Mapping the Past: A Journey Through the Geography of Old Palestine
Related Articles: Mapping the Past: A Journey Through the Geography of Old Palestine
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Past: A Journey Through the Geography of Old Palestine. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Past: A Journey Through the Geography of Old Palestine
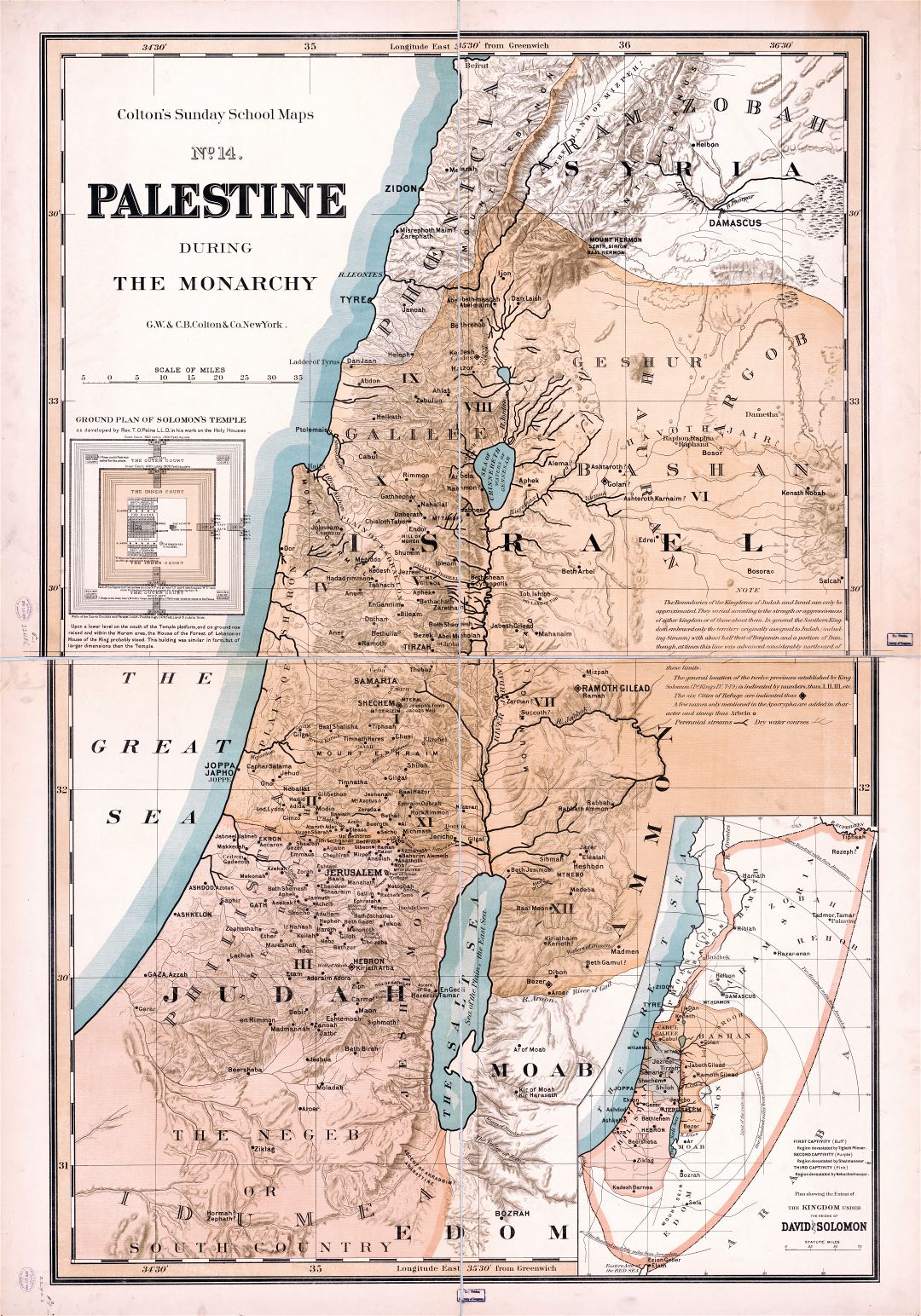
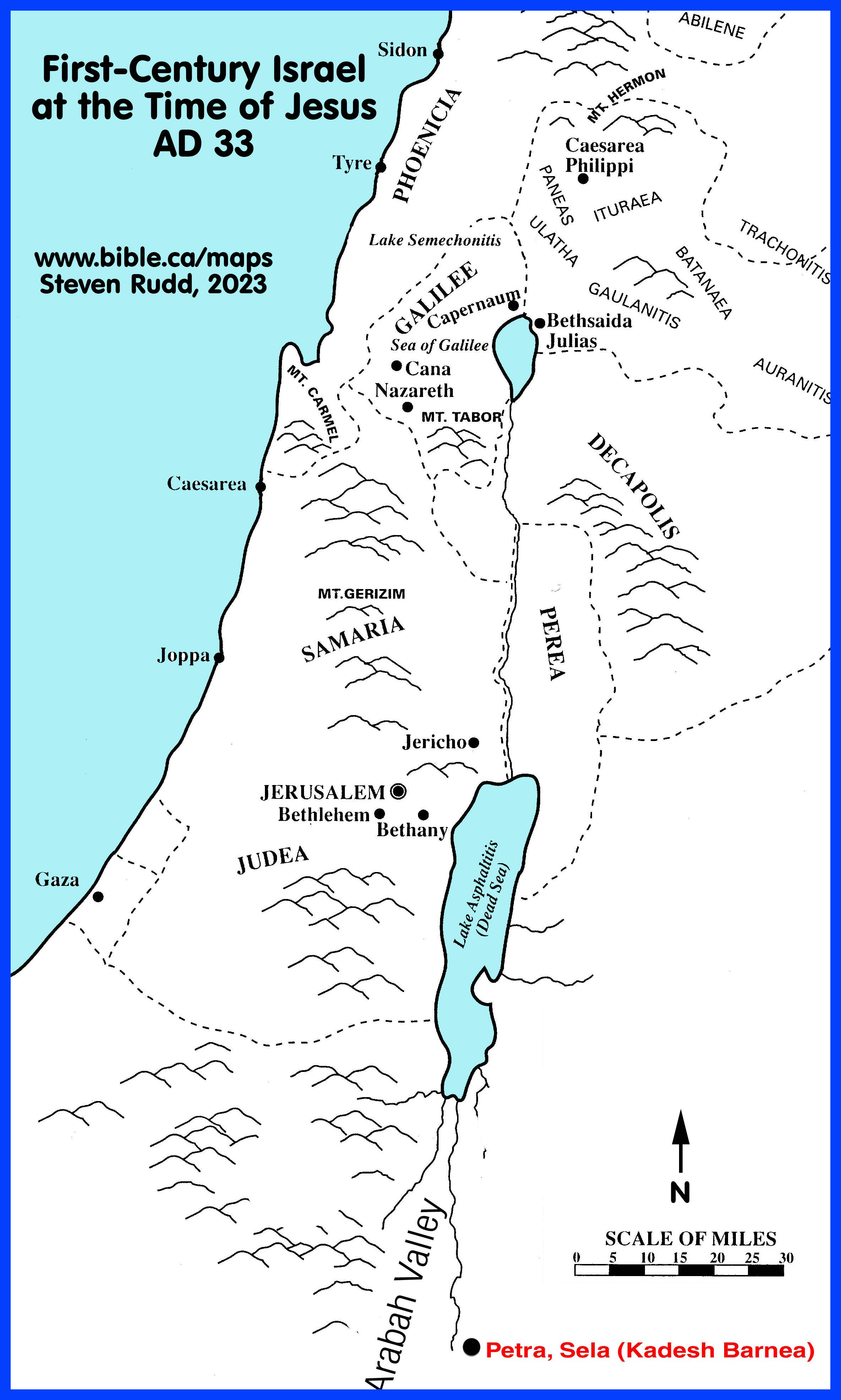
The land known as Palestine, a region steeped in history and religious significance, has witnessed countless transformations over millennia. Understanding its geographical evolution, particularly during its ancient and biblical periods, offers invaluable insights into its cultural, political, and religious development. This article delves into the complexities of mapping Old Palestine, highlighting its historical importance and the challenges inherent in reconstructing its past.
