Decoding the Whirlwind: Understanding Tornado Frequency Maps
Related Articles: Decoding the Whirlwind: Understanding Tornado Frequency Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Decoding the Whirlwind: Understanding Tornado Frequency Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Decoding the Whirlwind: Understanding Tornado Frequency Maps
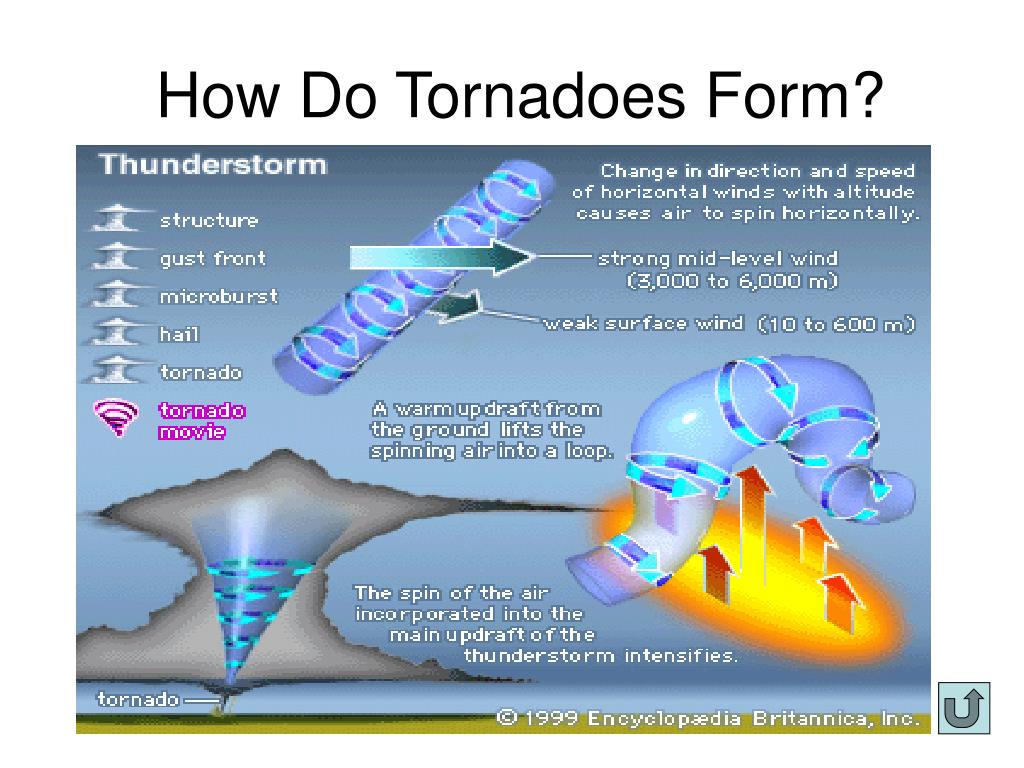
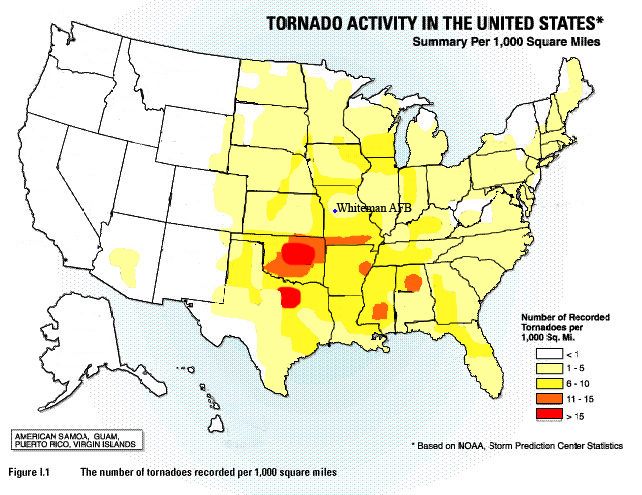
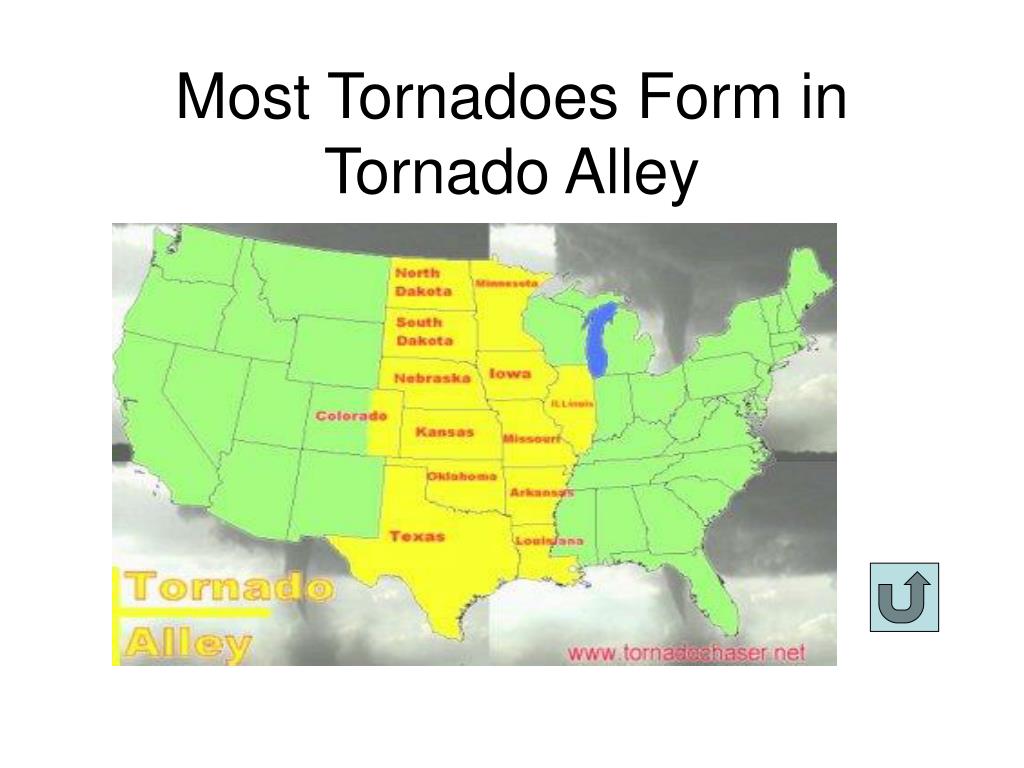
Tornadoes, nature’s violent and unpredictable dance, are a formidable force capable of causing widespread destruction and loss of life. While their occurrence is often localized and unpredictable, understanding their frequency and patterns is crucial for effective disaster preparedness and mitigation. This is where tornado frequency maps come into play, offering a visual representation of historical tornado activity, providing valuable insights into the likelihood of future events.
