Demography Unveiled: A Comprehensive Look at India’s Population Map
Related Articles: Demography Unveiled: A Comprehensive Look at India’s Population Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Demography Unveiled: A Comprehensive Look at India’s Population Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demography Unveiled: A Comprehensive Look at India’s Population Map
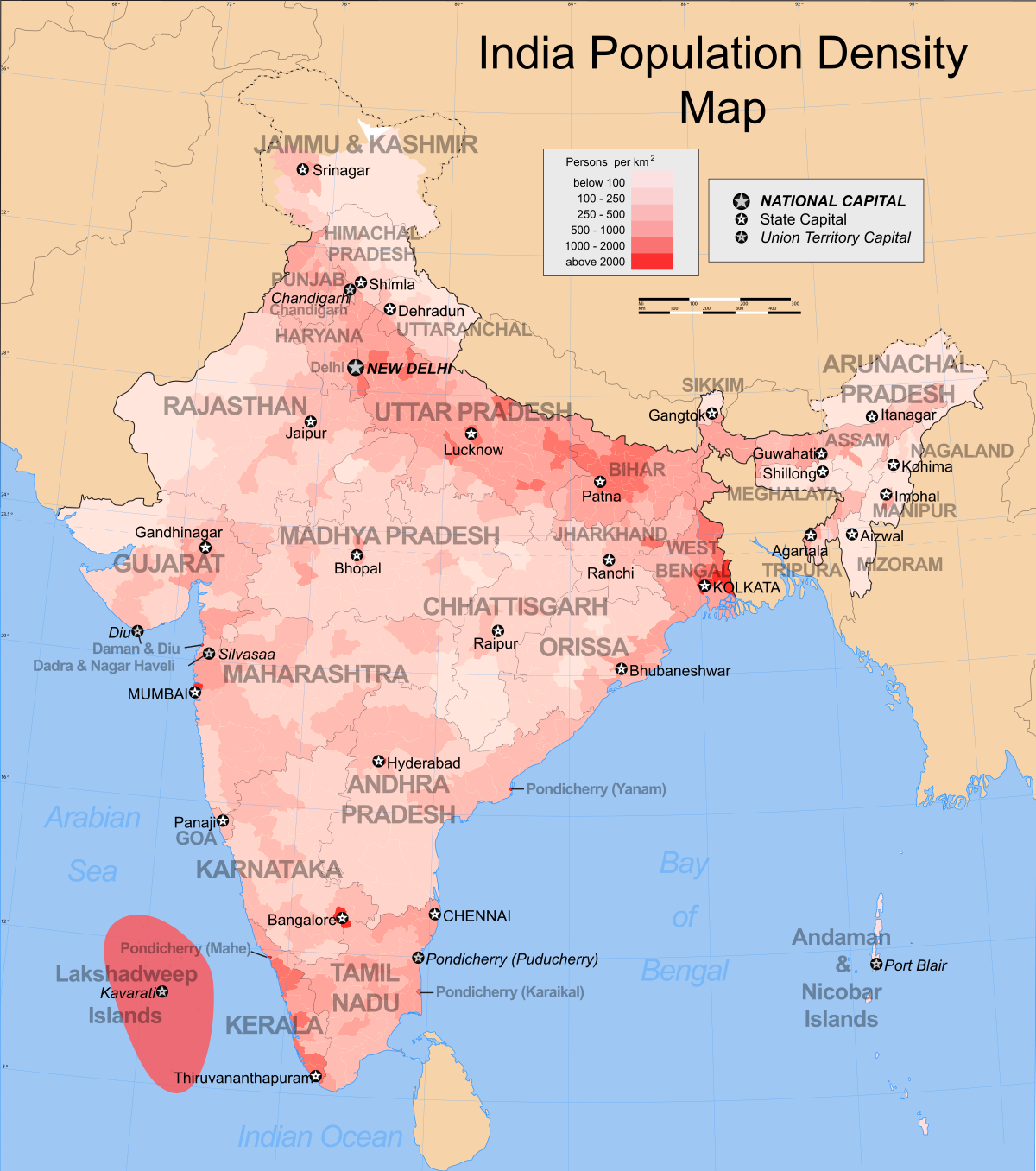
India, a land of diverse landscapes and cultures, is also home to the second largest population in the world. Understanding the distribution of this vast population is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and anyone interested in India’s development. This article delves into the intricacies of India’s population map, exploring its key features, underlying factors, and implications.
A Visual Representation of Human Geography
India’s population map is a powerful visual tool that reveals the complex spatial patterns of human settlement across the country. It provides a snapshot of population density, distribution, and growth trends, offering insights into the demographic dynamics that shape India’s social, economic, and environmental landscapes.
