A Global Perspective: Exploring the World’s Active Volcanoes
Related Articles: A Global Perspective: Exploring the World’s Active Volcanoes
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Global Perspective: Exploring the World’s Active Volcanoes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Global Perspective: Exploring the World’s Active Volcanoes
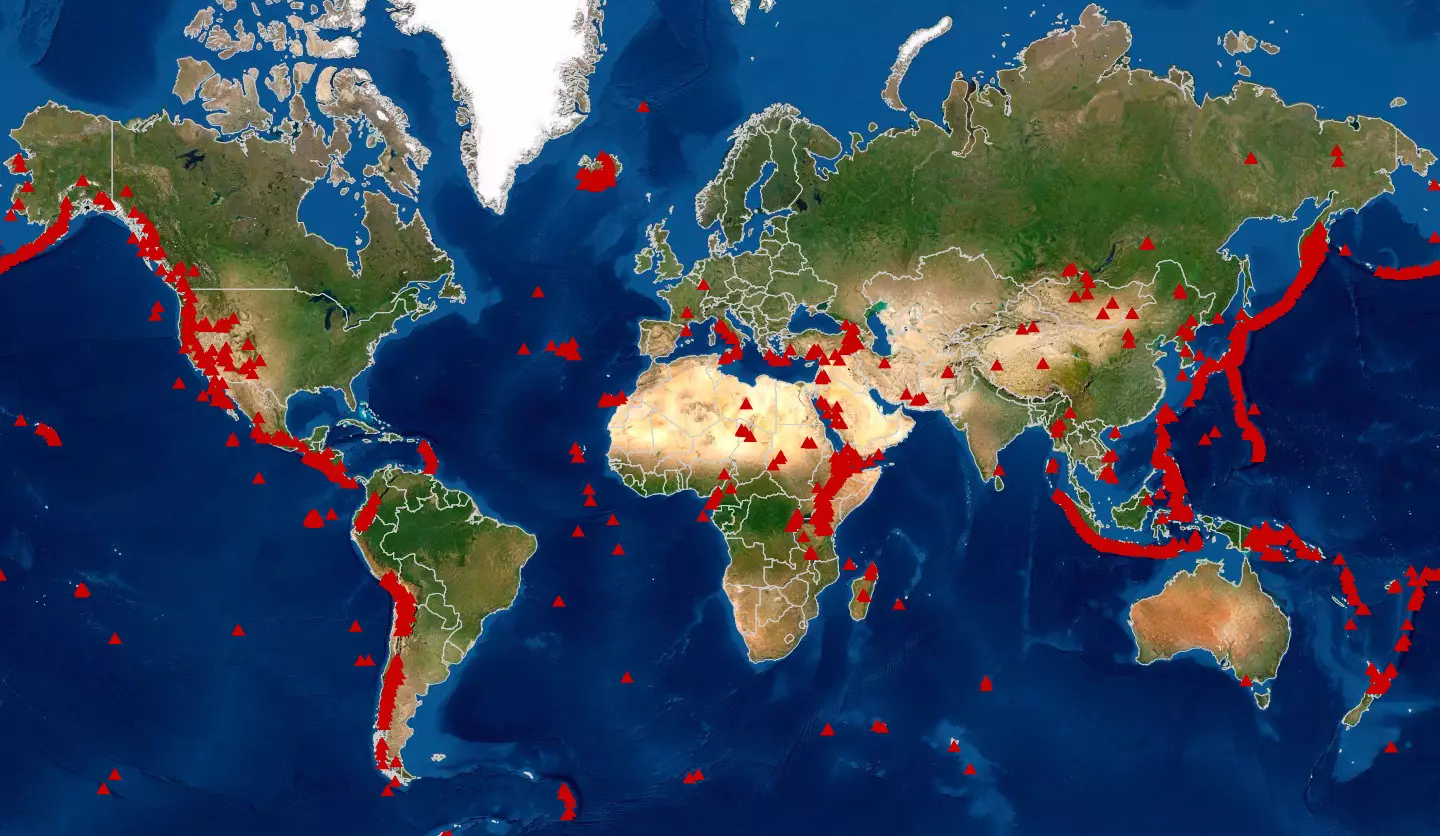
The Earth’s surface is a dynamic and ever-changing landscape, shaped by the relentless forces of plate tectonics. One of the most visible and dramatic manifestations of this geological activity is volcanism. Volcanoes, with their towering peaks and fiery eruptions, have captivated human imagination for millennia. Understanding the global distribution of active volcanoes is crucial for comprehending Earth’s dynamic nature, mitigating potential hazards, and appreciating the profound influence these geological features have on our planet.
