Charting the West: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of the Western World
Related Articles: Charting the West: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of the Western World
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the West: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of the Western World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the West: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of the Western World

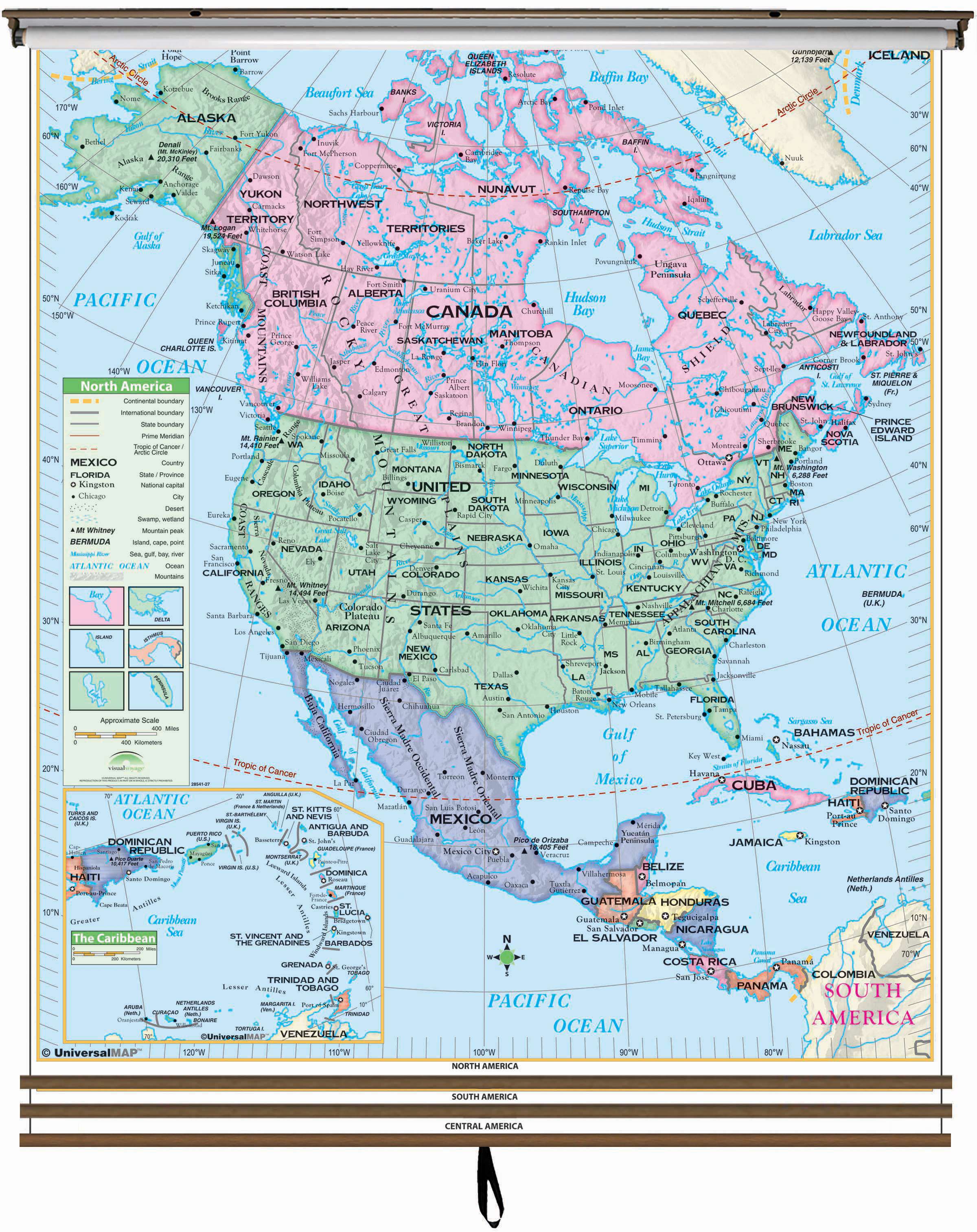
The map of the Western World, a geographical construct encompassing Europe, North America, and parts of South America, is a vital tool for understanding history, culture, and global dynamics. This article delves into the intricacies of this map, exploring its historical evolution, geographical components, cultural significance, and its enduring importance in the modern world.
Defining the Western World:
The term "Western World" is not a rigid geographical designation but rather a cultural and historical construct. It encompasses regions that share commonalities in their political, economic, and cultural development, often traced back to ancient Greece and Rome. While the boundaries are fluid, the Western World is generally understood to include:
- Europe: From the Atlantic Ocean to the Ural Mountains, encompassing a diverse range of nations with distinct histories and cultures.
- North America: Primarily encompassing the United States and Canada, with cultural and political ties deeply intertwined with Europe.
- Parts of South America: Notably, countries like Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, influenced by European colonization and immigration.
Historical Evolution:
The map of the Western World is not static. It has evolved over centuries, shaped by historical events and shifts in power dynamics. Key milestones include:
- Ancient Greece and Rome: The foundations of Western civilization, including democracy, philosophy, law, and architecture, were laid in ancient Greece and Rome. Their influence spread throughout Europe and beyond, leaving a lasting mark on Western culture.