A Visual Guide to Tornado Risk:
Tornado frequency maps, often referred to as tornado climatology maps, are powerful tools for visualizing historical tornado data. They typically depict the average number of tornadoes occurring within a specific geographic area over a set period, often spanning decades. These maps utilize color gradients or symbols to represent different frequency levels, allowing for a quick and intuitive understanding of tornado risk across regions.
The Data Behind the Map:
The creation of a reliable tornado frequency map hinges on a robust database of historical tornado occurrences. This data is painstakingly collected and verified by meteorological agencies, typically including:
- Location: Precise coordinates of the tornado’s path, including its starting and ending points.
- Date and Time: The exact date and time of the tornado’s formation and duration.
- Intensity: The Fujita scale (F-scale) or Enhanced Fujita scale (EF-scale) rating, which classifies tornado intensity based on wind speed and damage inflicted.
- Path Length and Width: The distance and width of the tornado’s path across the landscape.
Interpreting the Visual Landscape:
Once compiled, this data is processed and analyzed to generate the frequency map. Areas shaded in darker hues or marked with denser symbols generally indicate a higher historical frequency of tornadoes. Conversely, lighter shades or sparser symbols represent regions with lower tornado occurrence.
Beyond the Numbers: Understanding the Context:
While tornado frequency maps provide a valuable overview of historical activity, it’s crucial to remember that they represent averages. They do not predict future events with certainty. Other factors, such as meteorological conditions, terrain, and the presence of specific weather patterns, can significantly influence the likelihood and intensity of tornadoes in a given location.
Benefits and Applications of Tornado Frequency Maps:
Tornado frequency maps serve as indispensable tools for various stakeholders:
- Emergency Management Agencies: They provide valuable data for planning and executing emergency response protocols, including evacuation plans, resource allocation, and community outreach programs.
- Insurance Companies: Maps aid in risk assessment and pricing of insurance policies, particularly for property and casualty insurance.
- Urban Planners and Developers: Maps help in identifying areas prone to tornado activity, informing decisions on building codes, infrastructure development, and land use planning.
- Educational Institutions: Maps facilitate the understanding of weather patterns and the importance of tornado preparedness, promoting public awareness and safety.
- Researchers and Scientists: Maps serve as a foundation for further research into tornado dynamics, climate change impacts, and the development of improved forecasting models.
Addressing Common Questions:
Q: How often do tornadoes occur in a specific location?
A: Tornado frequency maps can help answer this question by providing historical averages for the area in question. However, it’s important to note that these are averages and do not guarantee future occurrences.
Q: Are tornado frequency maps accurate predictors of future events?
A: While maps offer valuable insights into historical patterns, they are not deterministic predictors of future events. Factors like weather conditions and terrain can significantly influence tornado formation and intensity.
Q: How are tornado frequency maps updated?
A: Tornado frequency maps are typically updated periodically, often every few years, to incorporate new data and reflect changes in tornado activity.
Q: What are the limitations of tornado frequency maps?
A: Tornado frequency maps are based on historical data, which may not fully capture the complexities of tornado formation and behavior. They do not account for real-time weather conditions or other factors that could influence tornado occurrence.
Tips for Utilizing Tornado Frequency Maps:
- Consider the timeframe: Pay attention to the time period covered by the map, as historical data can vary significantly depending on the duration.
- Look for trends: Analyze the map for patterns of tornado activity, identifying areas with higher or lower frequencies and potential hot spots.
- Consult other resources: Combine information from tornado frequency maps with other meteorological data, such as weather forecasts and radar images, for a more comprehensive understanding of potential risks.
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of weather updates and warnings, as real-time information is crucial for making informed decisions during severe weather events.
Conclusion:
Tornado frequency maps are powerful tools for visualizing historical tornado activity and understanding the potential risks associated with these destructive forces. By providing a visual representation of average tornado occurrence, they serve as valuable resources for disaster preparedness, risk assessment, and informed decision-making. While they do not predict future events with certainty, they offer valuable insights into patterns and trends, ultimately contributing to safer communities and reduced vulnerability to tornado threats. As our understanding of tornado dynamics evolves, so too will the accuracy and sophistication of these maps, further strengthening our ability to mitigate the impacts of these powerful weather events.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding the Whirlwind: Understanding Tornado Frequency Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!