A Journey Through the Redwood Forests of California: A Map to Understanding These Giants
Related Articles: A Journey Through the Redwood Forests of California: A Map to Understanding These Giants
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through the Redwood Forests of California: A Map to Understanding These Giants. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through the Redwood Forests of California: A Map to Understanding These Giants
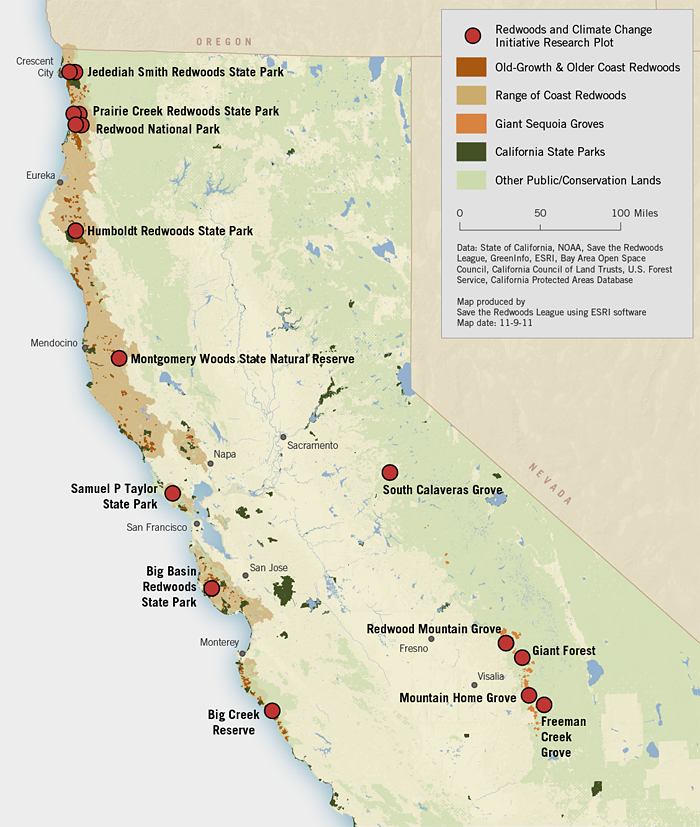
The redwood forests of California, home to the tallest trees on Earth, are a testament to the awe-inspiring power of nature. These ancient giants, with their towering heights and vibrant ecosystems, offer a unique and invaluable experience for visitors and researchers alike. Understanding the geography of these forests, their diverse inhabitants, and the threats they face is crucial for appreciating their significance and ensuring their continued existence.
A Map to the Heart of the Redwoods:
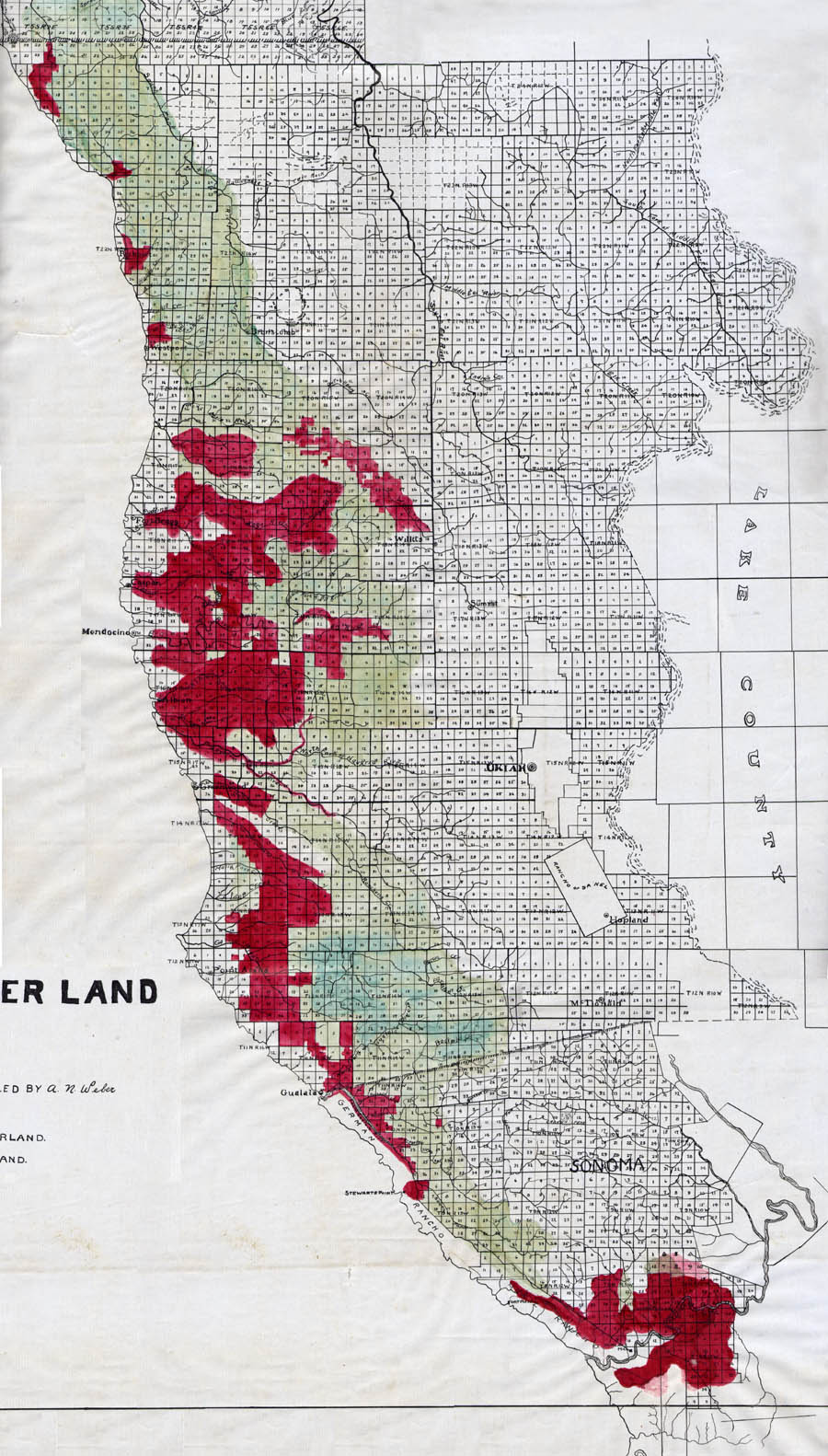
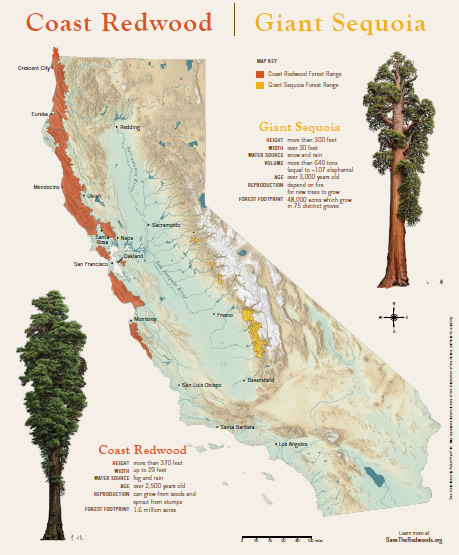
The redwood forests of California are primarily located along the state’s Pacific coast, stretching from the Oregon border to the Big Sur region. This narrow band, known as the "Redwood Coast," is characterized by its temperate climate, abundant rainfall, and fog, all of which contribute to the growth and survival of these magnificent trees.
Exploring the Redwood Regions:
The redwood forests are divided into two main regions:
- The Redwood National and State Parks: This complex, encompassing over 110,000 acres, is the largest protected area of old-growth redwoods in the world. It includes Redwood National Park, Jedediah Smith Redwoods State Park, Del Norte Coast Redwoods State Park, and Prairie Creek Redwoods State Park. This region is known for its towering redwoods, diverse wildlife, and scenic hiking trails.
- The Redwood Coast National Monument: This vast area, managed by the Bureau of Land Management, encompasses over 400,000 acres of redwood forests, including areas north of the Redwood National and State Parks. It offers a diverse landscape, including redwood groves, meadows, and coastal bluffs, providing a glimpse into the vastness of the redwood ecosystem.
A Tapestry of Life:
The redwood forests are not merely a collection of trees; they are vibrant ecosystems teeming with life. These forests support a diverse array of flora and fauna, including:
- Redwood Trees: The iconic coastal redwood (Sequoia sempervirens) is the tallest tree species on Earth, with some reaching heights of over 370 feet. These trees are known for their long lifespans, with some estimated to be over 2,000 years old.