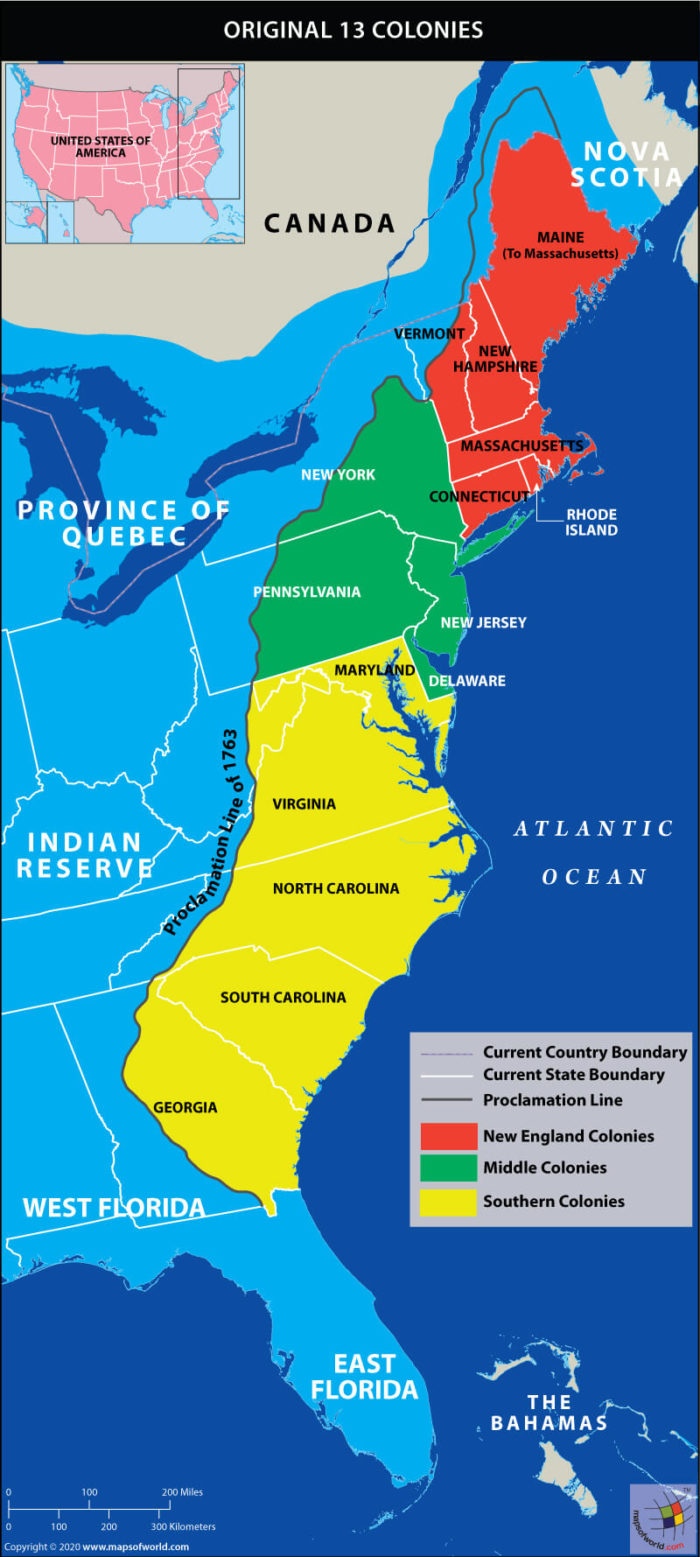
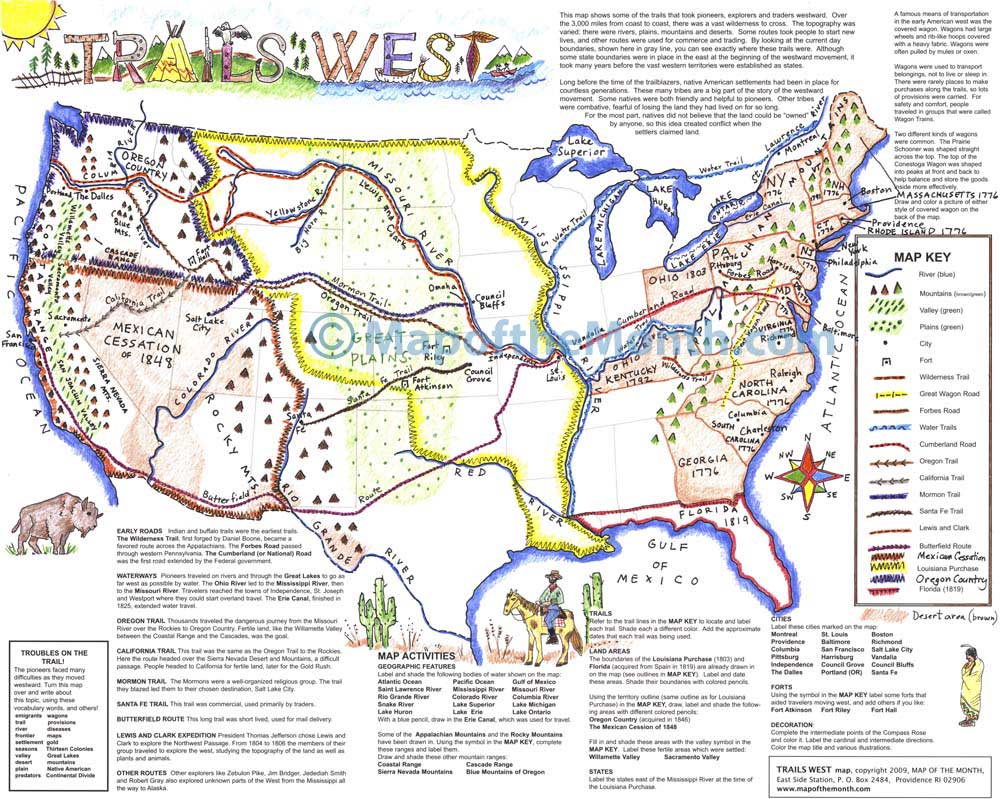
- The Age of Exploration: From the 15th century onward, European powers embarked on voyages of discovery, expanding their influence and trade networks across the globe. This led to the colonization of North and South America, shaping the modern map of the Western World.
