A Comprehensive Look at Mexico’s Climate Map: Unveiling the Diversity of a Nation
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at Mexico’s Climate Map: Unveiling the Diversity of a Nation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at Mexico’s Climate Map: Unveiling the Diversity of a Nation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at Mexico’s Climate Map: Unveiling the Diversity of a Nation
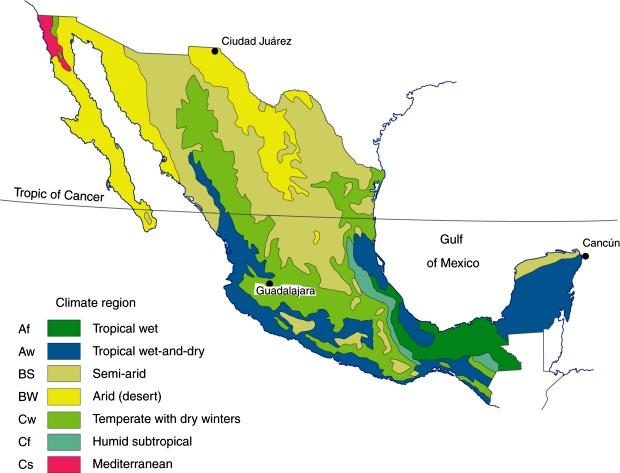
Mexico, a land of vibrant culture, ancient history, and diverse landscapes, is also a nation with a complex and varied climate. Understanding the nuances of Mexico’s climate is crucial for various aspects of life, from agriculture and tourism to urban planning and disaster preparedness. A climate map serves as a vital tool, visually representing the distribution of different climate types across the country, offering insights into temperature, precipitation, and other crucial meteorological factors.
Unveiling the Mosaic of Mexico’s Climate
Mexico’s climate map reveals a fascinating mosaic of climatic zones, primarily shaped by its geographical features and location. The country’s diverse topography, ranging from towering mountains to coastal plains, influences temperature and precipitation patterns. Mexico’s proximity to the Pacific Ocean and Gulf of Mexico further contributes to its climatic diversity, generating distinct wet and dry seasons.
Key Climate Zones of Mexico
-
Tropical Wet Climate: This climate zone, primarily found on the Yucatan Peninsula and along the Gulf Coast, experiences high temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year. The lush vegetation and warm temperatures make this region ideal for growing tropical fruits and crops.
-
Tropical Savanna Climate: Characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons, this climate zone dominates much of Mexico’s interior, including areas like the states of Veracruz and Oaxaca. The wet season brings heavy rainfall, while the dry season is marked by lower precipitation and occasional drought conditions.
-
Semiarid Climate: This climate zone, prevalent in northern and central Mexico, features hot summers and mild winters with limited rainfall. The arid landscapes of this region are often dominated by desert vegetation and scrubland.
-
Arid Climate: Found in the northernmost parts of Mexico, this climate zone experiences extremely low rainfall and high temperatures throughout the year. The arid landscape is characterized by deserts and scrubland, with limited vegetation and water resources.
-
Mediterranean Climate: Present in the Baja California peninsula, this climate zone is characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The Mediterranean climate is ideal for growing fruits and vegetables, contributing to the region’s agricultural economy.
-
Highland Climate: The mountainous regions of Mexico, particularly the Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental, experience a highland climate characterized by cool temperatures and high levels of precipitation. These areas support diverse ecosystems, including pine forests and grasslands.
Understanding the Importance of Mexico’s Climate Map
The climate map of Mexico serves as a crucial tool for various sectors:
Agriculture: Farmers rely on the climate map to understand the suitability of different regions for specific crops. This information aids in selecting the most appropriate crops for each area, optimizing yields and ensuring sustainable agricultural practices.
Tourism: The climate map helps tourists plan their trips, choosing destinations based on their preferred weather conditions. It also informs tourism operators about the best seasons for specific activities, ensuring a more enjoyable experience for visitors.