Key Features and Patterns
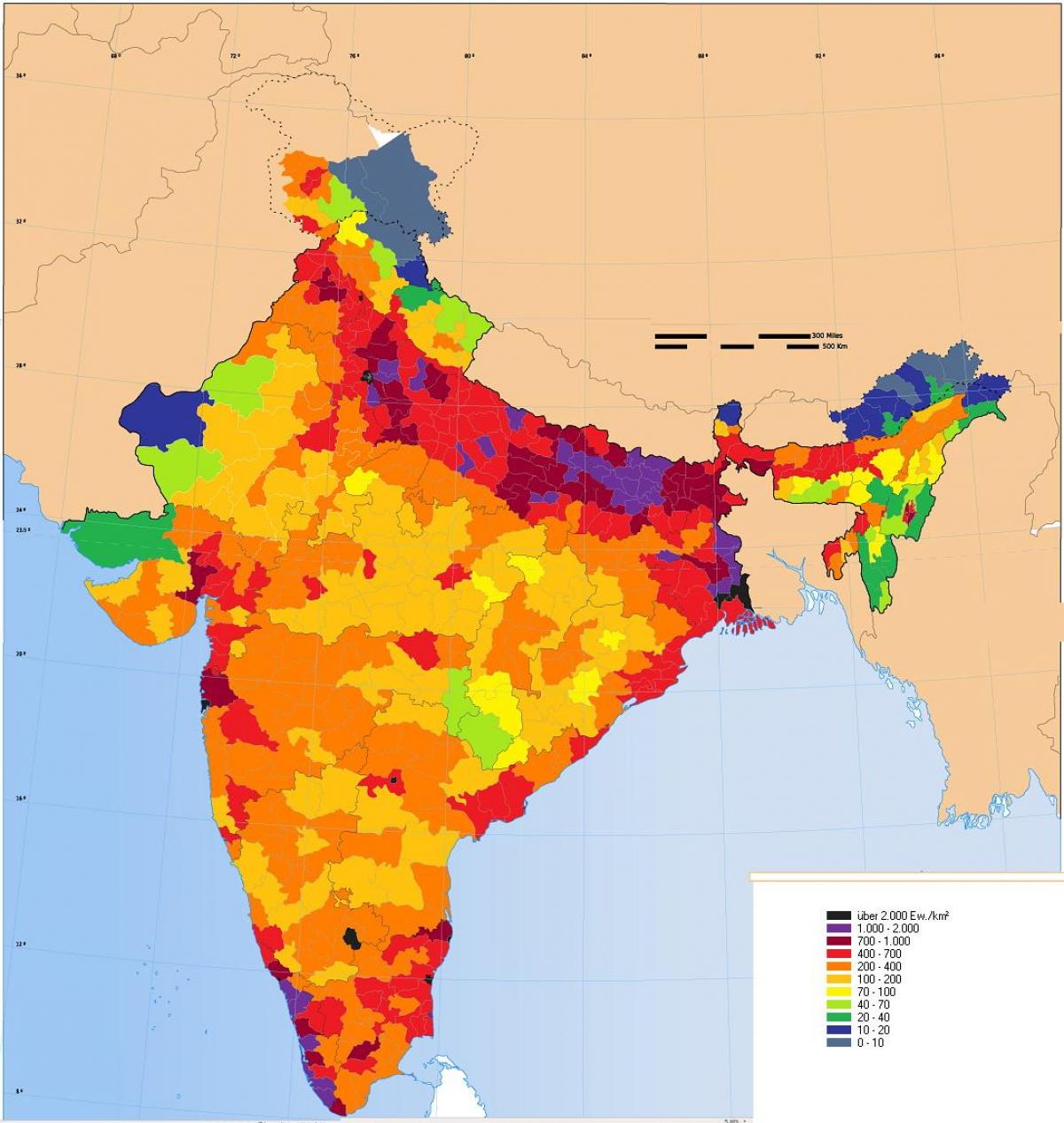
1. Densely Populated Regions: The map highlights areas of high population density, primarily concentrated along the fertile plains of the Ganges and Indus river valleys, the coastal regions, and major urban centers. These areas are often characterized by intensive agricultural activity, thriving industries, and robust infrastructure.
2. Sparsely Populated Regions: Conversely, the map also reveals regions with low population densities, particularly in the mountainous terrains of the Himalayas, the arid regions of Rajasthan, and the sparsely populated Northeast. These regions often face challenges related to accessibility, resource scarcity, and limited economic opportunities.
