Delving into the Depths of Heat Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Delving into the Depths of Heat Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Depths of Heat Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Depths of Heat Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

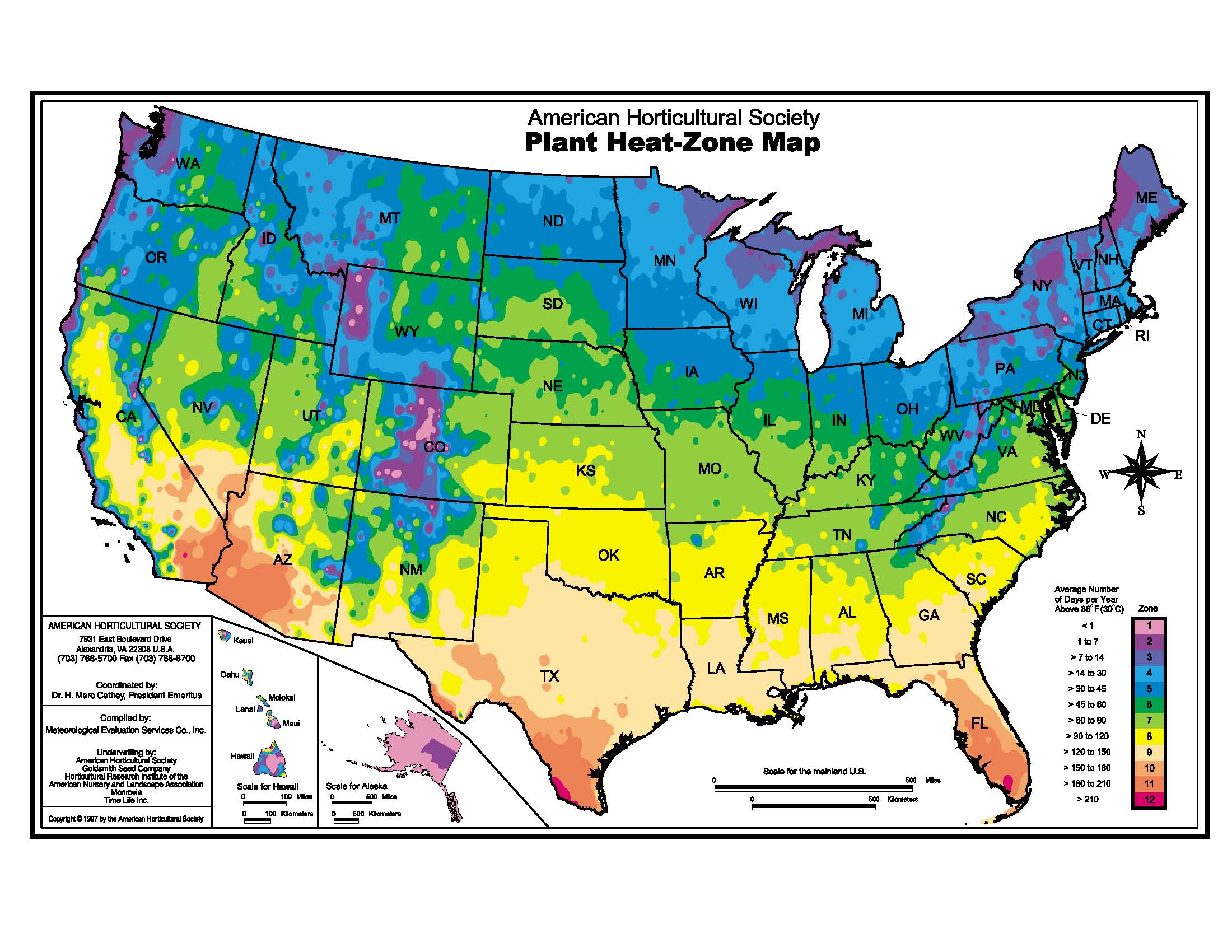
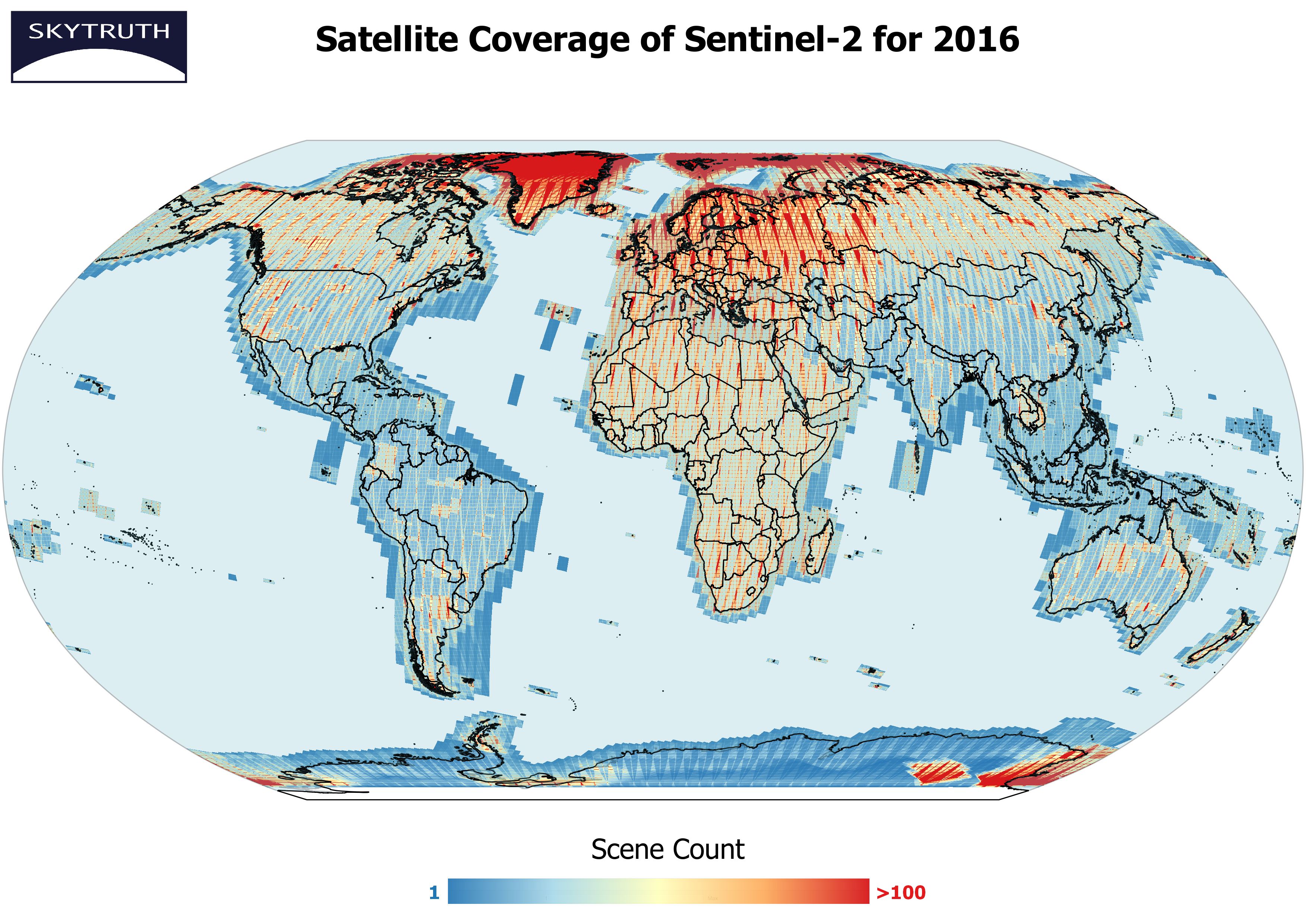
Heat zone maps, also known as heat maps, are powerful visual tools that represent data in a clear and easily understandable way. They use color gradients to depict the intensity of a particular phenomenon, allowing for quick identification of areas with the highest and lowest concentrations. This technique finds application in various fields, from marketing and healthcare to urban planning and environmental studies.
Understanding the Essence of Heat Zone Maps
At its core, a heat zone map translates numerical data into a visual representation, highlighting areas of high and low activity. Imagine a map of a city where the density of restaurants is represented by varying shades of red. The areas with the deepest red indicate a high concentration of restaurants, while lighter shades denote fewer establishments. This visual interpretation allows for a quick grasp of the distribution pattern, making it easier to identify clusters, trends, and anomalies.
The Mechanics of Creating a Heat Zone Map
The creation of a heat zone map involves several key steps:
-
Data Collection: The process begins with gathering relevant data. This could include anything from sales figures and customer demographics to traffic patterns and pollution levels. The accuracy and comprehensiveness of the data directly influence the reliability of the map.
-
Data Processing: Once collected, the data needs to be processed and organized. This might involve cleaning, filtering, and aggregating the data to ensure consistency and relevance.