- Other Tree Species: In addition to redwoods, the forests are home to a variety of other tree species, including Douglas fir, Sitka spruce, and western hemlock. These trees provide habitat for a wide range of wildlife.
- Wildlife: The redwood forests are home to a diverse array of wildlife, including black bears, elk, bobcats, and numerous bird species. The forests also provide critical habitat for endangered species such as the northern spotted owl and the marbled murrelet.
- Fungi and Lichens: The damp, cool environment of the redwood forests supports a rich diversity of fungi and lichens, playing a vital role in nutrient cycling and decomposition.
Challenges and Conservation Efforts:
Despite their resilience, redwood forests face a number of challenges, including:
- Logging: Historically, redwood forests were heavily logged, resulting in significant habitat loss. While logging has been significantly reduced in recent years, it remains a threat to the health of these forests.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns pose a significant threat to redwood forests. These changes can increase the risk of wildfires and drought, impacting the health and survival of these trees.
- Invasive Species: Invasive species, such as the European gypsy moth, can disrupt the delicate balance of the redwood ecosystem, potentially impacting native species.
Efforts to protect and conserve redwood forests are ongoing, with organizations like the Save the Redwoods League and the Redwood National and State Parks working to preserve these vital ecosystems. These efforts include:
- Land Acquisition: Organizations are working to acquire land and protect it from further development.
- Restoration: Efforts are underway to restore degraded redwood forests by planting new trees and managing invasive species.
- Education and Outreach: Organizations are working to educate the public about the importance of redwood forests and the threats they face.
FAQs about Redwood Forests:
- What is the average height of a redwood tree? The average height of a mature redwood tree is approximately 200-300 feet.
- What is the oldest redwood tree? The oldest known redwood tree is estimated to be over 2,200 years old.
- Are redwood forests endangered? While redwood forests are not officially classified as endangered, they face significant threats from logging, climate change, and invasive species.
- Can I visit redwood forests? Yes, redwood forests are open to the public. There are several state and national parks that offer access to these magnificent forests.
- How can I help protect redwood forests? You can support organizations working to protect redwood forests by donating, volunteering, or advocating for policies that protect these valuable ecosystems.
Tips for Visiting Redwood Forests:
- Plan your trip in advance: Reserve your camping spot or lodging, and plan your hiking routes.
- Pack for all weather conditions: The redwood forests can experience a wide range of weather conditions, from fog and rain to sunshine and heat.
- Be aware of wildlife: Be respectful of the wildlife you encounter and follow safety guidelines.
- Leave no trace: Pack out everything you pack in, and avoid disturbing the natural environment.
- Support local businesses: Consider staying at local hotels, eating at local restaurants, and purchasing souvenirs from local businesses.
Conclusion:
The redwood forests of California are a treasure trove of natural beauty and ecological importance. These forests provide a glimpse into the history of the Earth, offering a sanctuary for a vast array of life. By understanding the geography, inhabitants, and challenges facing these forests, we can appreciate their significance and contribute to their continued existence. As we explore these towering giants, let us remember that we are not just visitors; we are guardians of this extraordinary ecosystem, entrusted with the responsibility to protect and preserve its wonders for generations to come.