3. Urbanization Trends: The map clearly demonstrates the rapid pace of urbanization in India. Major metropolitan cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, and Bengaluru are depicted as population hubs, attracting migrants from rural areas seeking better job prospects and quality of life.
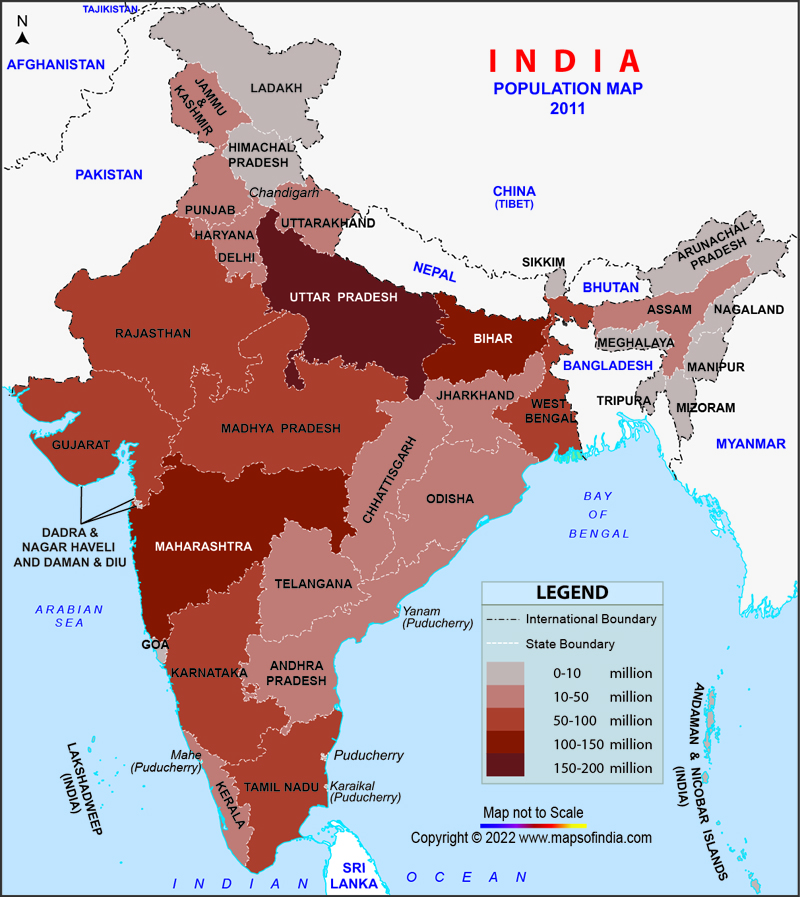
4. Regional Variations: India’s population map reveals significant regional variations in demographic characteristics. For instance, the northern states of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar have higher population densities than the southern states of Kerala and Tamil Nadu. These differences are influenced by factors like historical settlement patterns, fertility rates, and economic development.
Factors Shaping India’s Population Map
1. Historical Factors: India’s population distribution is deeply rooted in its historical past. The Indus Valley Civilization, the Mughal Empire, and British colonial rule have all left their mark on the country’s population dynamics.
2. Geographic Factors: India’s diverse topography, ranging from snow-capped mountains to fertile plains, plays a crucial role in shaping population distribution. Access to water resources, arable land, and natural resources heavily influences settlement patterns.
3. Socio-Economic Factors: Economic opportunities, access to education and healthcare, and social norms all contribute to population distribution. Rural-urban migration, driven by economic disparities and the lure of better prospects in urban areas, significantly alters population density.