Urban Planning: City planners use the climate map to understand the potential risks associated with extreme weather events, such as floods, droughts, and heatwaves. This information guides urban development strategies, ensuring sustainable and resilient cities.
Disaster Preparedness: The climate map helps identify areas vulnerable to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions. This information allows for better disaster preparedness strategies, minimizing damage and ensuring the safety of communities.
Environmental Management: The climate map is crucial for understanding the impact of climate change on different regions of Mexico. It helps scientists and policymakers identify areas at risk and develop strategies for mitigating climate change impacts and promoting environmental sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the average temperature in Mexico?
Mexico’s average temperature varies significantly across different regions. The warmest areas are located in the south and along the coast, with average temperatures exceeding 30°C (86°F). In contrast, mountainous regions experience cooler temperatures, averaging around 10°C (50°F) or lower.
2. What are the wettest and driest months in Mexico?
The wettest months in Mexico generally occur during the summer monsoon season, from June to September, with the heaviest rainfall in the south and along the Gulf Coast. The driest months are typically from December to May, with minimal rainfall in most parts of the country.
3. How does climate change affect Mexico?
Climate change is expected to exacerbate existing climate patterns in Mexico, leading to more frequent and intense heatwaves, droughts, and floods. Rising sea levels pose a threat to coastal areas, while changes in rainfall patterns can disrupt agricultural productivity.
4. What are some of the challenges related to climate change in Mexico?