Defining the Boundaries:
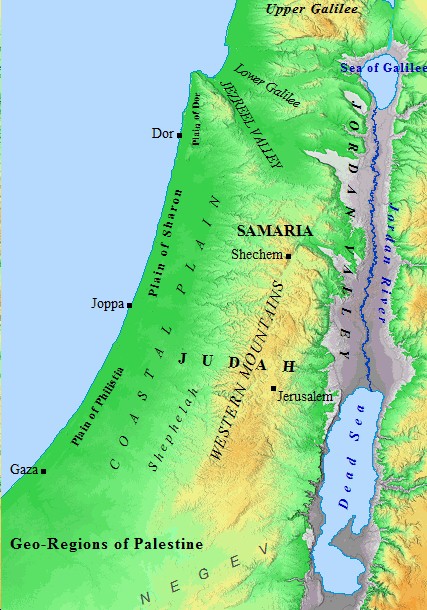
The term "Old Palestine" encompasses a broad swathe of land that has been subject to diverse interpretations and shifting borders throughout history. The region’s boundaries have been defined by various factors, including political control, religious affiliations, and geographical landmarks.
Early Interpretations:
Early maps, often found in biblical texts and ancient manuscripts, provide valuable glimpses into the perception of Palestine in antiquity. These depictions, often symbolic and lacking precise geographical accuracy, focused on key locations of religious and cultural significance. For instance, the "Tabula Peutingeriana," a Roman road map dating back to the 4th century CE, depicts Palestine as a narrow strip of land along the Mediterranean coast, highlighting major cities like Jerusalem, Caesarea Maritima, and Gaza.
The Roman Period and Beyond:
During the Roman period, Palestine’s geographical boundaries became more defined. The Roman province of Judea, established in 6 CE, encompassed the central region of Palestine, extending from the Mediterranean Sea to the Jordan River. This period saw the development of detailed maps, such as the "Madaba Map," a 6th-century mosaic map depicting the Holy Land with impressive accuracy. These maps, often created for administrative and military purposes, provided a more comprehensive understanding of the region’s topography, settlements, and infrastructure.
The Byzantine Period and the Rise of Pilgrimage:
