites in LEO orbit at altitudes ranging from 160 to 2,000 kilometers. They are used for various purposes, including Earth observation, communication, and navigation.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO): MEO satellites orbit at altitudes between 2,000 and 35,786 kilometers. They are typically used for navigation and communication systems like GPS and Galileo.
- Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO): GEO satellites orbit at an altitude of 35,786 kilometers, moving at the same speed as Earth’s rotation. This ensures they remain stationary relative to a specific point on the Earth’s surface, making them ideal for broadcasting and communication.
- Altitude: The height of a satellite above the Earth’s surface is a crucial factor determining its orbital period and visibility.
- Inclination: The angle between a satellite’s orbital plane and the Earth’s equator. An inclination of 0 degrees signifies an equatorial orbit, while an inclination of 90 degrees indicates a polar orbit.
- Orbital Period: The time it takes for a satellite to complete one full orbit around the Earth.
- Satellite Data: Orbit maps often include information about the satellite’s name, purpose, launch date, and other relevant details.
The Importance of Satellite Orbit Maps
Satellite orbit maps serve a crucial role in various fields:
- Space Traffic Management: As the number of satellites in orbit continues to grow, managing their trajectories and preventing collisions becomes increasingly important. Orbit maps help space agencies and commercial operators track satellite positions and plan safe maneuvers.
- Earth Observation: Earth observation satellites, such as those used for weather forecasting, environmental monitoring, and disaster relief, rely on accurate orbit data for effective operation. Orbit maps facilitate the planning and execution of these missions.
- Communication and Navigation: Orbit maps are essential for understanding the coverage areas of communication satellites and the positioning of navigation satellites. This information is crucial for optimizing communication networks and ensuring accurate location services.
- Scientific Research: Orbit maps play a vital role in scientific research, enabling researchers to track the movements of spacecraft and study the behavior of celestial bodies.
FAQs About Satellite Orbit Maps
1. What are some popular online resources for accessing satellite orbit maps?
Several online platforms provide access to satellite orbit maps, including:
- NASA’s Satellite Situation Center: This website offers real-time tracking of satellites and provides detailed information about their orbits and missions.
- Space-Track.org: This website, maintained by the United States Strategic Command, provides comprehensive data on satellites and space debris.
- Celestrak.org: This website offers a wide range of satellite data, including orbital parameters, launch information, and mission details.
- Heavens-Above.com: This website allows users to track satellites visible from their location and provides information about their orbits and missions.
2. How are satellite orbit maps created and updated?
Satellite orbit maps are generated using data collected from ground stations and space-based sensors. These data are processed and analyzed to determine the precise position and trajectory of each satellite. The maps are constantly updated as new data becomes available, ensuring their accuracy and relevance.
3. What are the limitations of satellite orbit maps?
While satellite orbit maps provide valuable information, they have certain limitations:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of orbit maps depends on the quality and frequency of data collection. Errors in data can lead to inaccuracies in the displayed information.
- Dynamic Nature of Orbits: Satellite orbits are constantly changing due to factors such as atmospheric drag, gravitational forces, and maneuvers. Orbit maps may not always reflect the most up-to-date information.
- Limited Information: Orbit maps typically focus on the orbital parameters of satellites, but they may not provide comprehensive information about their capabilities or missions.
Tips for Utilizing Satellite Orbit Maps
- Understand the Map’s Purpose: Before using a satellite orbit map, it’s crucial to understand its intended purpose and the type of information it provides.
- Familiarize Yourself with Key Elements: Learn the different elements of a satellite orbit map, such as orbit type, altitude, inclination, and orbital period.
- Use Multiple Resources: Compare information from different sources to ensure accuracy and gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Consider the Time Frame: Remember that satellite orbits are constantly changing. Consider the time frame of the data presented when interpreting the information.
Conclusion
Satellite orbit maps are indispensable tools for understanding and managing the ever-growing network of artificial objects in space. They provide a visual representation of the complex dance of satellites, enabling us to track their movements, predict their trajectories, and optimize their utilization. As we continue to explore and utilize space, the importance of these maps will only increase, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of our celestial highway.




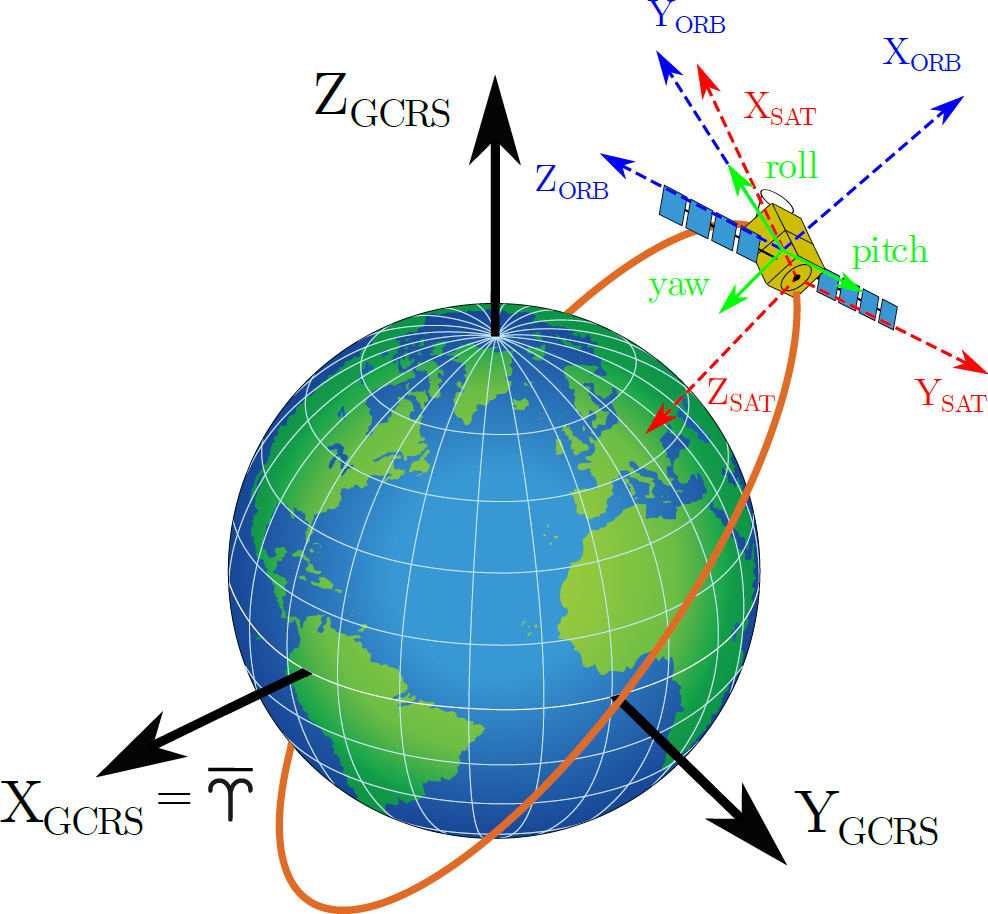
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Celestial Highway: Understanding Satellite Orbit Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!