Mexico faces various challenges related to climate change, including water scarcity, food insecurity, and increased vulnerability to natural disasters. These challenges require concerted efforts from government, communities, and businesses to mitigate climate change impacts and adapt to the changing environment.
Tips for Using Mexico’s Climate Map
-
Understand the legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and colors used on the climate map to represent different climate types.
-
Consider your purpose: Identify the specific information you need from the climate map, whether it’s temperature, precipitation, or other relevant factors.
-
Zoom in for detail: Use the map’s zoom function to focus on specific regions or locations of interest.
-
Compare different maps: Compare the climate map with other relevant maps, such as topographic maps or vegetation maps, for a more comprehensive understanding of the region.
-
Seek expert advice: Consult with experts in meteorology, climatology, or related fields for further guidance on interpreting the climate map and applying its information.
Conclusion
Mexico’s climate map is a powerful tool for understanding the complex and diverse climate of this remarkable nation. It provides valuable insights into temperature, precipitation, and other crucial meteorological factors, enabling informed decision-making in various sectors, including agriculture, tourism, urban planning, disaster preparedness, and environmental management. As Mexico navigates the challenges of climate change, the climate map will continue to serve as an essential guide for promoting sustainable development and ensuring the well-being of its people.


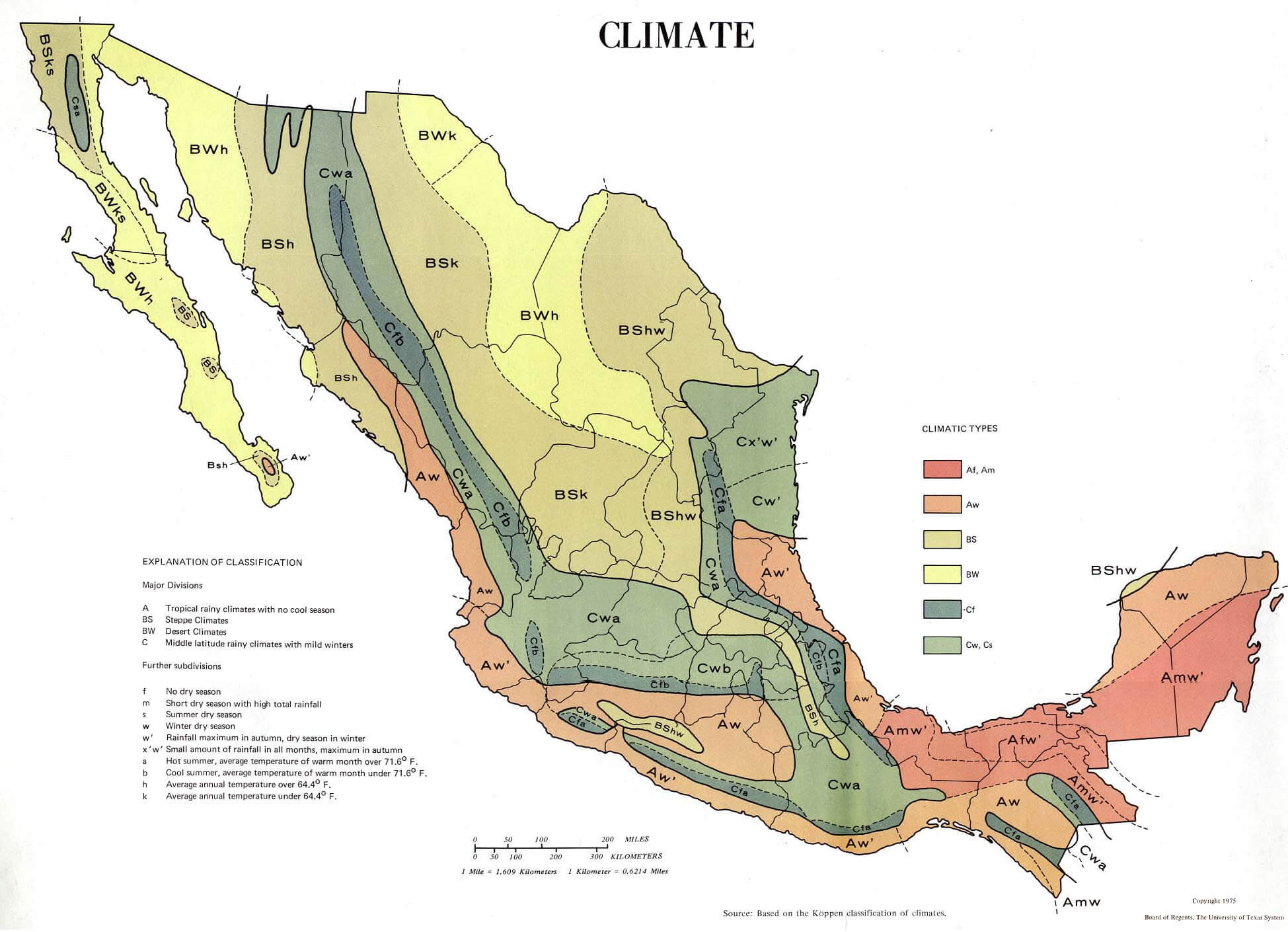
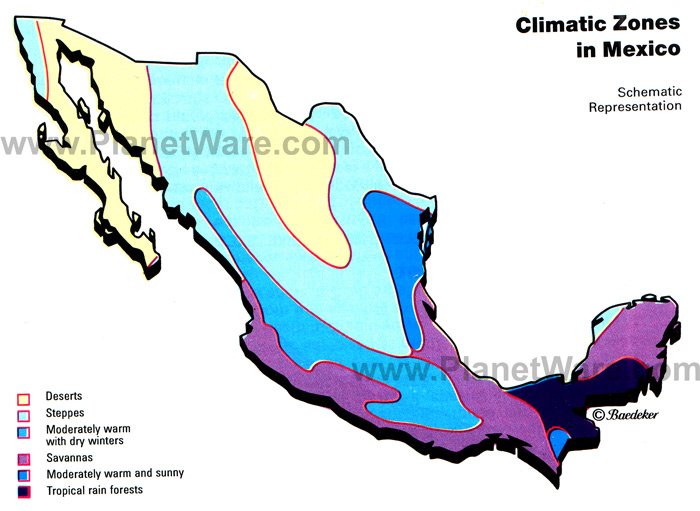




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at Mexico’s Climate Map: Unveiling the Diversity of a Nation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!