The Byzantine period, marked by the rise of Christianity, witnessed a surge in pilgrimage to the Holy Land. This resulted in the creation of maps specifically designed for pilgrims, such as the "Itinerary of Bordeaux," a 4th-century travel guide describing the journey to Jerusalem. These maps, often incorporating religious symbolism and narratives, highlighted pilgrimage routes and key religious sites.
The Islamic Period and the Expansion of Cartography:
Following the Arab conquests of the 7th century, the Islamic world embraced cartography, producing highly detailed maps based on astronomical observations and mathematical calculations. These maps, often crafted for navigational purposes, provided a more precise understanding of Palestine’s geography, including its coastal regions, mountain ranges, and river systems.
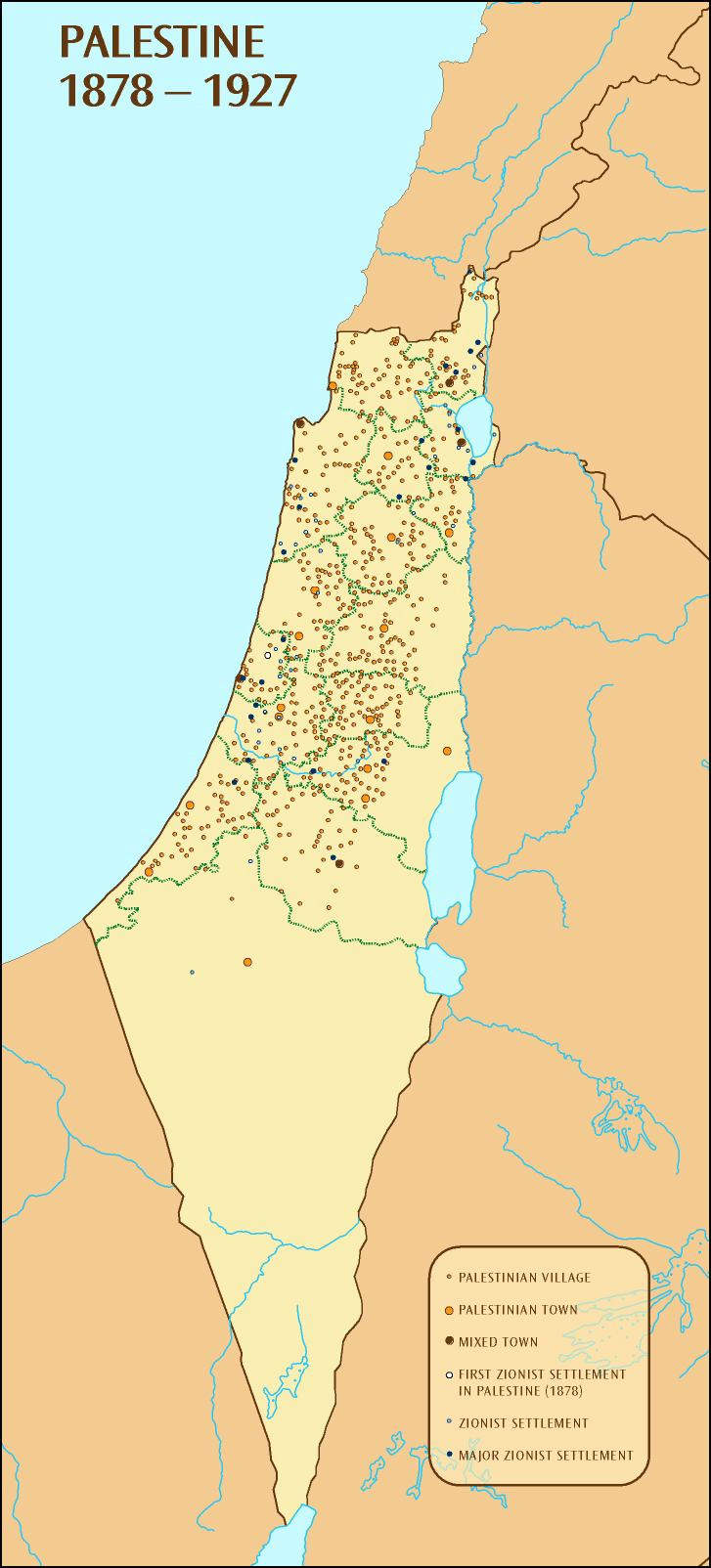
Modern Mapping and the Challenges of Reconstruction:
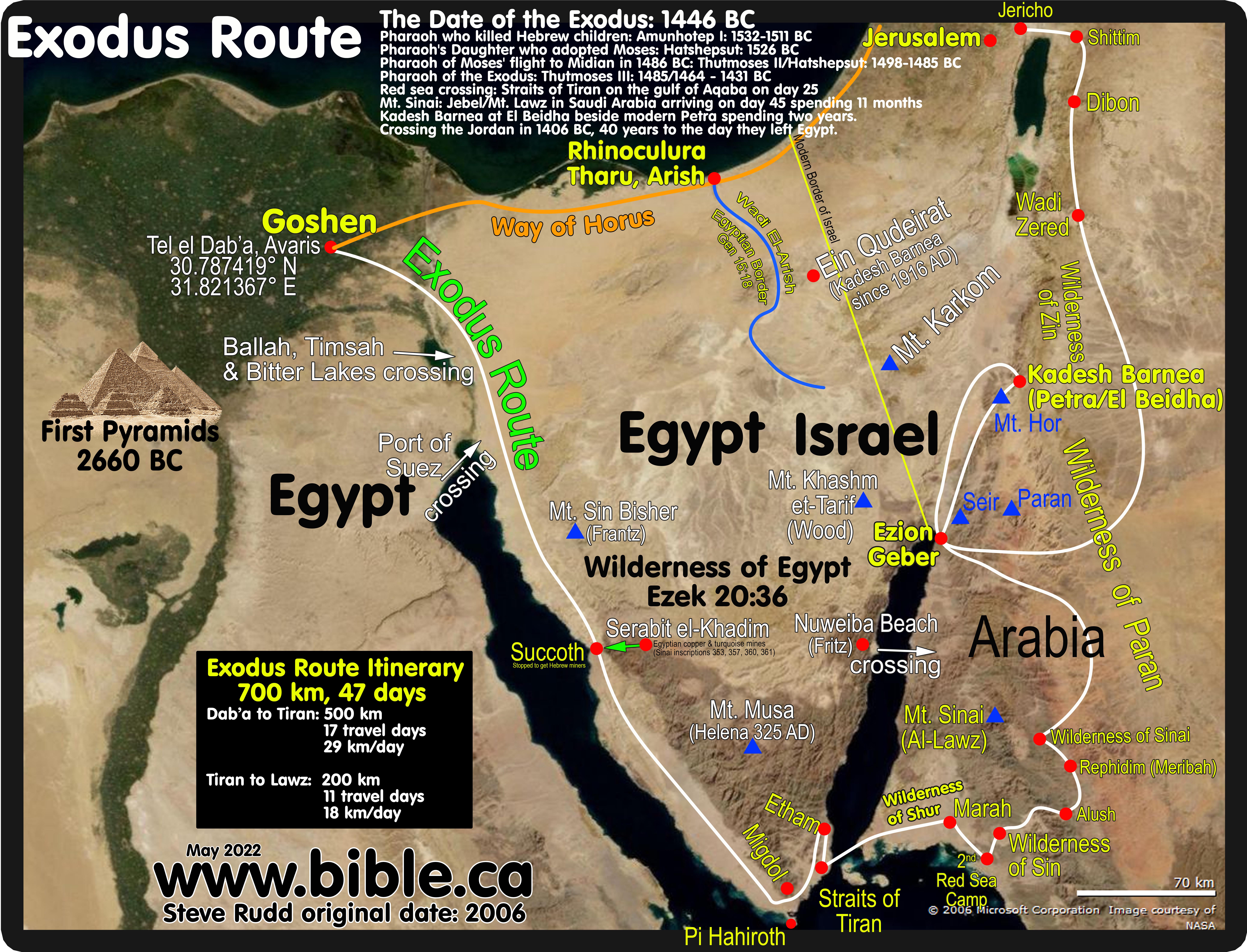
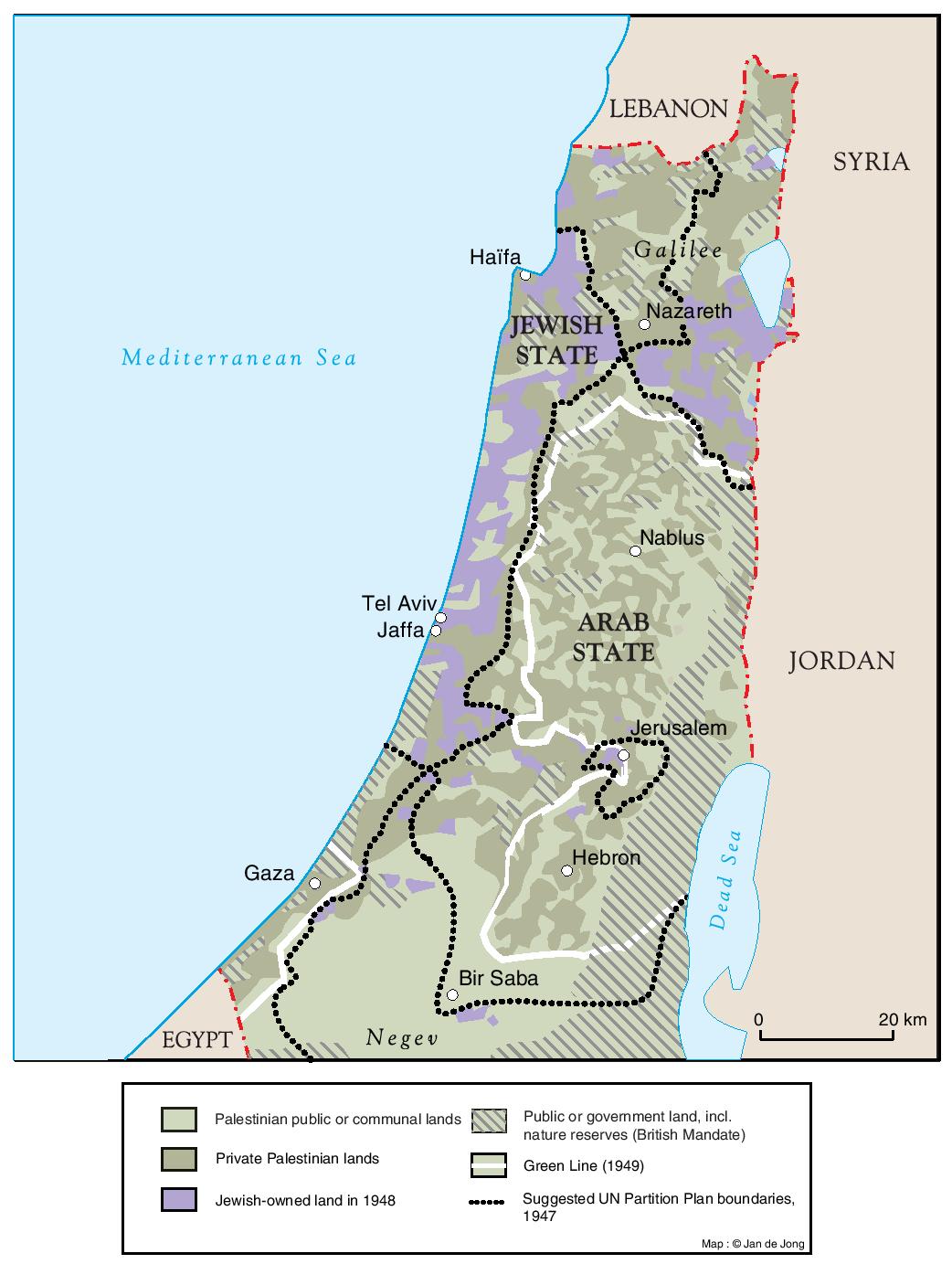
Modern mapping of Old Palestine relies on a multitude of sources, including archaeological evidence, historical texts, and comparative analysis of ancient maps. However, reconstructing the past poses significant challenges. The lack of precise geographical coordinates, the constant shifts in political boundaries, and the influence of religious narratives all contribute to the complexities of mapping Old Palestine.
The Importance of Mapping Old Palestine:
Despite these challenges, mapping Old Palestine remains a crucial endeavor for several reasons:
- Historical Understanding: Maps provide a visual framework for understanding the historical development of the region, including its political divisions, migration patterns, and cultural interactions.
- Archaeological Exploration: Maps serve as guides for archaeological investigations, helping to identify potential sites of interest and reconstruct past landscapes.