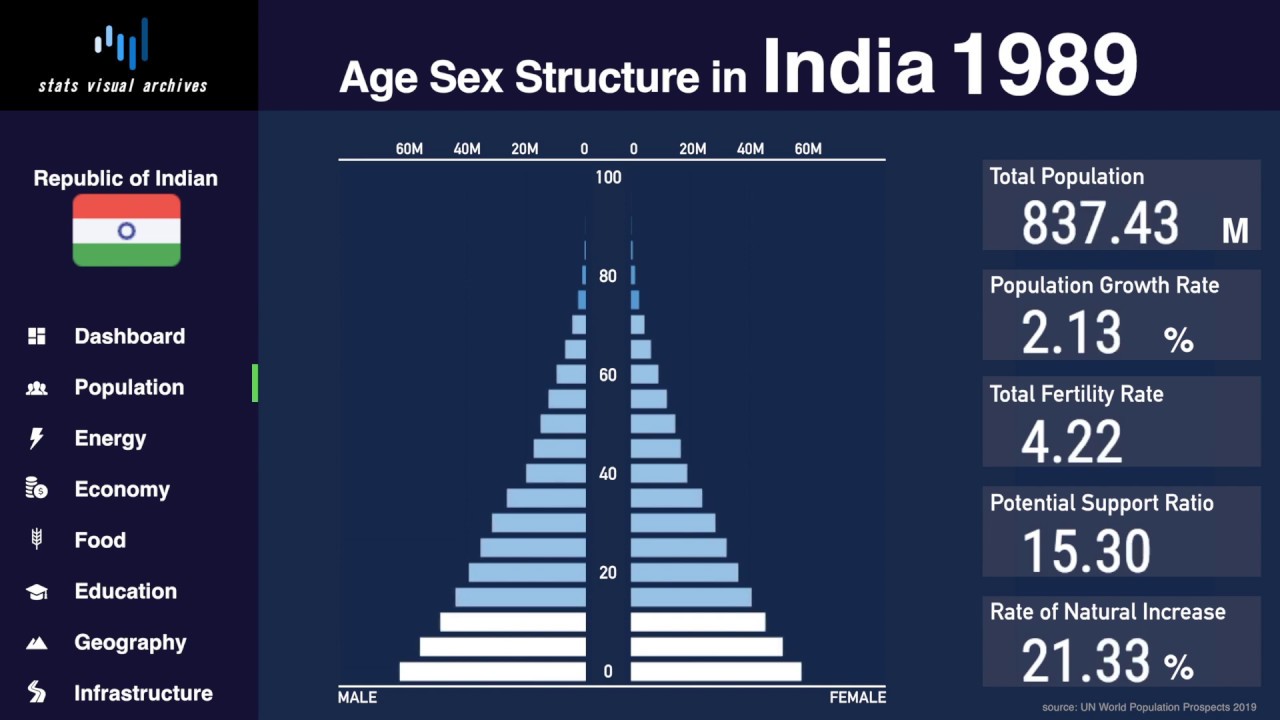
4. Demographic Factors: Factors like fertility rates, mortality rates, and age structure also influence population distribution. Lower fertility rates in urban areas and higher fertility rates in rural areas contribute to regional differences in population growth.
Implications and Importance
1. Resource Allocation: Understanding population distribution is crucial for efficient resource allocation. Government agencies can leverage population data to target development programs and allocate resources effectively, ensuring equitable access to services and opportunities.
2. Infrastructure Development: Population maps guide infrastructure development, ensuring that transportation, communication, and energy infrastructure are strategically placed to cater to the needs of densely populated areas and support economic growth.
3. Urban Planning: As urbanization accelerates, population maps become critical for urban planning. They help city planners understand population density, growth trends, and spatial patterns to create sustainable and livable urban environments.
4. Disaster Management: In the event of natural disasters, population maps provide valuable information for emergency response and evacuation planning. They help identify vulnerable areas and ensure efficient distribution of relief resources.
5. Social and Economic Development: Population distribution insights are crucial for understanding social and economic dynamics. They help policymakers address issues like poverty, inequality, and access to education and healthcare, contributing to inclusive and sustainable development.
FAQs about India’s Population Map
Q: What is the most densely populated state in India?
A: The most densely populated state in India is Bihar, followed by West Bengal and Uttar Pradesh.
Q: How often is India’s population map updated?
A: India’s population map is updated every ten years, coinciding with the national census.
Q: What are the limitations of India’s population map?
A: While a valuable tool, India’s population map has limitations. It provides a snapshot of population distribution at a specific point in time, and does not capture dynamic changes like migration or seasonal variations.
Q: How can I access India’s population map?
A: India’s population map is publicly available on the website of the Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India.
Tips for Using India’s Population Map
1. Explore the map’s different layers: The map often includes various layers, such as population density, age structure, and literacy rates. Explore these layers to gain deeper insights into specific demographic characteristics.
2. Compare data across different time periods: Use the map to compare population distribution data over time to understand trends and patterns of change.
3. Combine the map with other data sources: Integrate population data with other relevant data sources, such as economic indicators or environmental data, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing population distribution.
4. Use the map for policy analysis: Analyze population distribution data to inform policy decisions and ensure that development programs are targeted effectively.
Conclusion
India’s population map is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s demographic landscape. It provides insights into population distribution, growth trends, and the factors that shape these patterns. By leveraging the information contained in this map, policymakers, researchers, and citizens alike can contribute to sustainable development, equitable resource allocation, and a more informed understanding of India’s complex social and economic dynamics. As India continues to grow and evolve, the population map will remain a crucial resource for navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demography Unveiled: A Comprehensive Look at India’s Population Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!