- The Industrial Revolution: Beginning in the 18th century, the Industrial Revolution transformed Europe and North America, leading to rapid urbanization, technological advancement, and economic growth. It also contributed to the rise of Western dominance in global affairs.
- The Cold War: The 20th century witnessed a geopolitical rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, shaping the map of the Western World and its relationship with other regions. The fall of the Soviet Union in 1991 marked a significant shift in the global power structure.
Geographical Components:
The map of the Western World encompasses a wide range of geographical features, each contributing to the region’s diversity and complexity:
- Mountains: From the Alps and Pyrenees in Europe to the Rockies in North America, mountain ranges have historically shaped human settlement patterns, trade routes, and cultural identities.
- Rivers: The Rhine, Danube, Mississippi, and St. Lawrence rivers have played crucial roles in transportation, agriculture, and urban development, connecting different regions and facilitating economic growth.
- Seas and Oceans: The Atlantic Ocean has served as a vital trade route and a bridge between Europe and North America, while the Mediterranean Sea has been a cradle of civilization and a crossroads of cultures.
- Climate: The Western World experiences a wide range of climates, from the temperate regions of Western Europe to the frigid Arctic in North America. This diversity has influenced agricultural practices, urban development, and cultural traditions.
Cultural Significance:
The Western World is renowned for its rich cultural heritage, shaped by centuries of artistic, literary, scientific, and philosophical achievements:
- Art and Architecture: From the Renaissance masterpieces of Italy to the Gothic cathedrals of France and the modern skyscrapers of New York City, the Western World boasts a diverse and influential artistic tradition.
- Literature: The Western canon of literature includes works by Shakespeare, Dante, Cervantes, and countless other literary giants, shaping the world’s understanding of human nature, society, and history.
- Music: From classical music to jazz, rock, and pop, the Western World has contributed significantly to the global music landscape, influencing musical styles and trends worldwide.
- Philosophy: Western philosophy, rooted in ancient Greece, has explored fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, morality, and politics, shaping intellectual discourse and cultural values.
Enduring Importance:
The map of the Western World remains a crucial tool for understanding global affairs in the 21st century. Its historical legacy, cultural influence, and economic power continue to shape international relations, technological advancements, and cultural trends.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the defining characteristics of the Western World?
A: The Western World is characterized by its shared historical roots in ancient Greece and Rome, its emphasis on individualism and democracy, its embrace of scientific inquiry and technological innovation, and its dominant role in global affairs for centuries.
Q: How has the Western World influenced other regions?
A: The Western World has had a profound impact on other regions through colonization, trade, and cultural exchange. Its ideas, institutions, and technological advancements have shaped the development of many societies around the world.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the Western World today?
A: The Western World faces a range of challenges, including economic inequality, political polarization, environmental degradation, and the rise of new geopolitical powers.
Q: Is the Western World in decline?
A: The question of whether the Western World is in decline is a complex one. While its dominance in global affairs has diminished, it remains a significant player in the world, and its cultural influence continues to be felt worldwide.
Tips for Understanding the Map of the Western World:
- Study historical maps: Examining historical maps can provide valuable insights into how the map of the Western World has evolved over time.
- Explore cultural landmarks: Visiting historical sites, museums, and art galleries can offer a deeper understanding of the region’s cultural heritage.
- Engage with current events: Following news and current affairs related to the Western World can help to understand its role in global affairs.
- Read historical and contemporary literature: Engaging with works by Western authors can provide a nuanced perspective on the region’s history, culture, and values.
Conclusion:
The map of the Western World, while a complex and evolving construct, offers a valuable framework for understanding the history, culture, and global dynamics of this influential region. By appreciating its historical evolution, geographical components, cultural significance, and enduring importance, we can gain a deeper understanding of the world we live in and the forces that shape it.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the West: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of the Western World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!