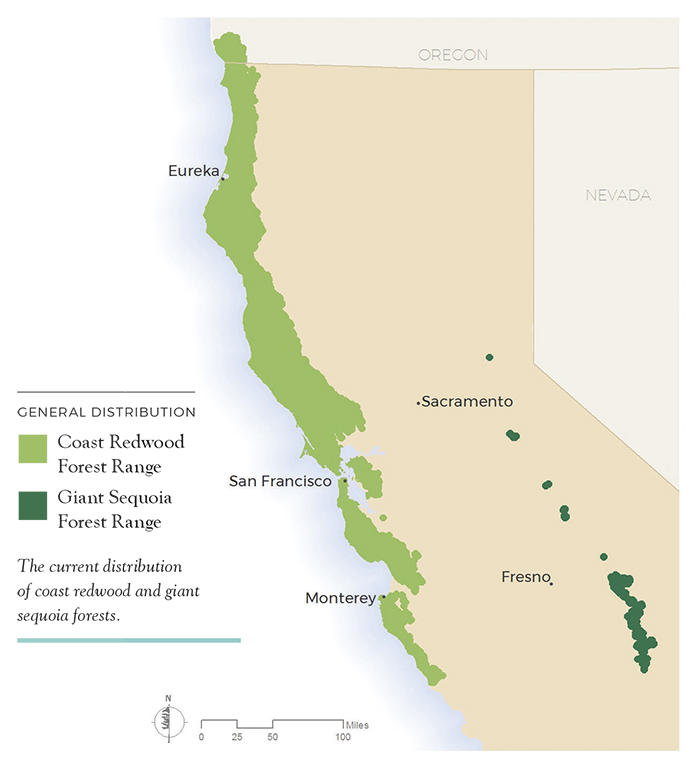

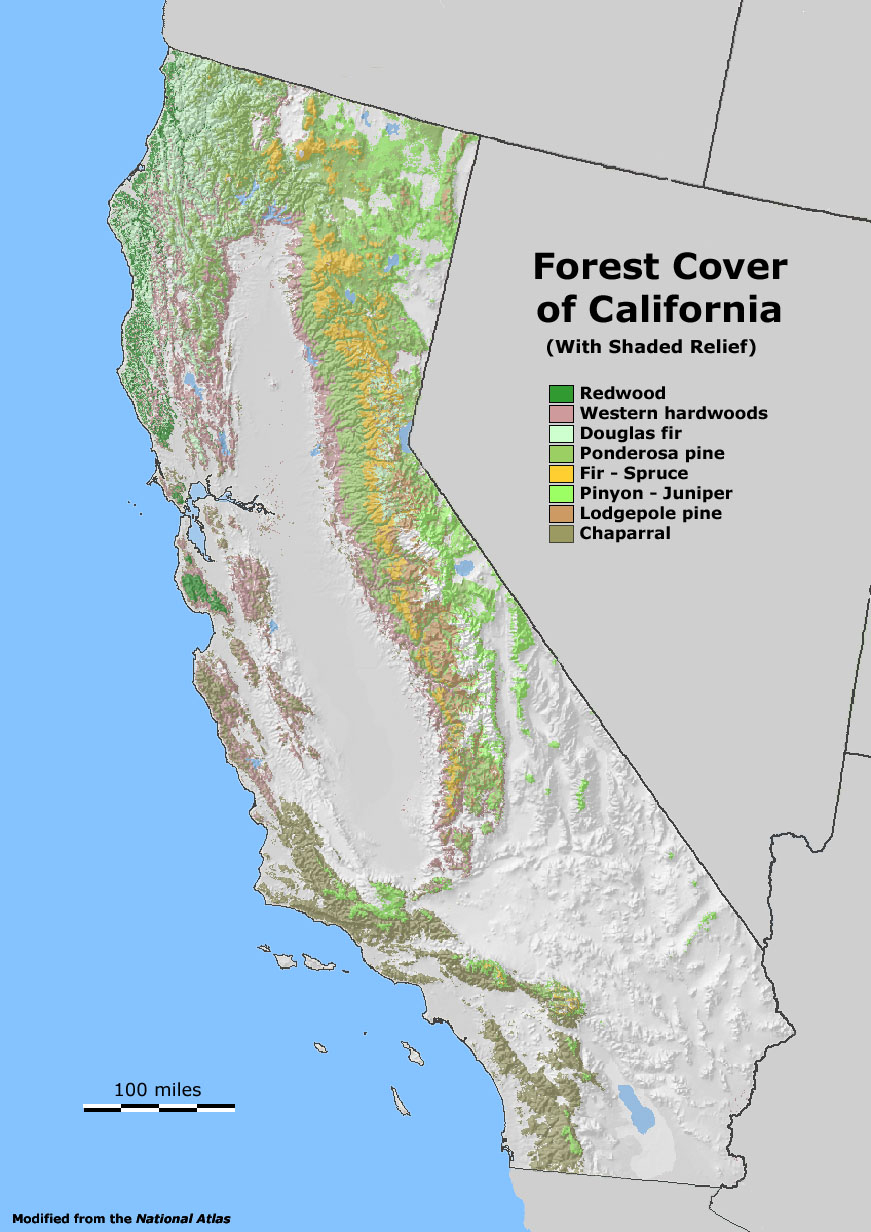
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through the Redwood Forests of California: A Map to Understanding These Giants. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!