-
Map Generation: The processed data is then used to generate the heat zone map. This step involves assigning a color gradient to the data, with darker shades representing higher values and lighter shades representing lower values. Various software tools are available for this purpose, allowing users to customize the map according to their specific needs.
-
Visualization: The final heat zone map is then visualized, often overlaid on a geographical base map. This allows for easy interpretation and analysis of the data, highlighting areas of interest and providing insights into the distribution patterns.
Diverse Applications of Heat Zone Maps
Heat zone maps find their way into a diverse range of applications, each offering unique insights and benefits:
1. Marketing and Sales:
- Customer Segmentation: Heat zone maps can be used to identify areas with high customer density, allowing businesses to target their marketing efforts more effectively.
- Product Placement: Analyzing sales data through heat maps helps retailers optimize product placement and inventory management, ensuring maximum visibility and sales.
- Campaign Effectiveness: Heat maps can visualize the geographical impact of marketing campaigns, enabling businesses to track their reach and identify areas for improvement.
2. Healthcare and Epidemiology:
- Disease Spread Tracking: Heat maps are crucial in tracking the spread of infectious diseases, identifying hotspots and facilitating targeted interventions.
- Resource Allocation: By highlighting areas with high demand for healthcare services, heat maps guide resource allocation, ensuring optimal service delivery.
- Public Health Planning: Understanding the distribution of health risks and access to healthcare facilities through heat maps informs public health policies and initiatives.
3. Urban Planning and Development:
- Traffic Flow Optimization: Heat maps visualize traffic congestion points, enabling planners to implement solutions like traffic light adjustments or road infrastructure improvements.
- Urban Development Planning: By identifying areas with high population density or economic activity, heat maps inform urban development strategies, guiding infrastructure projects and community development initiatives.
- Crime Prevention: Heat maps can visualize crime hotspots, allowing law enforcement agencies to allocate resources effectively and implement targeted crime prevention strategies.
4. Environmental Studies and Sustainability:
- Pollution Monitoring: Heat maps visualize pollution levels, identifying areas with high concentrations and enabling targeted environmental interventions.
- Climate Change Impact: Heat maps can depict the impact of climate change on various environmental factors, such as temperature, precipitation, and sea level rise, informing adaptation strategies.
- Resource Management: By visualizing the distribution of natural resources, heat maps aid in their efficient management and sustainable utilization.
FAQs About Heat Zone Maps
1. What are the advantages of using heat zone maps?
Heat zone maps offer several advantages:
- Visual Clarity: They present complex data in a visually intuitive way, making it easier to understand and interpret.
- Data Exploration: Heat maps allow for the identification of patterns, trends, and anomalies within data, providing valuable insights.
- Decision Support: They provide a visual framework for informed decision-making, supporting strategic planning in various fields.
- Effective Communication: Heat maps are a powerful tool for communicating complex data to a wider audience, fostering understanding and collaboration.
2. What are the limitations of heat zone maps?
While powerful, heat zone maps do have limitations:
- Data Dependence: The accuracy of the map relies heavily on the quality and comprehensiveness of the underlying data.
- Oversimplification: Heat maps can sometimes oversimplify complex phenomena, potentially overlooking important nuances.
- Interpretation Bias: The interpretation of heat maps can be subjective, leading to potentially misleading conclusions.
3. How can I create a heat zone map?
Various software tools are available for creating heat zone maps. Popular options include:
- GIS software: ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo are powerful tools for creating and analyzing spatial data, including heat zone maps.
- Data visualization software: Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio offer intuitive interfaces for creating interactive heat zone maps.
- Online mapping tools: Websites like Google Maps and Leaflet provide tools for creating basic heat zone maps.
Tips for Creating Effective Heat Zone Maps
- Choose the Right Data: Select data relevant to your objectives and ensure its accuracy and comprehensiveness.
- Define Clear Boundaries: Set appropriate geographic boundaries for the map to focus on the relevant area.
- Optimize Color Scheme: Select a color gradient that effectively highlights areas of high and low values, avoiding confusing or misleading interpretations.
- Include Relevant Context: Add labels, legends, and other contextual information to enhance the map’s clarity and understanding.
- Consider Interactivity: Explore interactive map features like zoom, pan, and data filtering to allow for deeper exploration and analysis.
Conclusion: The Power of Visual Representation
Heat zone maps are a powerful tool for visualizing data and extracting meaningful insights. Their ability to translate complex data into easily understandable visual representations makes them valuable across diverse fields, from marketing and healthcare to urban planning and environmental studies. By leveraging the power of visual representation, heat zone maps empower informed decision-making, fostering progress and innovation in various sectors.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Depths of Heat Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!