- Religious Studies: Maps play a vital role in understanding the geographical context of religious narratives, providing insights into the locations of significant events and the spatial dimensions of faith.
- Cultural Heritage: Maps contribute to the preservation and understanding of cultural heritage, highlighting the rich history and diverse traditions of the region.
FAQs by Map of Old Palestine:
Q: What is the most accurate map of Old Palestine?
A: There is no single "most accurate" map of Old Palestine. Different maps, created for specific purposes and using varying sources, offer distinct perspectives on the region’s geography. Modern maps, drawing upon archaeological evidence and historical texts, provide a more comprehensive understanding, but even they are subject to interpretation and ongoing research.
Q: How does the map of Old Palestine differ from modern maps?
A: Maps of Old Palestine differ from modern maps in several ways:
- Scale: Ancient maps often lacked the detailed scale of modern maps, focusing on key locations and routes rather than precise geographical measurements.
- Projection: Ancient maps employed different projection methods, resulting in distortions of shape and size compared to modern maps.
- Data Sources: Modern maps rely on advanced technologies and data sources, including satellite imagery and geographic information systems (GIS), which were not available in ancient times.
Q: What are the limitations of mapping Old Palestine?
A: Mapping Old Palestine is subject to several limitations:
- Incomplete Data: Archaeological evidence is often fragmented, and historical texts may be biased or incomplete, making it difficult to reconstruct the past with complete accuracy.
- Shifting Boundaries: Political boundaries have constantly shifted over time, making it challenging to define a consistent geographical framework for Old Palestine.
- Interpretations: Different scholars may interpret historical data and archaeological evidence in different ways, leading to variations in mapping and historical narratives.
Tips by Map of Old Palestine:
- Consult Multiple Sources: When studying maps of Old Palestine, consult a variety of sources, including archaeological reports, historical texts, and maps from different periods.
- Consider Context: Analyze maps within their historical and cultural context, understanding the motivations and biases of their creators.
- Engage with Specialists: Seek guidance from experts in archaeology, history, and cartography to deepen your understanding of the complexities of mapping Old Palestine.
Conclusion by Map of Old Palestine:
Mapping Old Palestine is an ongoing process of discovery and interpretation. By carefully analyzing historical maps, archaeological evidence, and textual sources, we can gain valuable insights into the region’s rich past. This knowledge serves not only to deepen our understanding of history but also to foster appreciation for the enduring cultural and religious significance of the land. As research continues, our understanding of Old Palestine will continue to evolve, revealing new layers of its fascinating and complex history.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Past: A Journey Through the Geography of Old Palestine. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!