A Map of Fire and Fury:
The world map of active volcanoes serves as a visual representation of the Earth’s volcanic hotspots. These hotspots are not randomly distributed but rather concentrated along specific regions, primarily at the boundaries of tectonic plates. These boundaries are zones of intense geological activity where plates collide, separate, or slide past each other, creating conditions favorable for volcanic eruptions.
The Ring of Fire: A Hotspot of Activity:
The most prominent example of this concentration is the Pacific Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped zone encircling the Pacific Ocean. This region accounts for approximately 75% of the world’s active volcanoes, making it a prime area for studying volcanic activity. The Ring of Fire is characterized by a high density of subduction zones, where one tectonic plate dives beneath another. This process triggers the melting of rock in the Earth’s mantle, generating magma that eventually rises to the surface, forming volcanoes.
Beyond the Ring of Fire: Other Volcanic Zones:
While the Ring of Fire dominates the global map, other significant volcanic zones exist across the globe. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a vast underwater mountain range, represents a divergent plate boundary where new oceanic crust is being formed. This process is accompanied by volcanic activity, giving rise to underwater volcanoes and volcanic islands.
The African Rift Valley, a region stretching across eastern Africa, is another prominent example of a divergent plate boundary. This zone is characterized by a series of volcanoes, including Mount Kilimanjaro and Mount Kenya, which have played a significant role in shaping the landscape and ecosystems of the region.
The Importance of Understanding Active Volcanoes:
The world map of active volcanoes serves as a vital tool for scientists, policymakers, and communities living near these geological features. Understanding the distribution and activity of volcanoes is crucial for:
- Predicting and mitigating volcanic hazards: Volcanic eruptions can pose significant threats to human life and infrastructure. Monitoring volcanic activity and understanding eruption patterns is essential for developing early warning systems and evacuation plans.
- Assessing volcanic risks: The world map of active volcanoes helps in identifying areas at risk from volcanic eruptions. This information is critical for land-use planning, infrastructure development, and disaster preparedness.
- Exploring geothermal energy potential: Volcanic areas are rich in geothermal energy, a renewable and sustainable energy source. Understanding the distribution of volcanoes can guide the exploration and development of geothermal power plants.
- Studying Earth’s internal processes: Volcanic activity provides valuable insights into the Earth’s interior, including the composition, temperature, and dynamics of the mantle and crust.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What is the difference between active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes?
A: Active volcanoes are those that have erupted in recent history and are likely to erupt again. Dormant volcanoes have not erupted in recent history but could potentially erupt in the future. Extinct volcanoes are unlikely to erupt again.
Q: How do scientists monitor volcanic activity?
A: Scientists use a variety of techniques to monitor volcanic activity, including:
- Seismic monitoring: Detecting earthquakes and tremors associated with magma movement.
- Ground deformation monitoring: Measuring changes in the shape of a volcano, which can indicate magma movement.
- Gas monitoring: Analyzing the composition and abundance of gases released from a volcano.
- Thermal monitoring: Detecting changes in heat flow, which can indicate magma activity.
Q: What are some of the most famous active volcanoes in the world?
A: Some of the most famous active volcanoes in the world include:
- Mount Vesuvius (Italy): Famous for its eruption in 79 AD that buried the Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum.
- Mount Etna (Italy): The tallest active volcano in Europe, known for its frequent eruptions.
- Mount Fuji (Japan): A sacred mountain and a popular tourist destination, with a history of eruptions.
- Mount Kilauea (Hawaii): One of the most active volcanoes in the world, known for its effusive eruptions.
- Mount St. Helens (USA): Famous for its catastrophic eruption in 1980.
Tips for Understanding the World Map of Active Volcanoes:
- Focus on the tectonic plate boundaries: Pay attention to the locations where tectonic plates converge, diverge, or slide past each other. These areas are prone to volcanic activity.
- Consider the volcanic history of a region: Look for past eruptions and their impact on the surrounding environment.
- Explore the different types of volcanic eruptions: Understand the characteristics of different types of eruptions, such as effusive and explosive eruptions, and their potential hazards.
- Learn about volcanic risk assessment: Familiarize yourself with the methods used to assess the risks associated with volcanic eruptions.
Conclusion:
The world map of active volcanoes is a powerful tool for understanding the dynamic nature of our planet. By studying the distribution and activity of volcanoes, we can gain insights into the Earth’s internal processes, mitigate potential hazards, and explore renewable energy sources. As we continue to monitor and study these geological wonders, we can better appreciate their role in shaping our world and prepare for the challenges they present.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Global Perspective: Exploring the World’s Active Volcanoes. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!